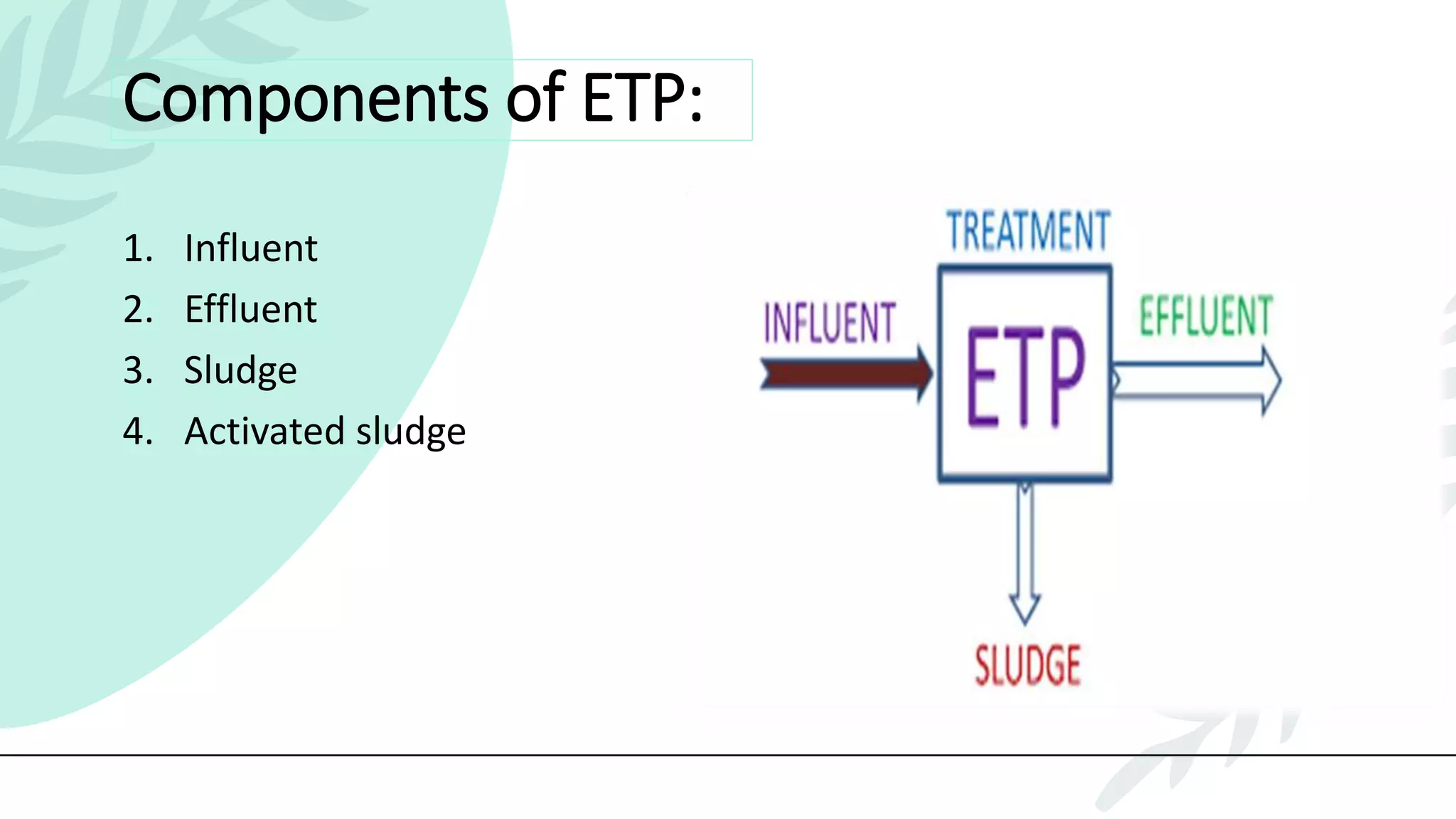
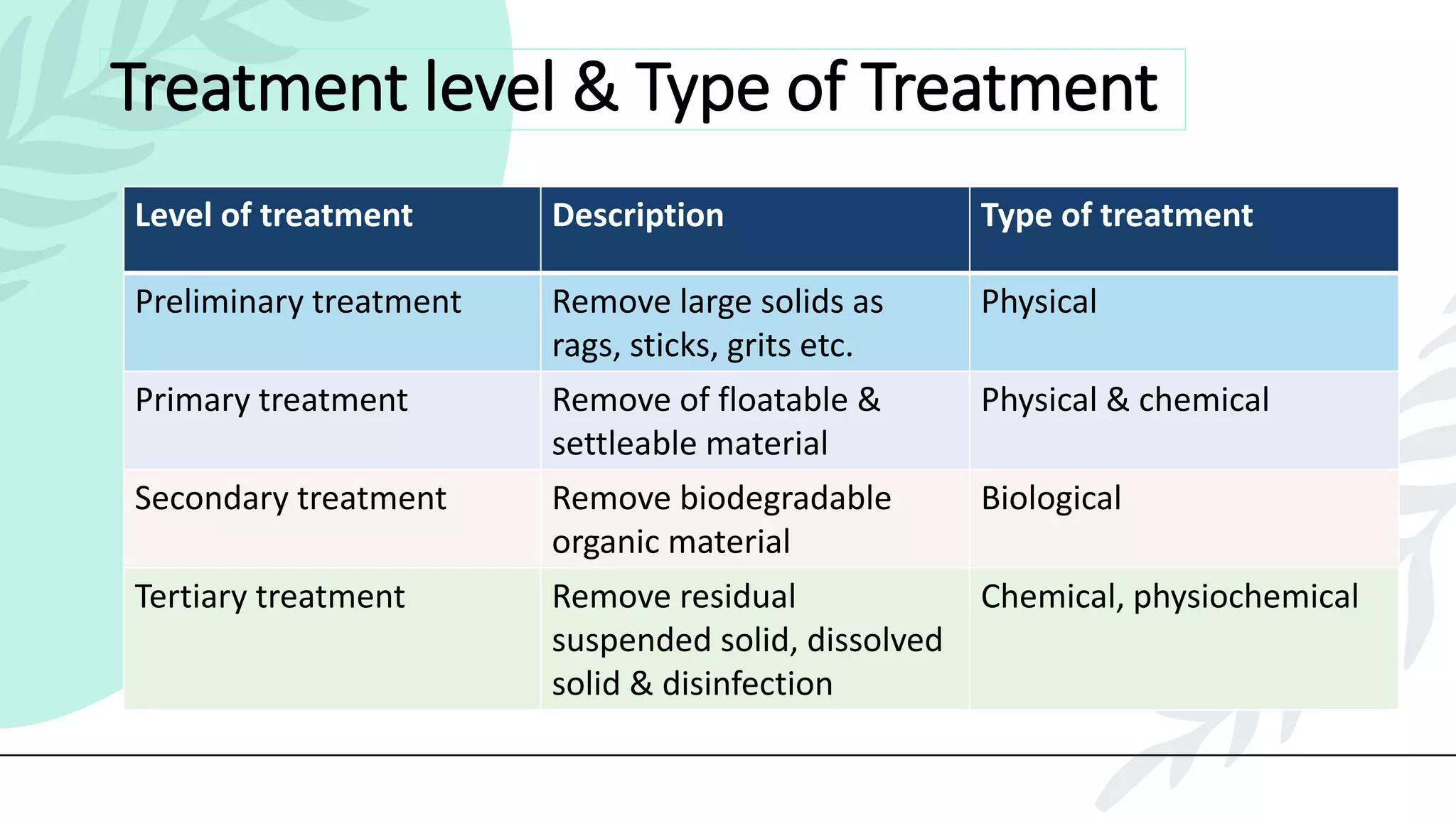
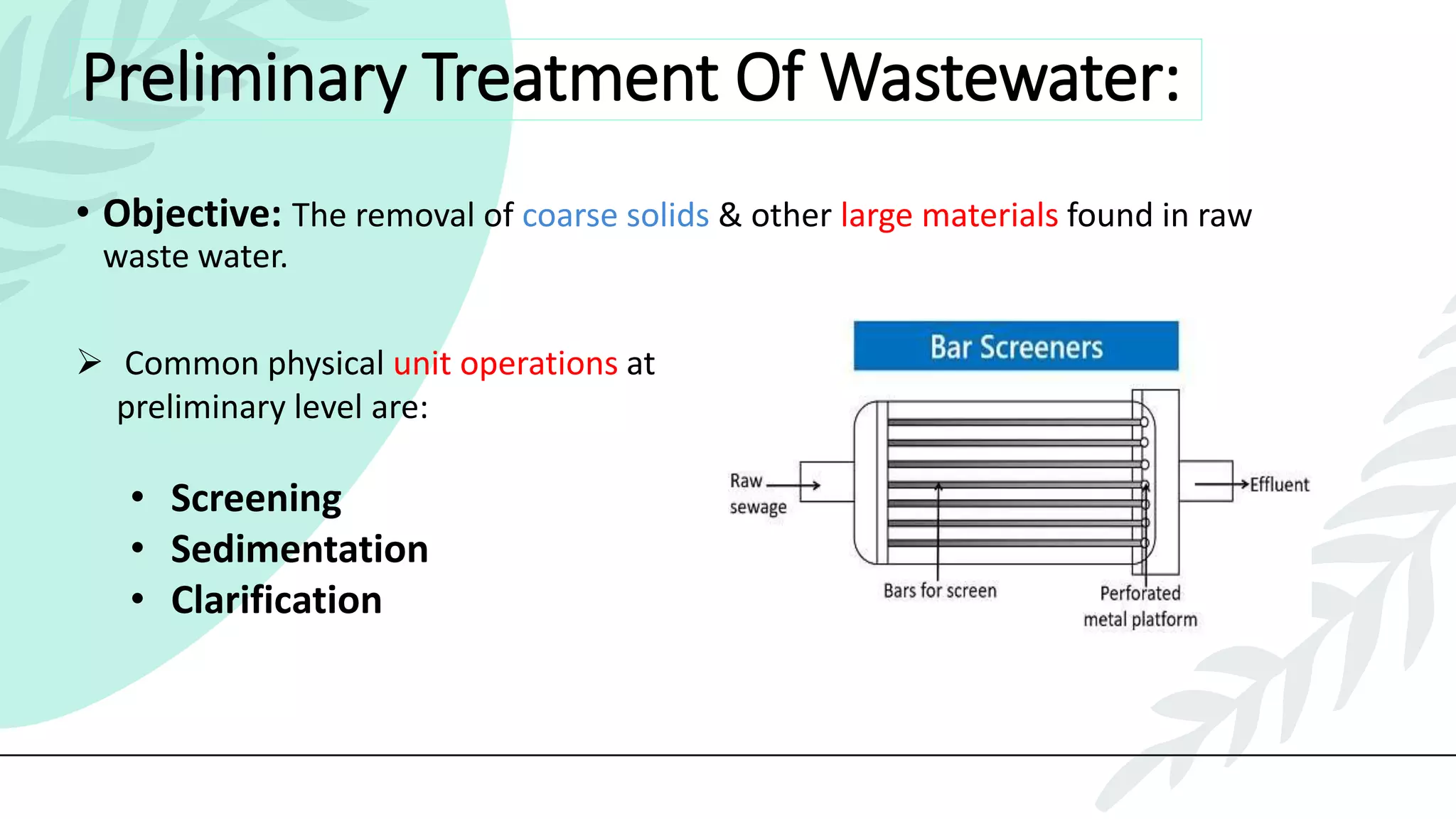
