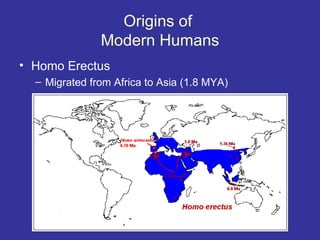
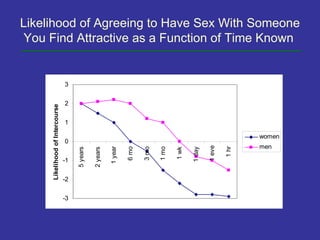
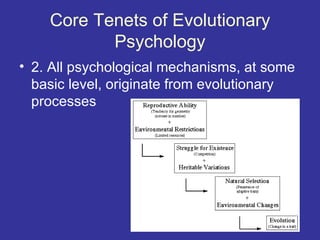
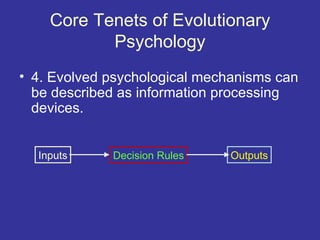
Evolutionary psychology combines evolutionary biology and cognitive psychology to study the evolution of human mind and behavior. Key ideas include:
1. Natural and sexual selection shaped the development of psychological mechanisms over generations to solve adaptive problems faced by our ancestors.
2. These mechanisms can be described as information processing systems that take in inputs and produce outputs through decision rules.
3. They are instantiated in the brain and work largely unconsciously to influence our thoughts and behavior. Understanding them provides insight into human nature.