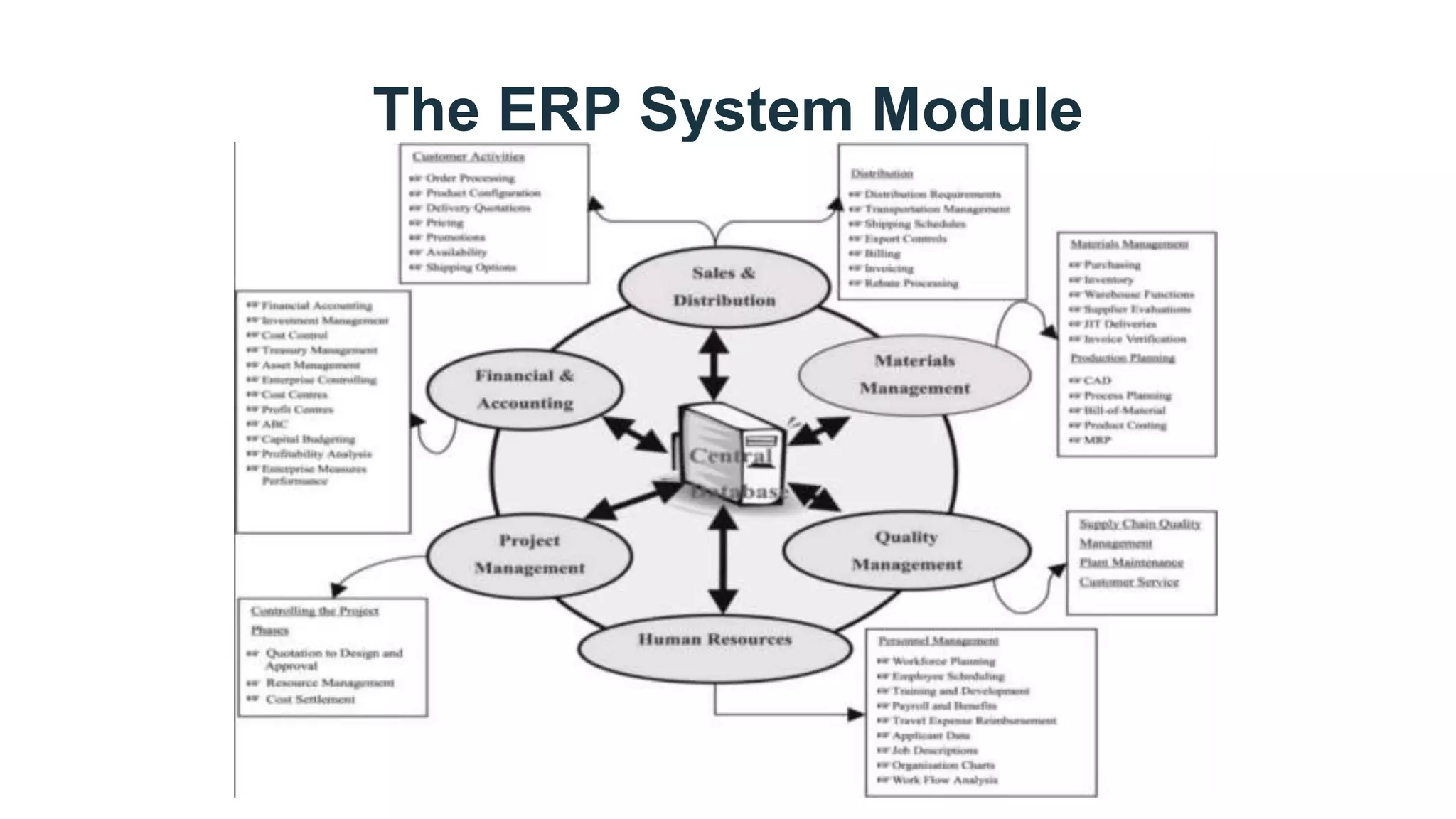
