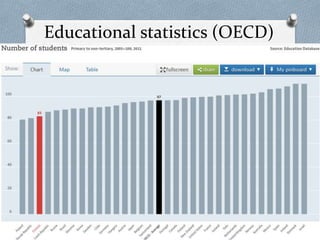
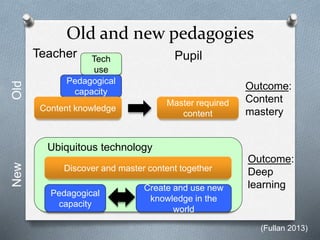
The document discusses Estonia's education system, highlighting its success in PISA rankings, particularly in mathematics, reading, and science. Estonia's focus on digital integration in education, equal opportunities regardless of socio-economic status, and the active role of e-learning have contributed to positive outcomes. It also mentions the importance of qualified teachers and innovative pedagogies in shaping modern learning experiences.