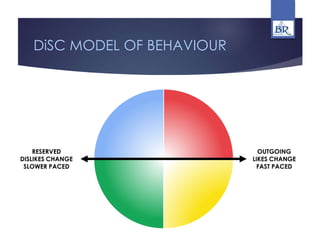
The document discusses the importance of performance management in aligning employee performance with organizational goals, improving communication, and contributing to business results. It also covers best practices for effective performance management such as communication, understanding personality differences, consistency, motivation, and focusing on development rather than punishment. Communication skills are emphasized, including listening actively and providing specific, constructive feedback.