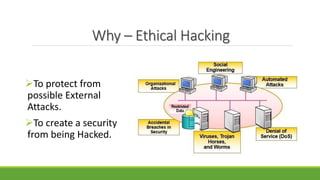
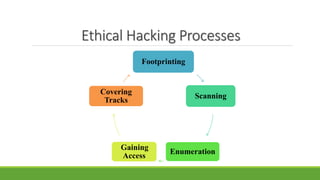
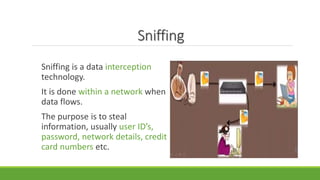
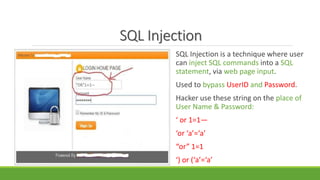
The document provides an overview of ethical hacking, which is legal hacking performed with organizational permission to enhance security. It categorizes hackers into white hat, black hat, and grey hat, explains the ethical hacking process in stages such as footprinting, scanning, enumeration, gaining access, and covering tracks, and discusses methods like sniffing and SQL injection. The conclusion advises caution in sharing passwords and using the internet securely.