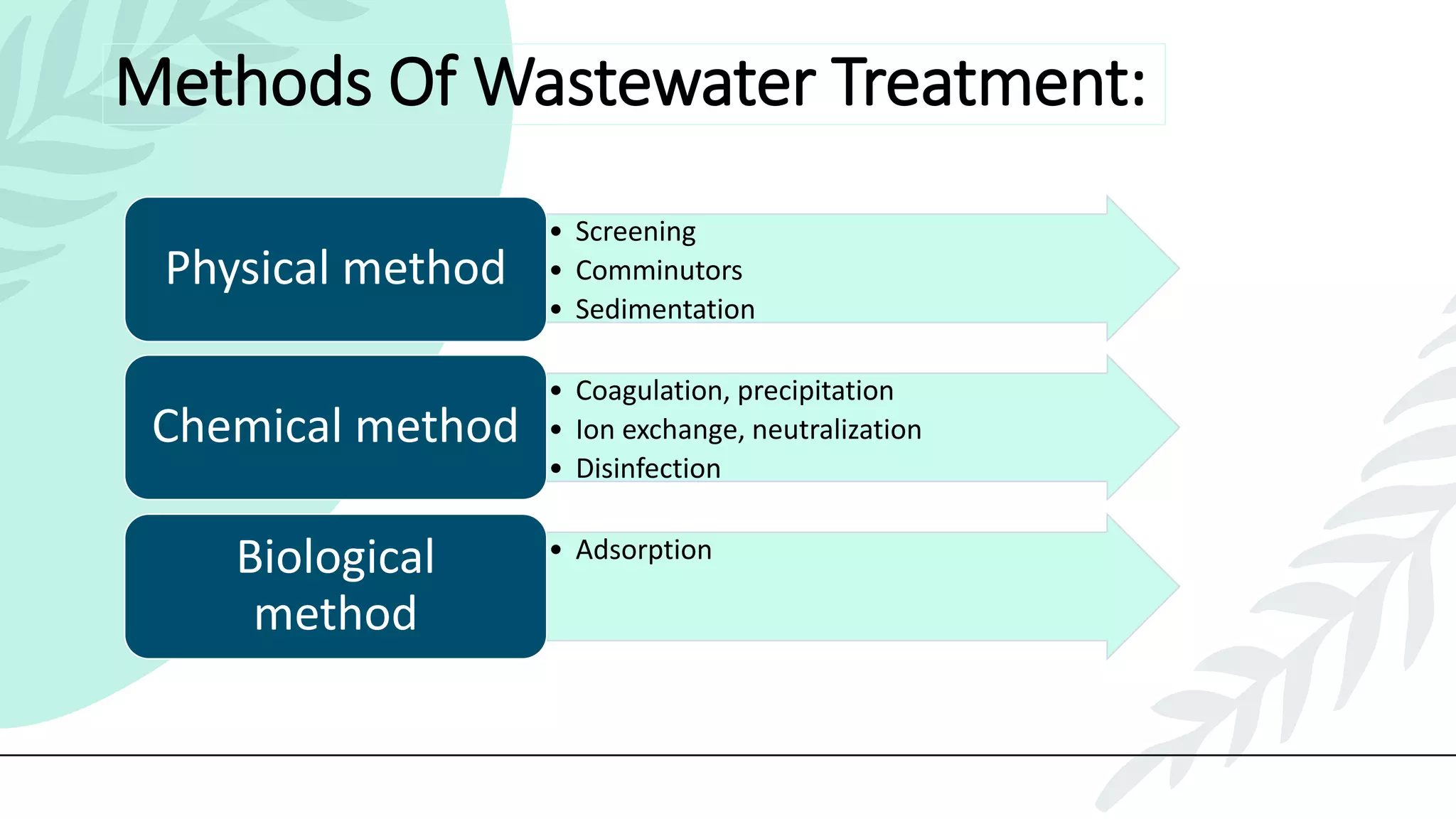
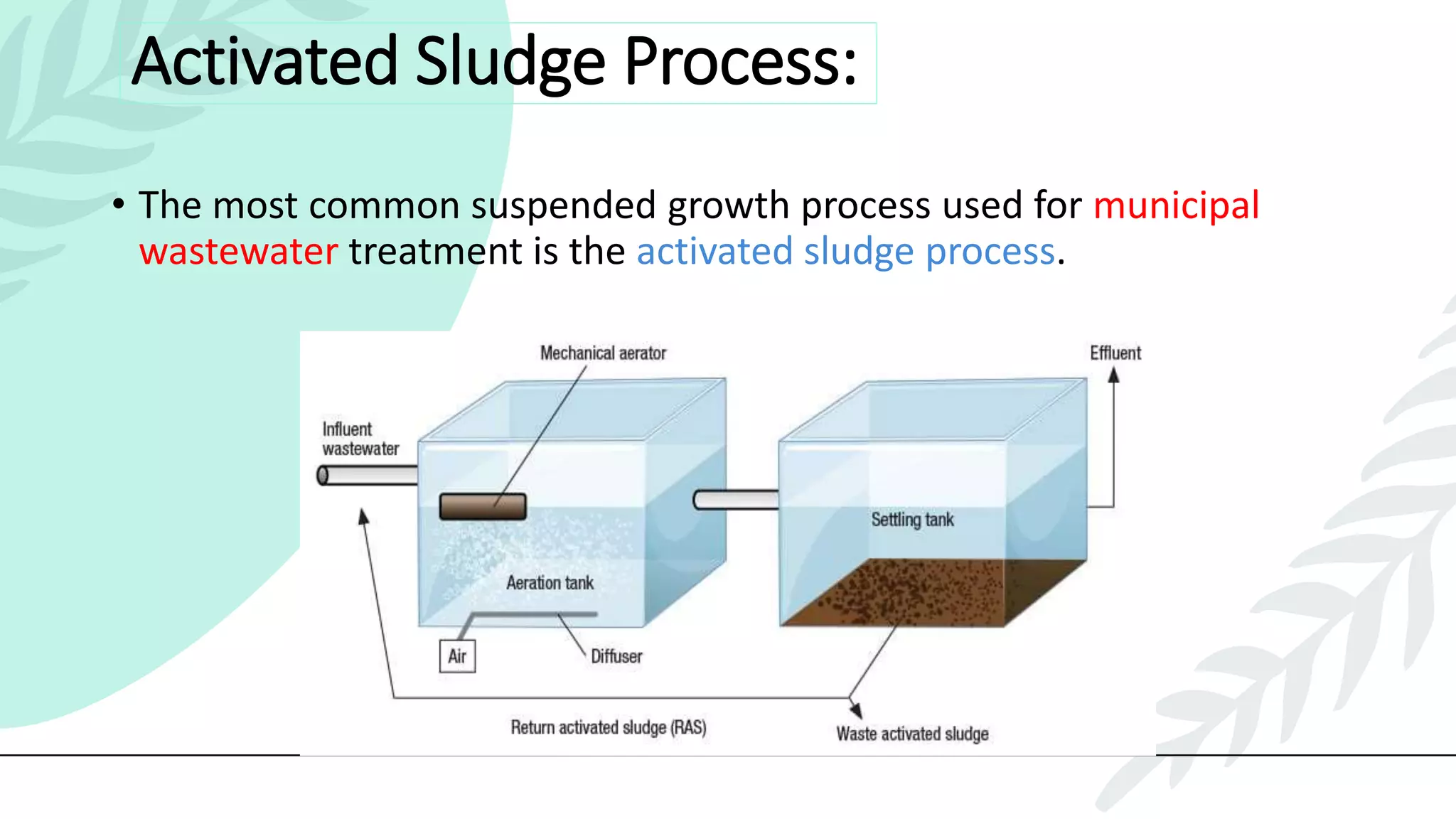
