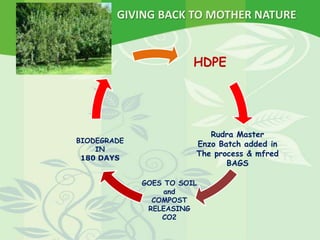
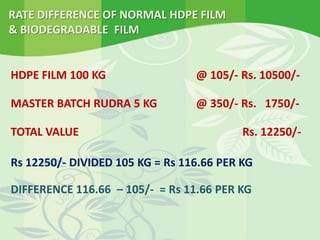
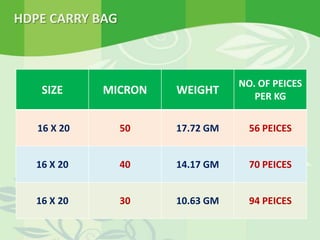
The document promotes the use of biodegradable plastics as a solution to the growing problem of plastic waste, highlighting their environmental benefits over traditional plastic products. It details the technology behind these biodegradable plastics, including the use of enzymes and bacteria to accelerate degradation and the composting process. The conclusion emphasizes the necessity of adopting biodegradable solutions to protect the environment and reduce reliance on non-degradable plastic materials.