The document outlines a lecture on quantitative analysis focusing on equivalent weight, normality, and conversions between various concentration units. Key learning objectives include calculating equivalent weight for acids, bases, and salts, as well as deriving normality from equivalent weights and solution volumes. It also includes sample calculations for normality using sodium carbonate and oxalic acid, along with relations between ppm, ppb, and molarity.








![Dr Brima Monday 01/02//2016---22/4/1437 11
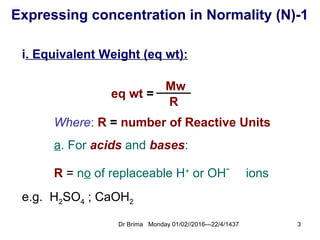
Normality calculation-1
- *Calculate the normality for 0.212g of Na2CO3
dissolved in 100ml water?
- Answer:
[212mg/(106/2)]/100ml = 0.04N
[0.212g/(106/2)]/0.1L = 0.04N
No of g eq wt’s of solute
sol.n Volume in Liters
=
wt / eq wt
VL
∴ N =
83](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-170321224510/85/Expressing-concentrations-11-320.jpg)
![Dr Brima Monday 01/02//2016---22/4/1437 12
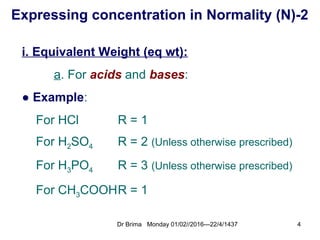
Normality calculation-2
- *Calculate the normality for 0.25g/L of Oxalic
acid (H C O₂ ₂ 4) dissolved in 100ml water?
- Answer:
- N = wt(mg)/[Mwt/R]/Vml
= 250mg/[290.4/2]/1000ml = 0.006N
—84-85](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-170321224510/85/Expressing-concentrations-12-320.jpg)


