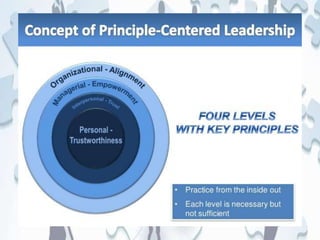
This document discusses managing ethical employee behavior through organizational leadership and culture. It argues that leadership must meet moral challenges through demonstrating integrity, empathy, consistency, and vision to build trust. Companies should clearly communicate ethical standards and have policies, training, and processes to encourage ethical conduct and address violations. Leaders must exemplify ethical behavior and shape an ethical culture where employees feel comfortable raising concerns without fear of retribution. Fostering an ethical environment through open communication and accountability benefits both business and society.