The document discusses various perspectives on the concept of sustainability from practitioners. It explores definitions of sustainability from English, Malay, and Sanskrit terminology as well as Islamic perspectives focusing on integration and balance. Examples of sustainability challenges like deforestation and examples of potential solutions from areas like education, stakeholder engagement, and research are provided. The University of Malaya's Sustainable Development Solutions Network which aims to support sustainable development through scientific and technical expertise is also mentioned.

![“It suddenly struck me that that tiny
pea, pretty and blue, was the Earth. I
put up my thumb and shut one eye,
and my thumb blotted out the planet
Earth. I didn't feel like a giant. I felt
very, very small”.
[Neil Armstrong on Apollo 11, July
20, 1969]
Image taken from: http://www.wikinewforum.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sustainabilityscienceikim18112014nms-150918070147-lva1-app6892/85/Exploring-Sustainability-Concept-and-Definition-from-Practitioner-s-Perspective-2-320.jpg)








![Integration of Islamic Perspective
on Sustainability
Translation:
“Indeed, the wasteful are brothers of the devils, and
ever has Satan been to his Lord ungrateful”
[Surah al-Isra’: 27]
• Badzara = root word for tabdzir / mubazirun which means the act of wasteful
• ‘wasteful’ in this context is mentioned thrice (3) in Quran: Surah al-Isra’: 26-27
info](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sustainabilityscienceikim18112014nms-150918070147-lva1-app6892/85/Exploring-Sustainability-Concept-and-Definition-from-Practitioner-s-Perspective-12-320.jpg)
![Integration of Islamic Perspective
on Sustainability
Prophet Muhammad S.A.W said:
“Do not waste water, even if you perform your
ablution on the banks of an abundantly-flowing river”
[HR Imam Ahmad]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sustainabilityscienceikim18112014nms-150918070147-lva1-app6892/85/Exploring-Sustainability-Concept-and-Definition-from-Practitioner-s-Perspective-13-320.jpg)
![Integration of Islamic Perspective
on Sustainability
Translation:
O Children of Adam! wear your beautiful apparel at
every time and place of prayer: eat and drink: But
waste not by excess, for Allah loveth not the wasters.
[Surah al-A’araf: 31]
• Sarafa = root word for Israf / Musrifin which means the act of wasteful in excess,
transgression beyond limit, excessive
• ‘excessive’ in this context is mentioned twenty three (23) time in 21 verses in
Quran: with different or similar connotation
info](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sustainabilityscienceikim18112014nms-150918070147-lva1-app6892/85/Exploring-Sustainability-Concept-and-Definition-from-Practitioner-s-Perspective-14-320.jpg)








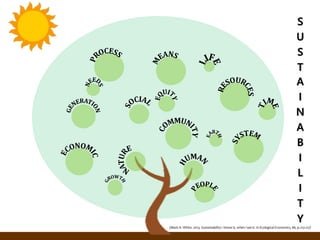



![2 Mode of Science: Practitioner’s Perspective
Mode-1
Science
Academic
Mono-
disciplinary
Technocratic
Certain
Predictive
Mode-2
Science
Academic &
Social
Multi-Inter-
Trans-
disciplinary
Participative
Uncertain
Exploratory
Reference: [AKEPT Material] - Martens, P. (2006) Sustainability:
science or fiction? Sustainability: Science, Practice and Policy, 2(1), 1-
5. (also published as: Solidarity & Sustainability, Reflections on
Solidarity, Sustainability and Religious Violence, 2 (9), September
2006.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sustainabilityscienceikim18112014nms-150918070147-lva1-app6892/85/Exploring-Sustainability-Concept-and-Definition-from-Practitioner-s-Perspective-32-320.jpg)
![The role of Sustainability + Science in Policy Process
Reference: [AKEPT Material] - Martens, P. (2006) Sustainability:
science or fiction? Sustainability: Science, Practice and Policy, 2(1), 1-
5. (also published as: Solidarity & Sustainability, Reflections on
Solidarity, Sustainability and Religious Violence, 2 (9), September
2006.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sustainabilityscienceikim18112014nms-150918070147-lva1-app6892/85/Exploring-Sustainability-Concept-and-Definition-from-Practitioner-s-Perspective-33-320.jpg)
![Definitions of Sustainable Development
Reference: [AKEPT Material] - Kemp R. & Martens P. 2007. Sustainable development:
how to manage something that is subjective and never can be achieved?.
Sustainability: Science, Practice, & Policy 3(2):5-14. Published online Aug 30, 2007.
http://www.google.com.my/archives/vol3iss2/0703-007.kemp.html
What is to be
sustained?
Nature: Earth, Biodiversity, Ecosystems
Life Support: Ecosystem Services,
Resources, Environment
Community: Cultures, Groups, Places
What is to be
developed?
People: child survival, Life expectancy,
education, Equity, Equal opportunity
Economy: wealth, productive sectors,
consumption
Society: institutions, social capital
states, regions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sustainabilityscienceikim18112014nms-150918070147-lva1-app6892/85/Exploring-Sustainability-Concept-and-Definition-from-Practitioner-s-Perspective-34-320.jpg)