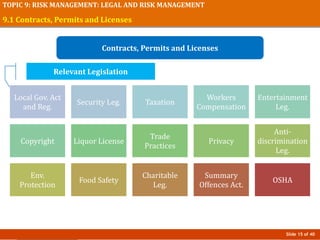
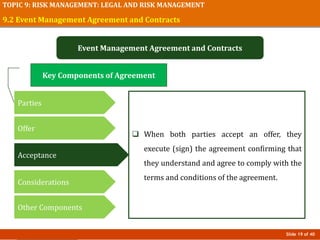
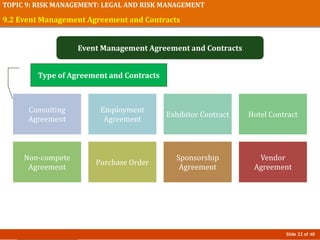
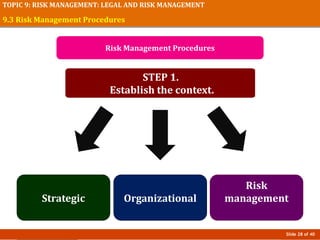
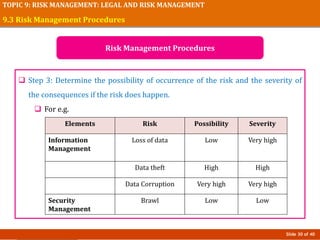
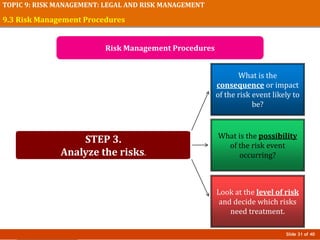
The document discusses risk management in event planning, including legal compliance and risk management. It covers key topics like contracts, permits, licenses and their importance in protecting legal interests. Event management agreements and contracts are also examined, outlining essential components like parties, offers, acceptance and considerations. Risk management procedures and their role in event planning is explored. The importance of compliance and managing risks is emphasized for honoring ethics, ensuring safety, and protecting financial investments in events.