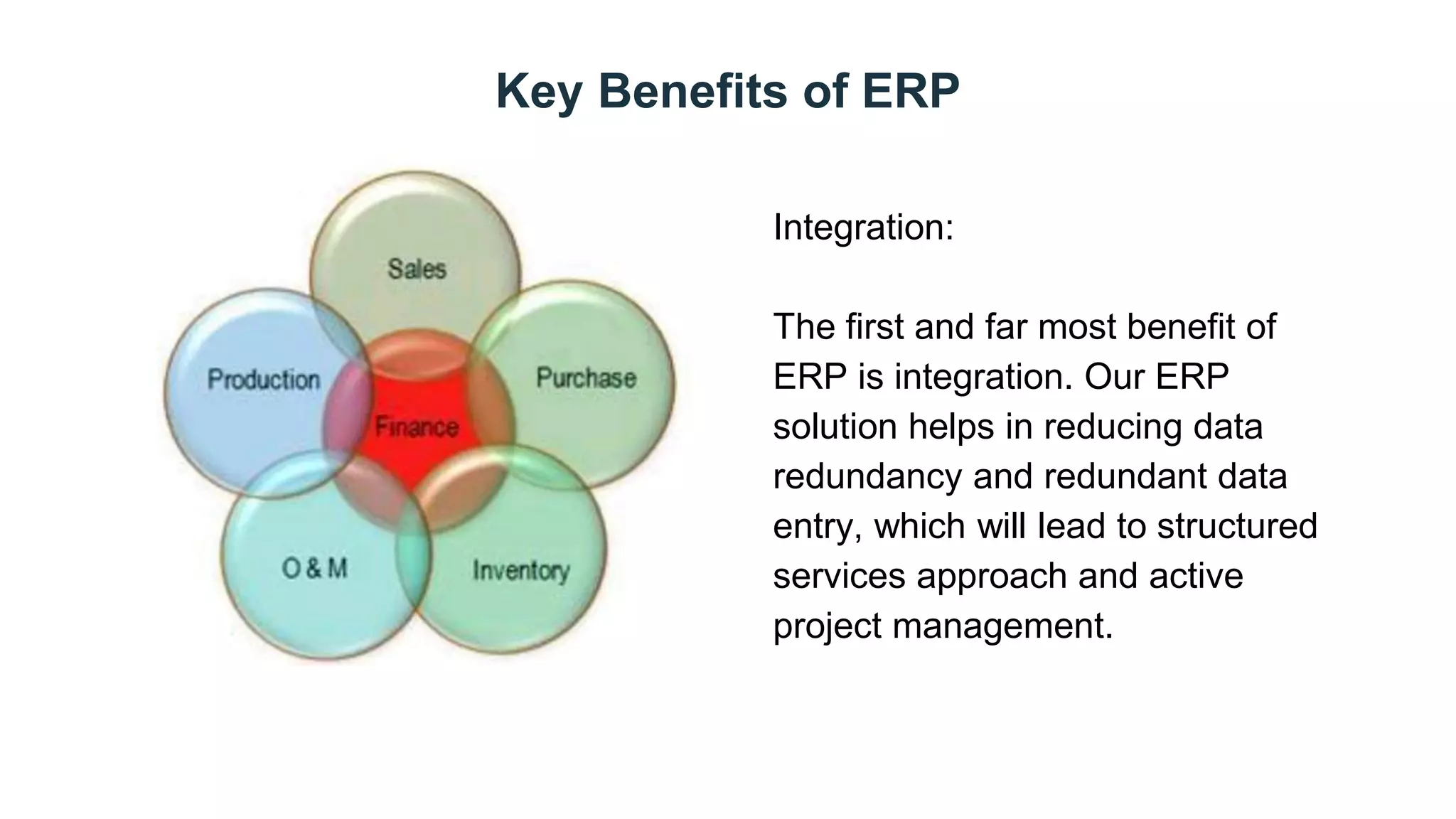
