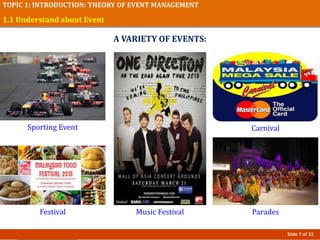
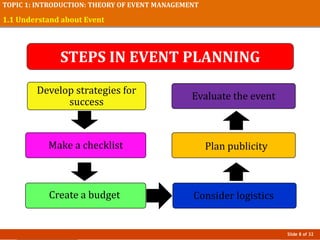
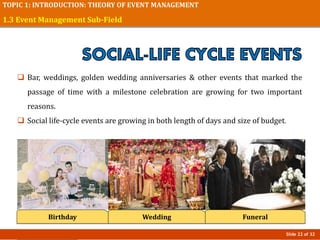
This document provides an introduction to event management, including definitions of events and the profession. It outlines key topics that will be covered, such as understanding different types of events, the event management field and subfields, changes in the industry, and challenges and opportunities. The presentation concludes by stating that a good event manager works hard to ensure events run smoothly from start to finish.