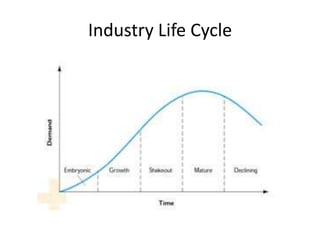
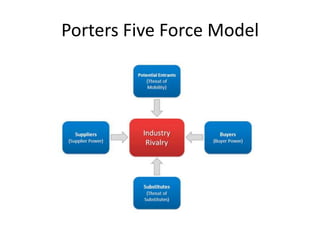
The document discusses external analysis for understanding an industry's competitive environment. It defines key concepts like industry, sector, strategic groups. It also explains Porter's five forces model for analyzing competitive forces that shape an industry - threat of new entry, rivalry among existing firms, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of substitutes. Finally, it discusses how the general environment/macro factors like political, economic, social and technological aspects (PEST analysis) can impact Porter's five forces.