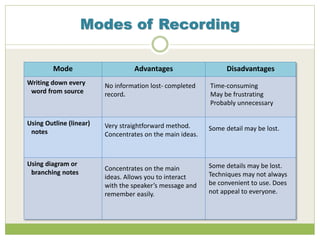
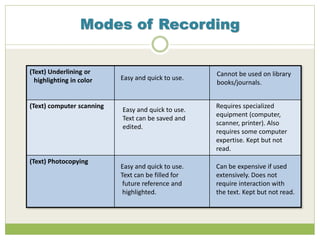
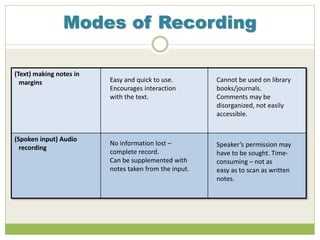
This document discusses effective note-taking strategies from research resources. It outlines different modes of recording information like writing everything down, using outlines, diagrams, highlighting text, audio recording, and their advantages and disadvantages. For example, writing everything allows no information to be lost but is time-consuming. The document emphasizes taking notes in your own words to avoid plagiarism, understanding the information fully before recording it, and questioning sources of information.