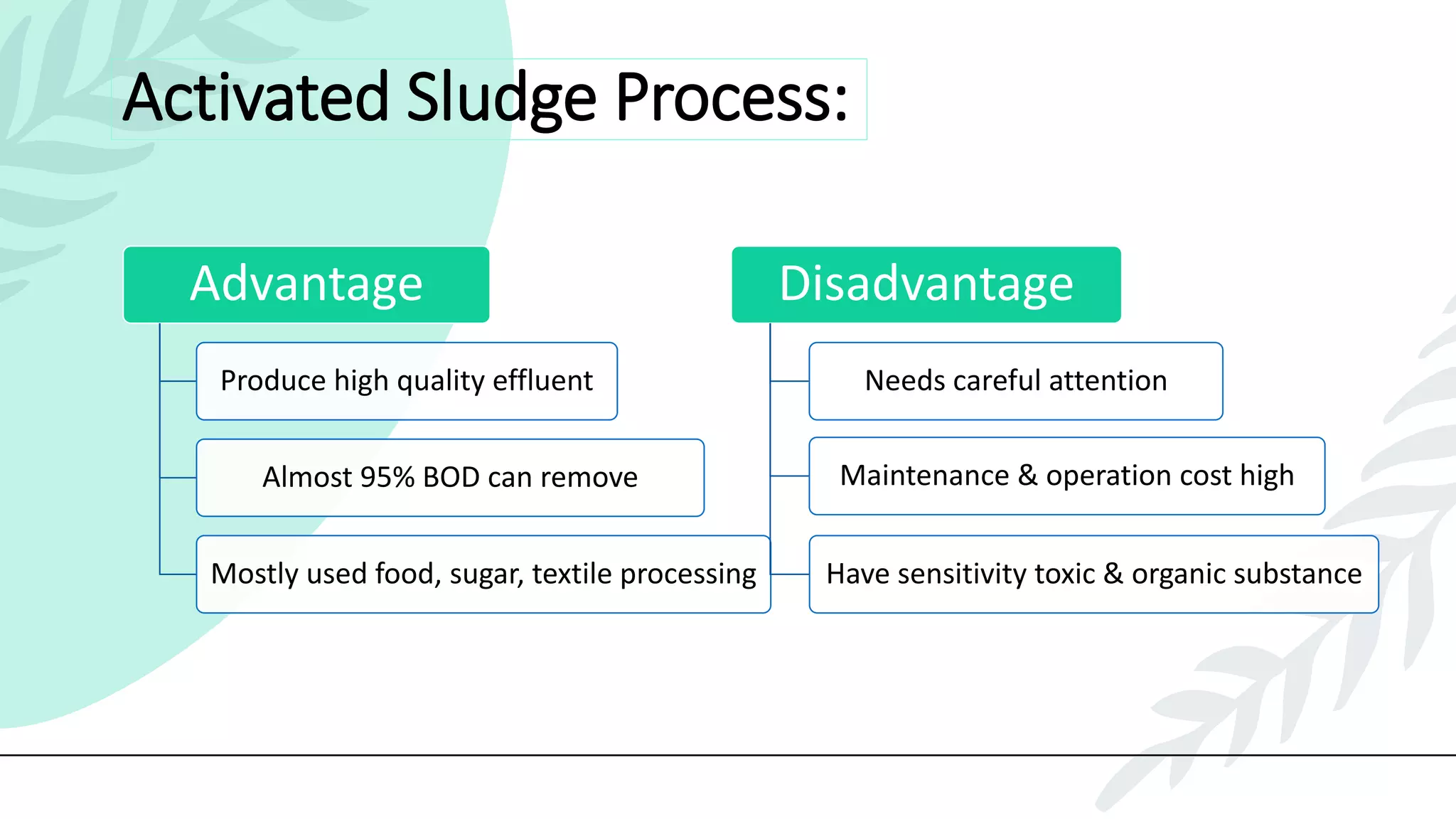
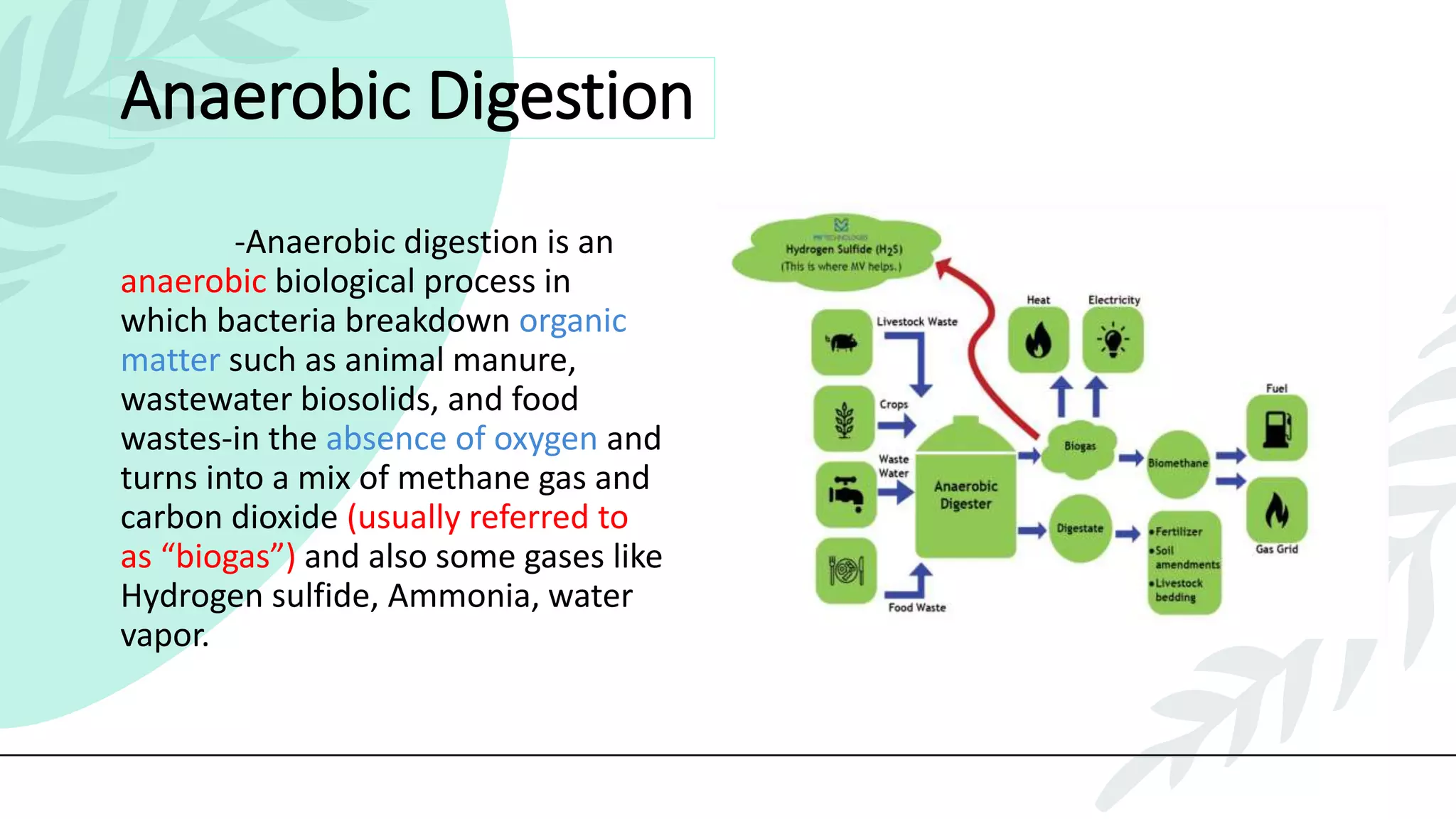
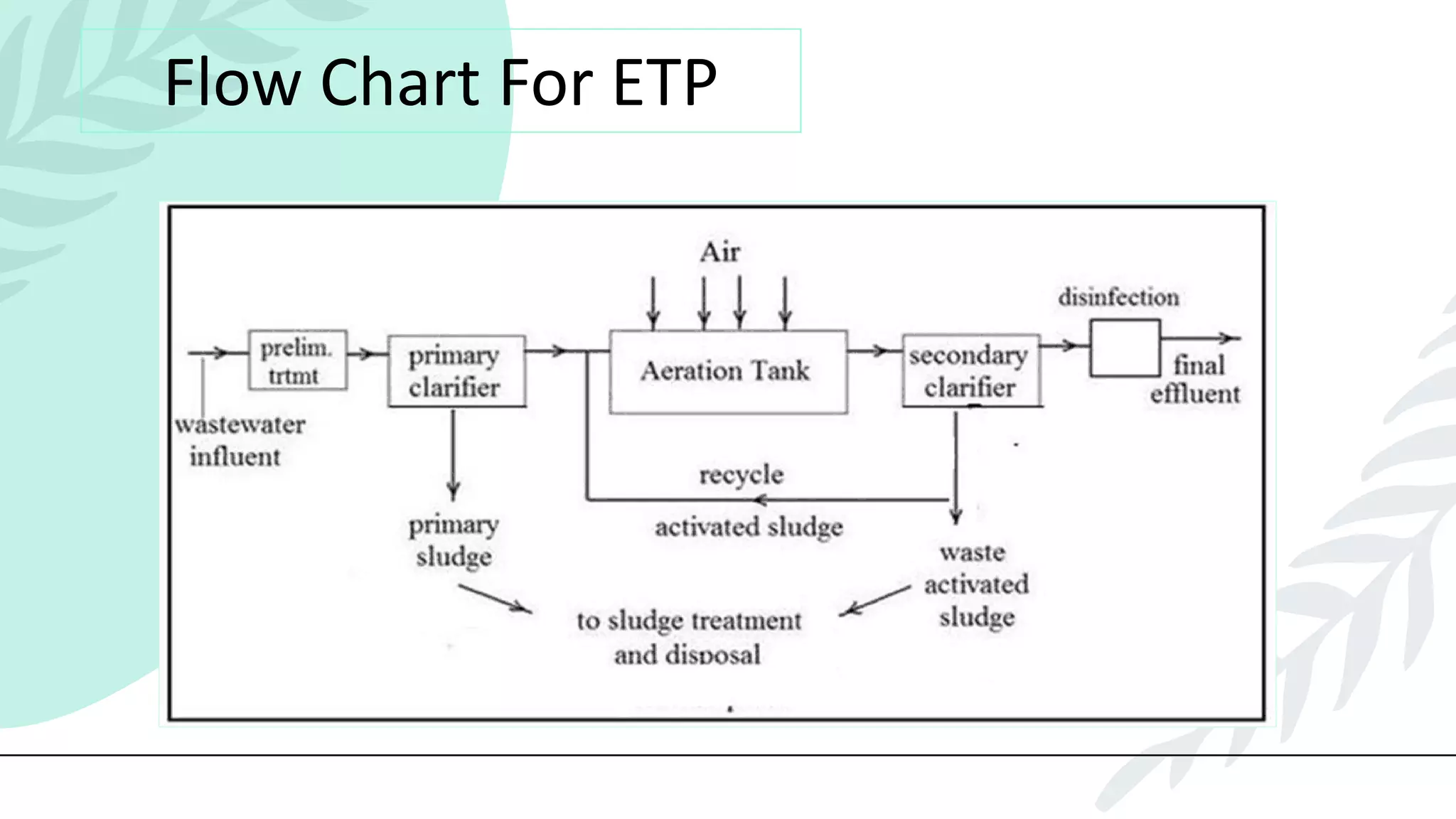
This presentation discusses effluent treatment plants (ETPs). It begins with introducing the presenters and contents to be covered. The contents section outlines the key concepts to be discussed including the need for ETPs, major treatment units, and different treatment stages. Diagrams are provided explaining the ETP process flow and components. The conclusion emphasizes that ETPs treat industrial wastewater through stages to remove contaminants for environmental and public health protection.