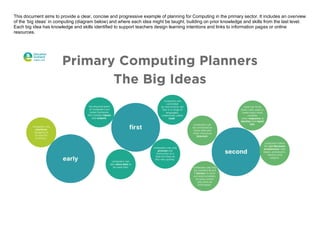
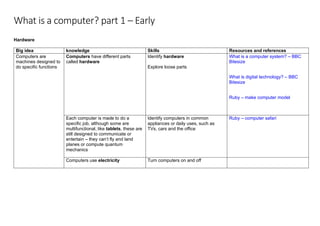
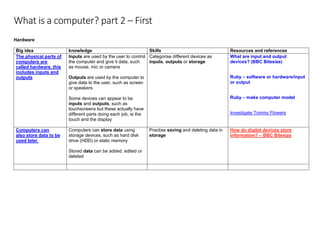
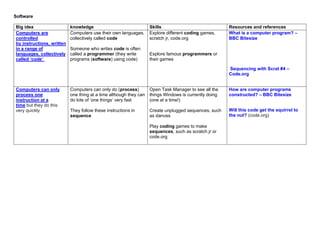
The document outlines a progressive plan for teaching computing in the primary sector, discussing key concepts such as hardware, software, and the internet. It includes various learning intentions, resources, and activities designed to help students understand the functions of computers, including inputs, outputs, and data storage. Emphasizing foundational programming skills, the document also explores coding principles such as sequence, selection, and repetition.