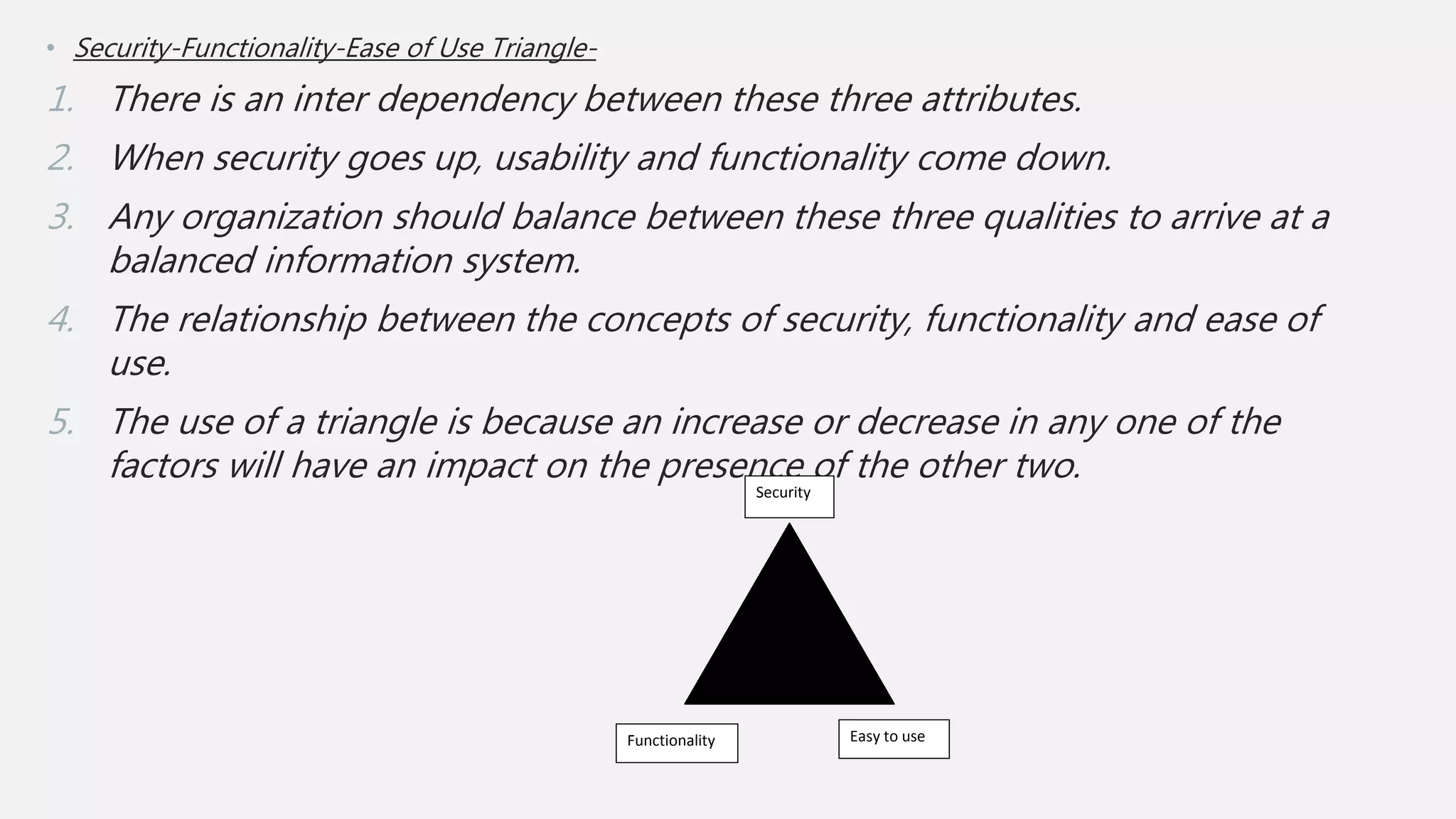
The document provides an overview of key concepts in information security, including definitions of terms such as information security, asset, access control, and the CIA triad (confidentiality, integrity, availability). It discusses the relationships between risks, threats, vulnerabilities, and types of attacks, as well as the importance of authentication and authorization. Additionally, the document highlights the trade-offs between security, functionality, and ease of use in designing secure systems.