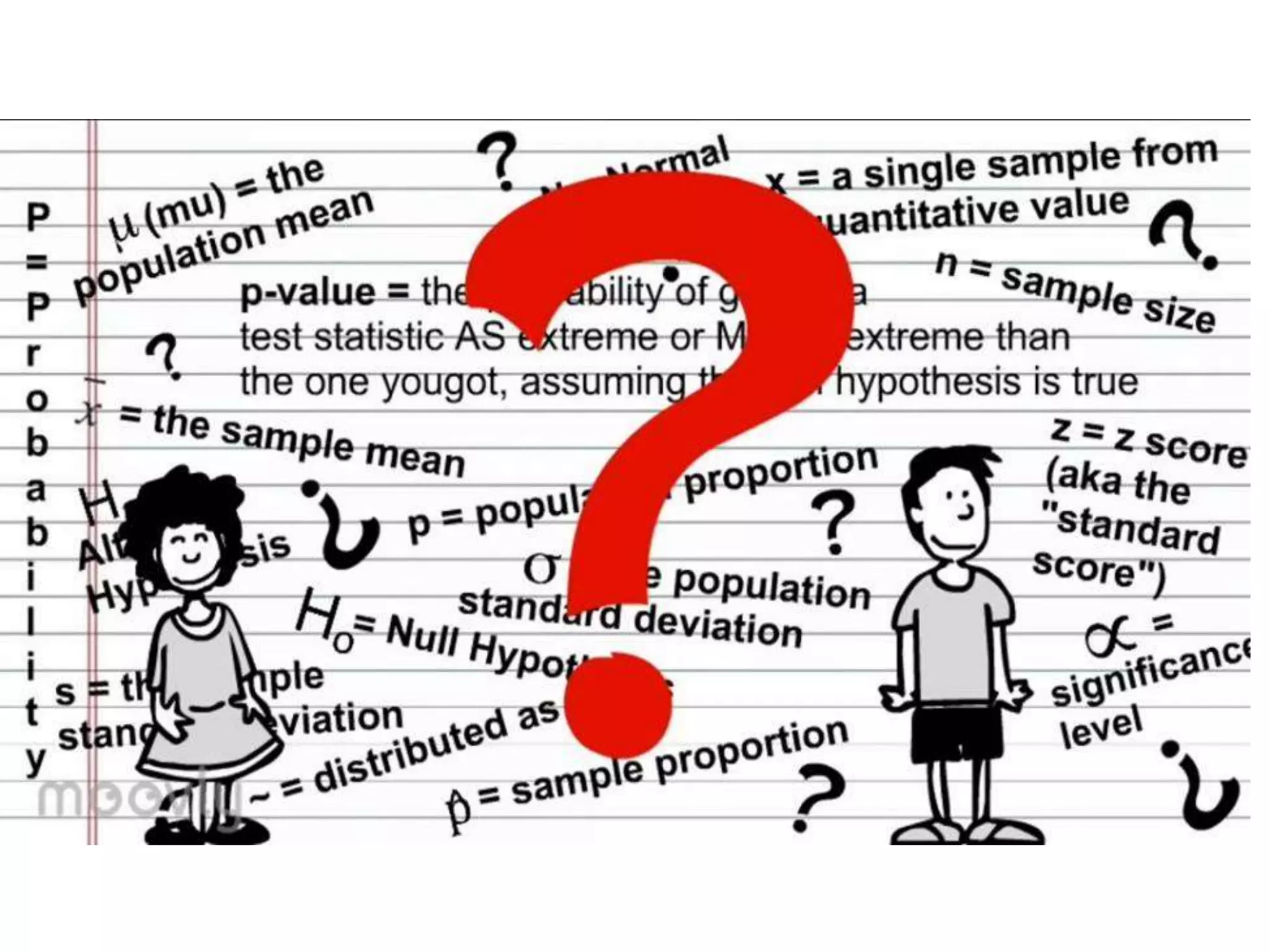
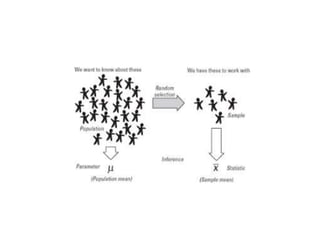
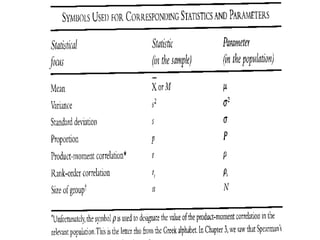
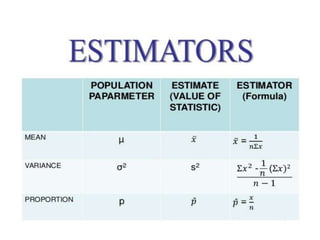
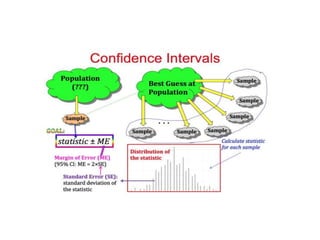
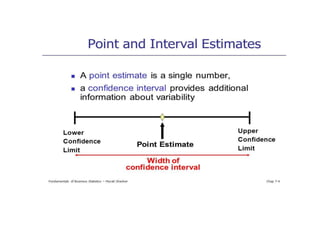
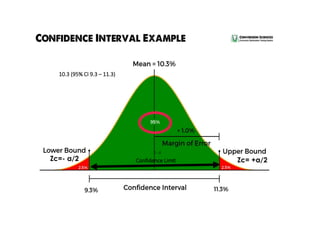
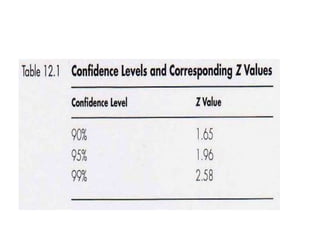
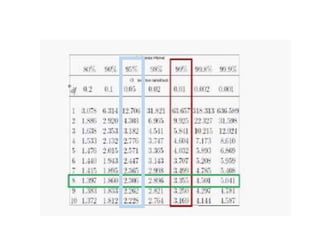
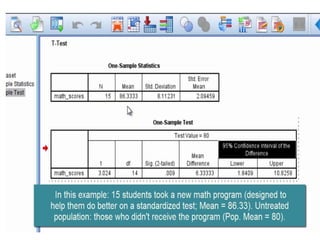
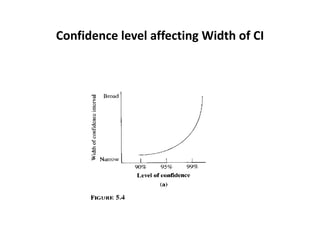
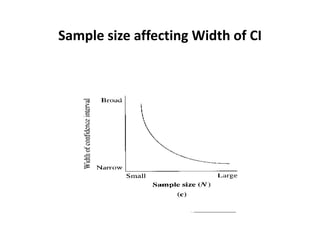
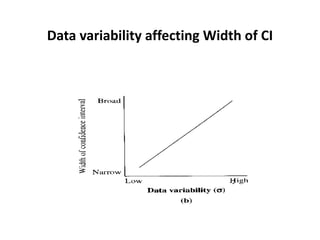
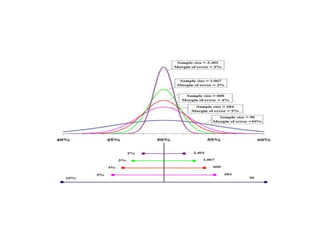
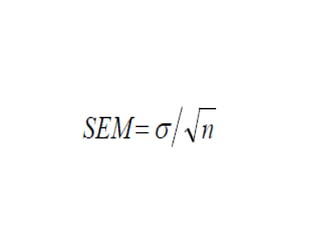Estimation involves making inferences about a population based on a sample. An estimator is a statistic used to estimate unknown population parameters, and the estimate is the computed value. A good estimator is unbiased, efficient, and consistent. Confidence intervals provide a range of values that are likely to contain the true population parameter, depending on the sample size, confidence level, and variability of the data. Both confidence intervals and p-values provide important information but confidence intervals also convey the magnitude and strength of an effect.