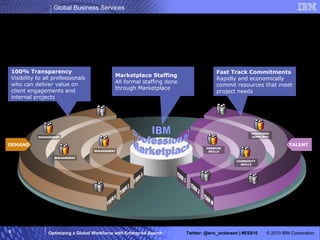
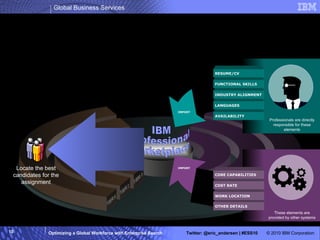
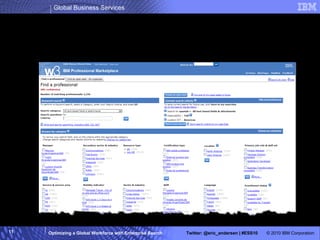
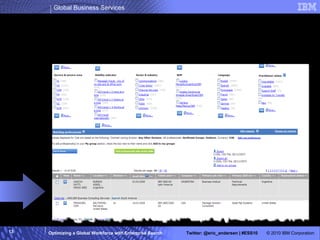
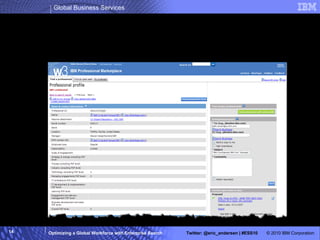
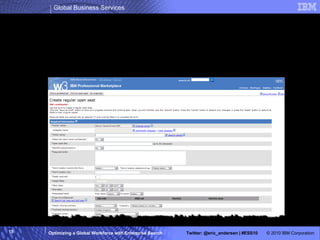
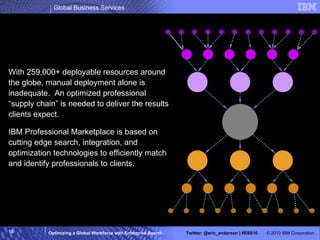
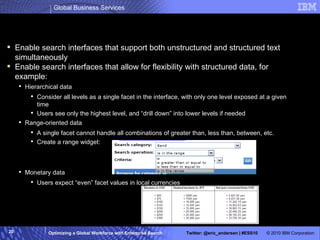
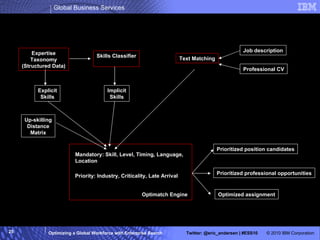
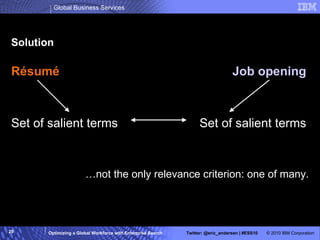
The IBM Professional Marketplace is designed to optimize workforce engagement by matching supply and demand in a global context, featuring a dynamic self-service model for staffing decisions. It leverages advanced search technologies to enable efficient matching of a large pool of over 259,000 professionals with client needs, addressing complexities inherent in a global workforce. The system enhances transparency, agility, and decision-making while providing comprehensive profiles to ensure quality staffing for diverse projects.