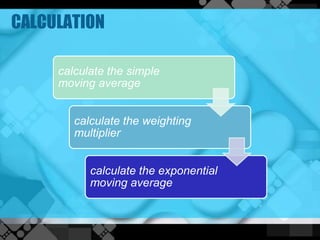
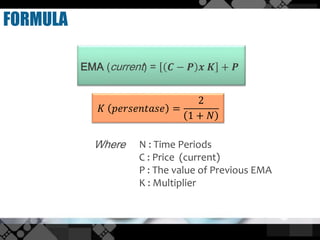
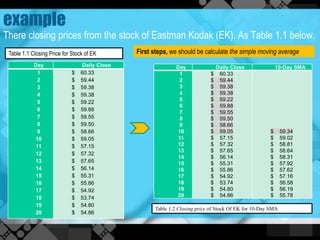
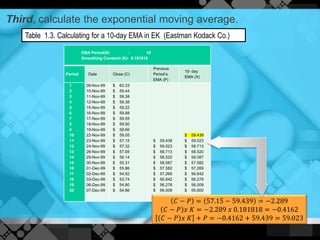
The exponential moving average (EMA) assigns more weight to recent data points compared to older data points. It is calculated by taking the previous EMA value and adding a percentage of the difference between the current closing price and the previous EMA. This percentage decreases exponentially as the data points get older. An example calculates the 10-day EMA for stock closing prices, applying an 18.18% weighting to the most recent price. The EMA responds more quickly to recent price changes than the simple moving average but can also generate false signals about market trends.