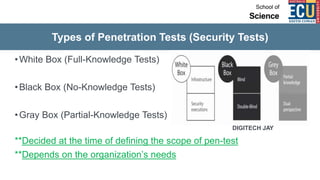
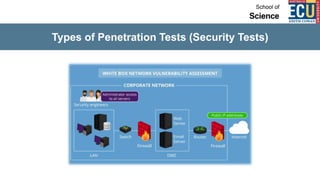
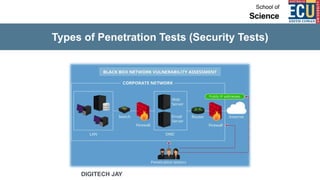
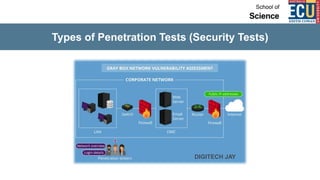
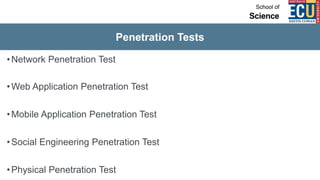
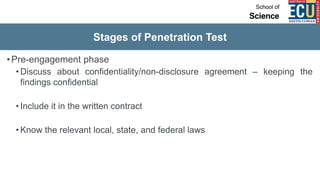
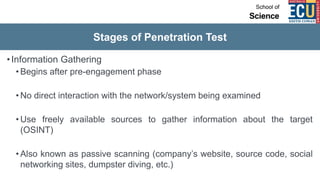
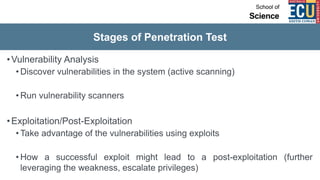
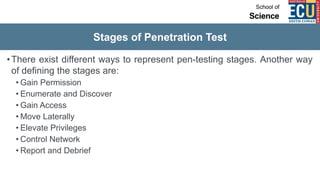
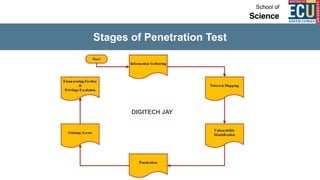
The document discusses ethical hacking and penetration testing. It begins by defining hacking and clarifying that hacking is not always illegal, harmful, or unethical. It then differentiates between vulnerability assessments, penetration tests, and security tests. Various types of hackers (white hat, black hat, gray hat) and penetration tests (white box, black box, gray box) are defined. The stages of a penetration test are outlined as pre-engagement, information gathering, threat modeling, vulnerability analysis, exploitation/post-exploitation, and reporting. Different penetration testing methodologies and activities like network penetration tests and mobile application tests are also mentioned.