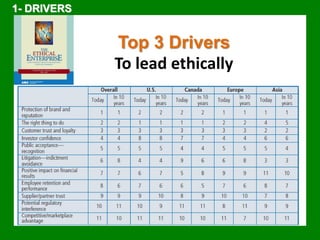
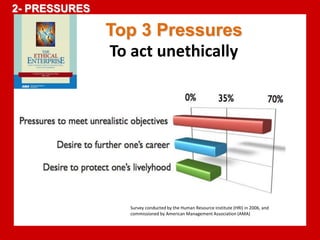
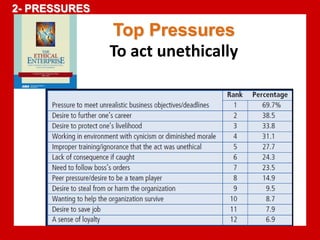
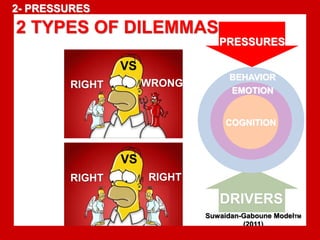
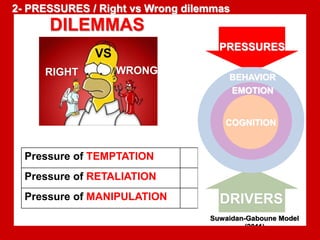
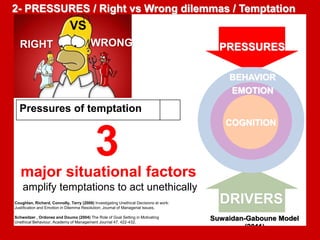
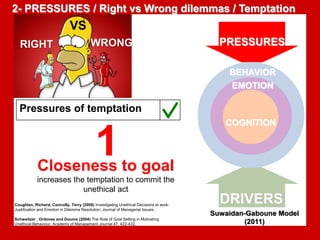
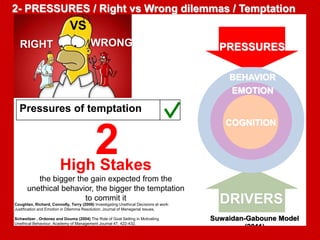
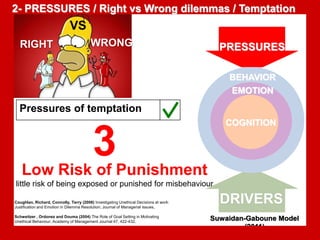
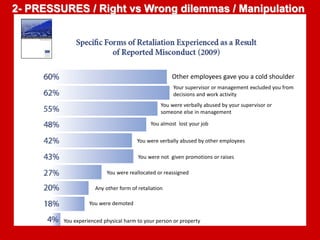
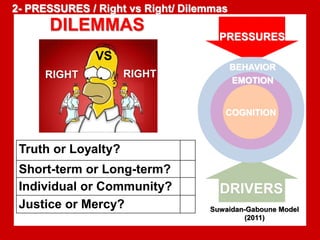
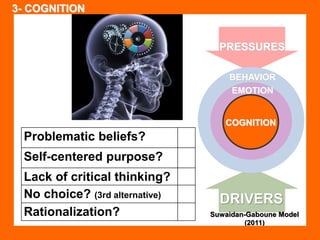
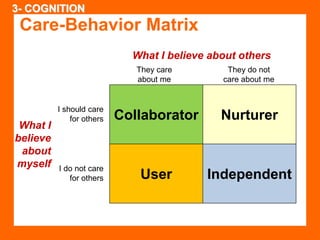
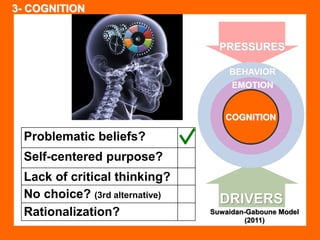
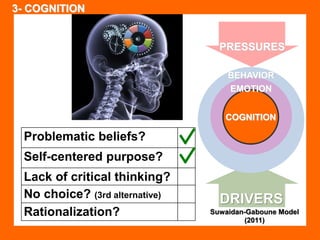
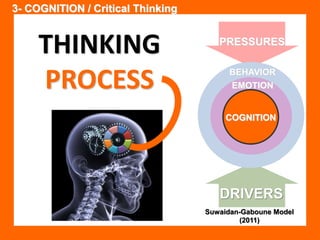
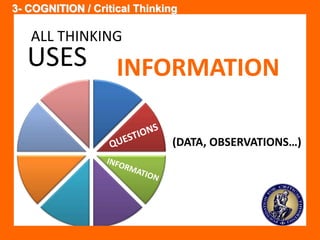
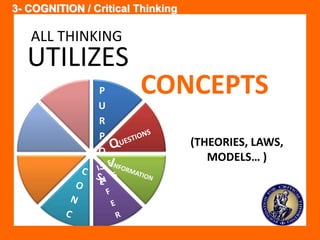
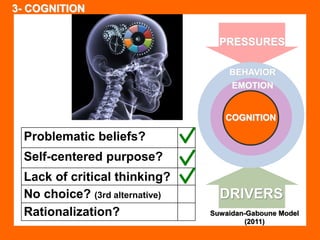
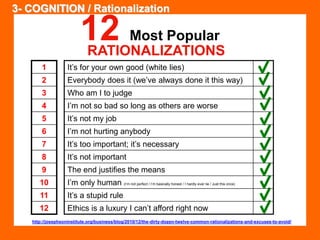
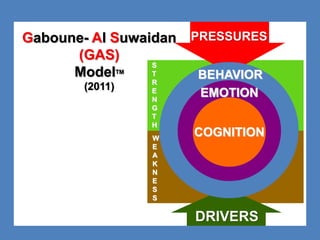
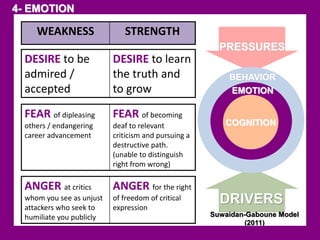
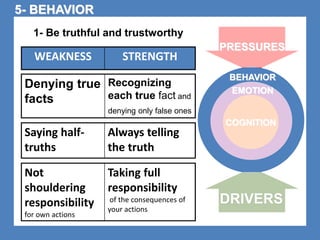
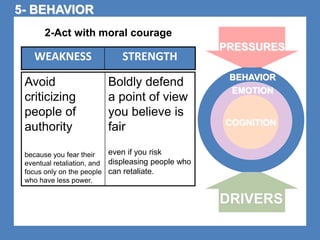
