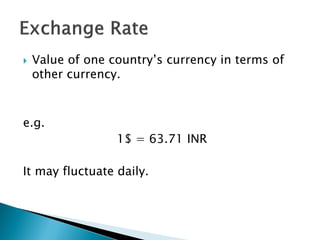
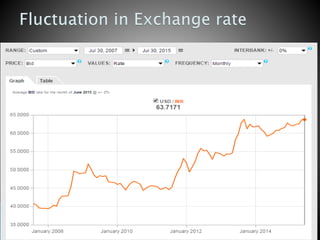
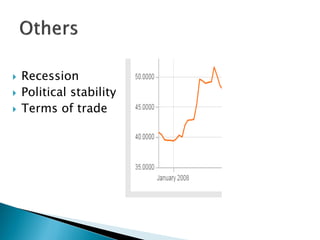
The document discusses factors that influence currency exchange rates, including inflation rates, interest rates, balance of trade, government debt, economic conditions, and demand. A country's currency will appreciate if it has lower inflation or raises interest rates. Higher government debt or a recession can lead to currency depreciation. Exchange rates also depend on demand from foreign investors and international economic and political uncertainties. Models for predicting exchange rates incorporate factors like spot rates, forward rates, and demand and supply trends.