This document provides information on various networking components:
- A modem converts digital signals to analog and vice versa to transmit data over telephone lines between computers.
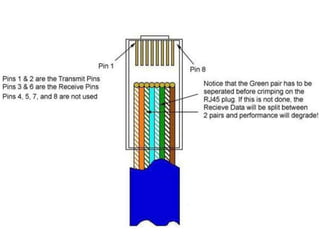
- An RJ-45 connector is used to connect devices to a local area network and houses 8 wires.
- An Ethernet card allows a computer to connect to a network using different connection types like RJ-45, BNC, or AUI.
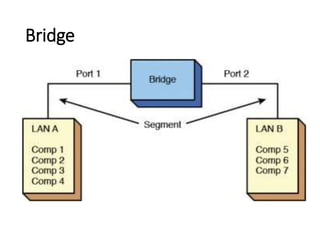
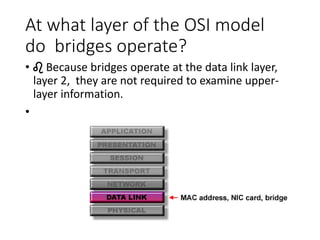
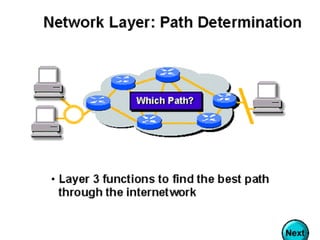
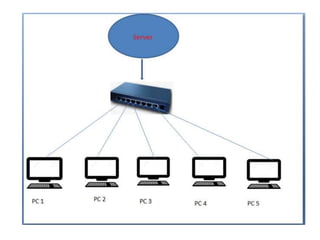
- Devices like switches, bridges and routers are used to segment networks and allow communication between different nodes.