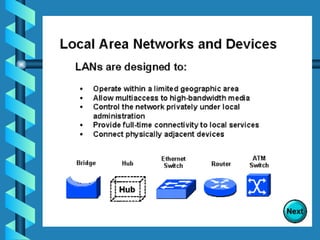
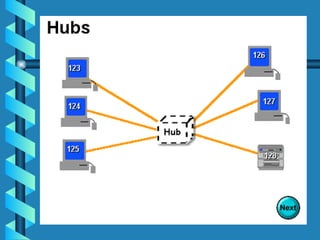
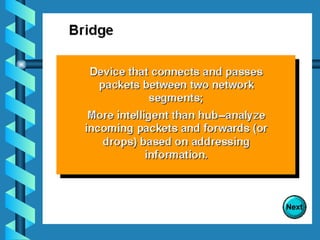
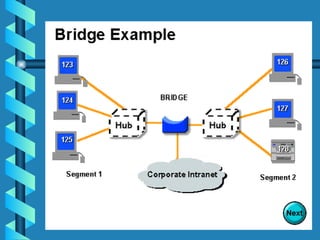
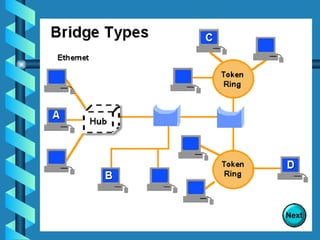
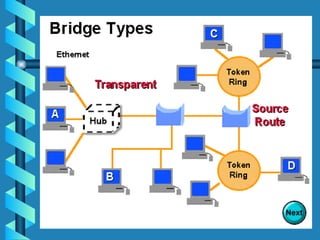
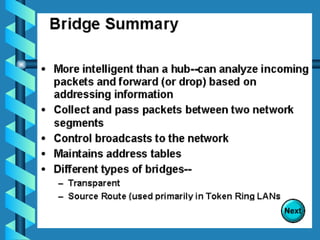
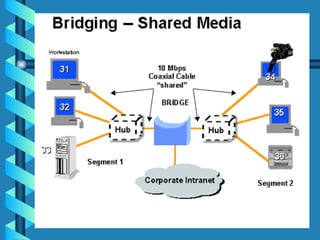
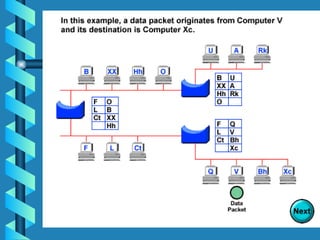
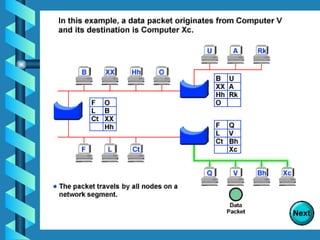
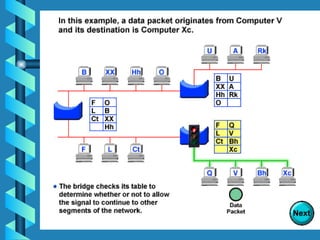
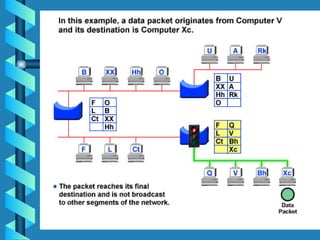
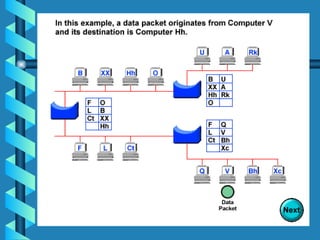
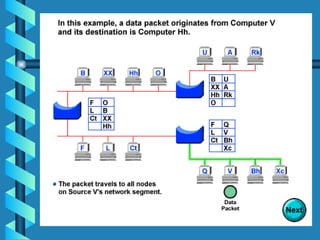
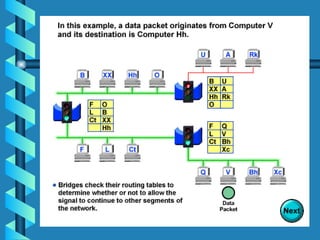
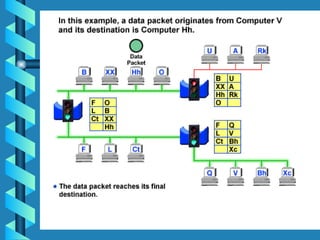
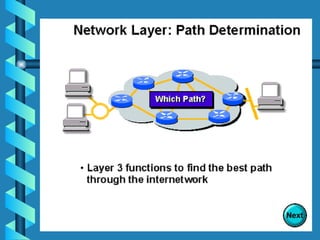
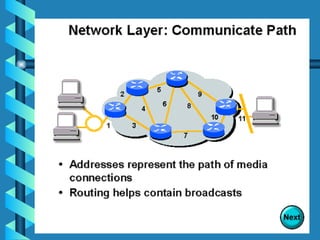
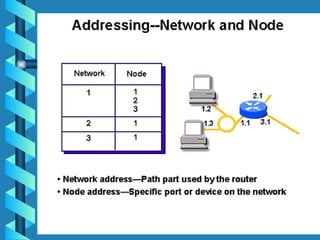
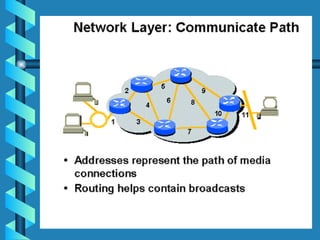
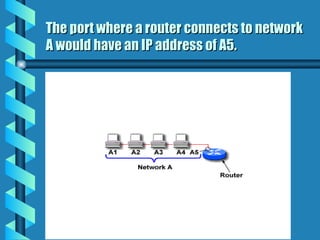
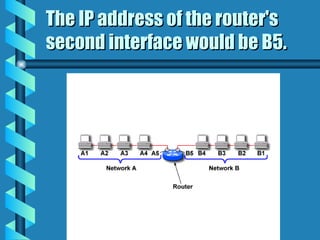
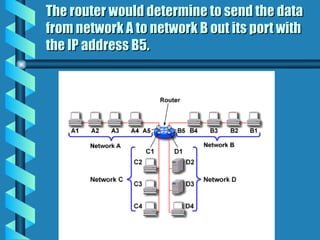
The document outlines various networking devices utilized for connecting networks, including repeaters, hubs, bridges, and routers. It explains their functions such as extending network distances, localizing traffic, and filtering data to minimize collisions. Additionally, it highlights the differences between MAC and IP addresses and describes how routers operate at the network layer to manage data packet delivery effectively.