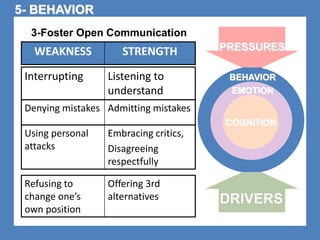
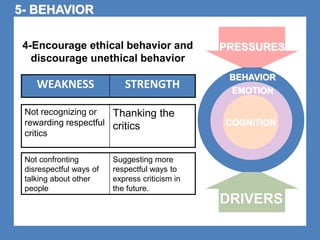
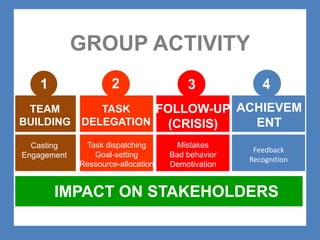
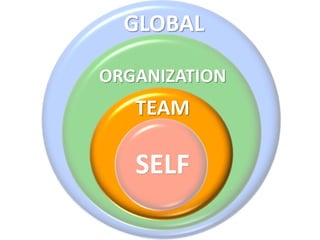
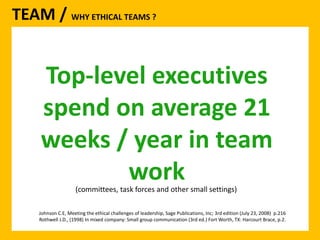
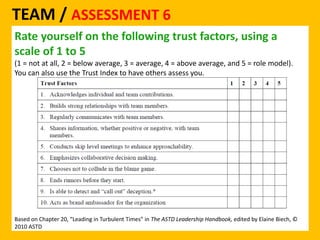
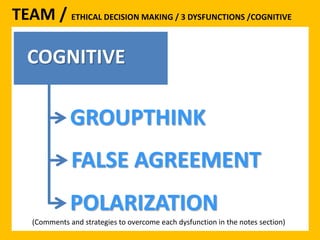
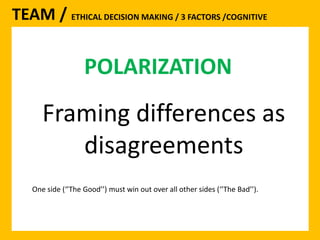
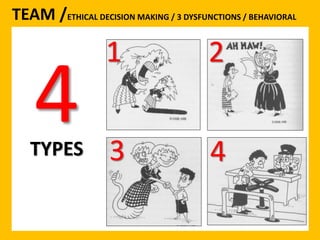
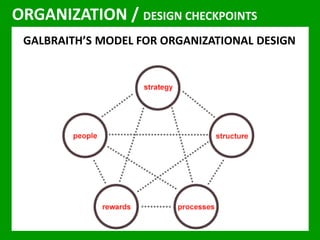
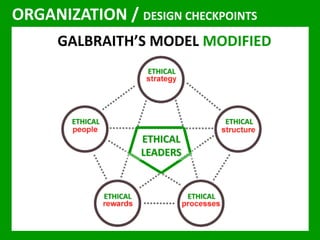
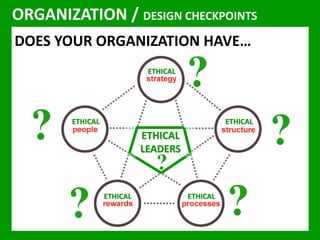
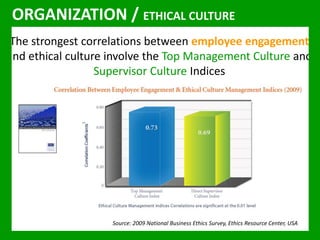
The document outlines the Ethical Leadership Ambassador Training program, focusing on the importance of ethical leadership and its relevance in current times. It describes the skills and behaviors needed to identify, grow, and role model ethical leadership, along with common ethical challenges leaders face. The training aims to equip participants to navigate ethically challenging situations through structured discussions, assessments, and practical exercises.