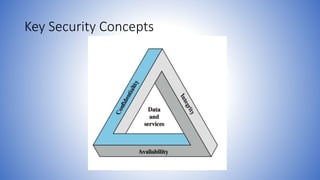
The document discusses the evolution of information security, highlighting the shift from physical and administrative measures to automated tools with the advent of computers. It emphasizes the importance of the CIA triad—confidentiality, integrity, and availability—as fundamental objectives in computer security, along with additional concepts like authenticity and accountability. A comprehensive understanding of these security principles is vital for protecting data in today’s interconnected systems.