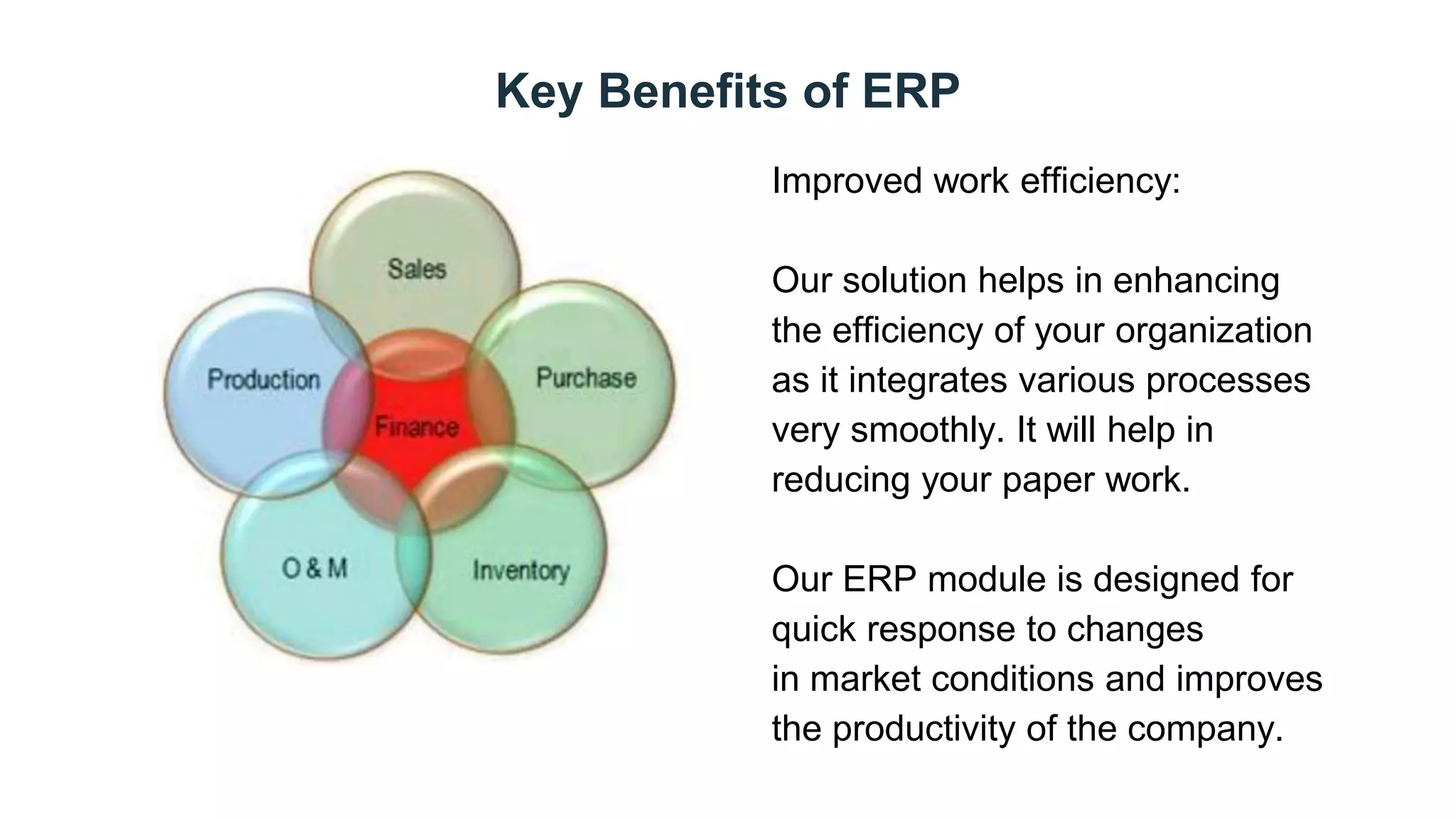
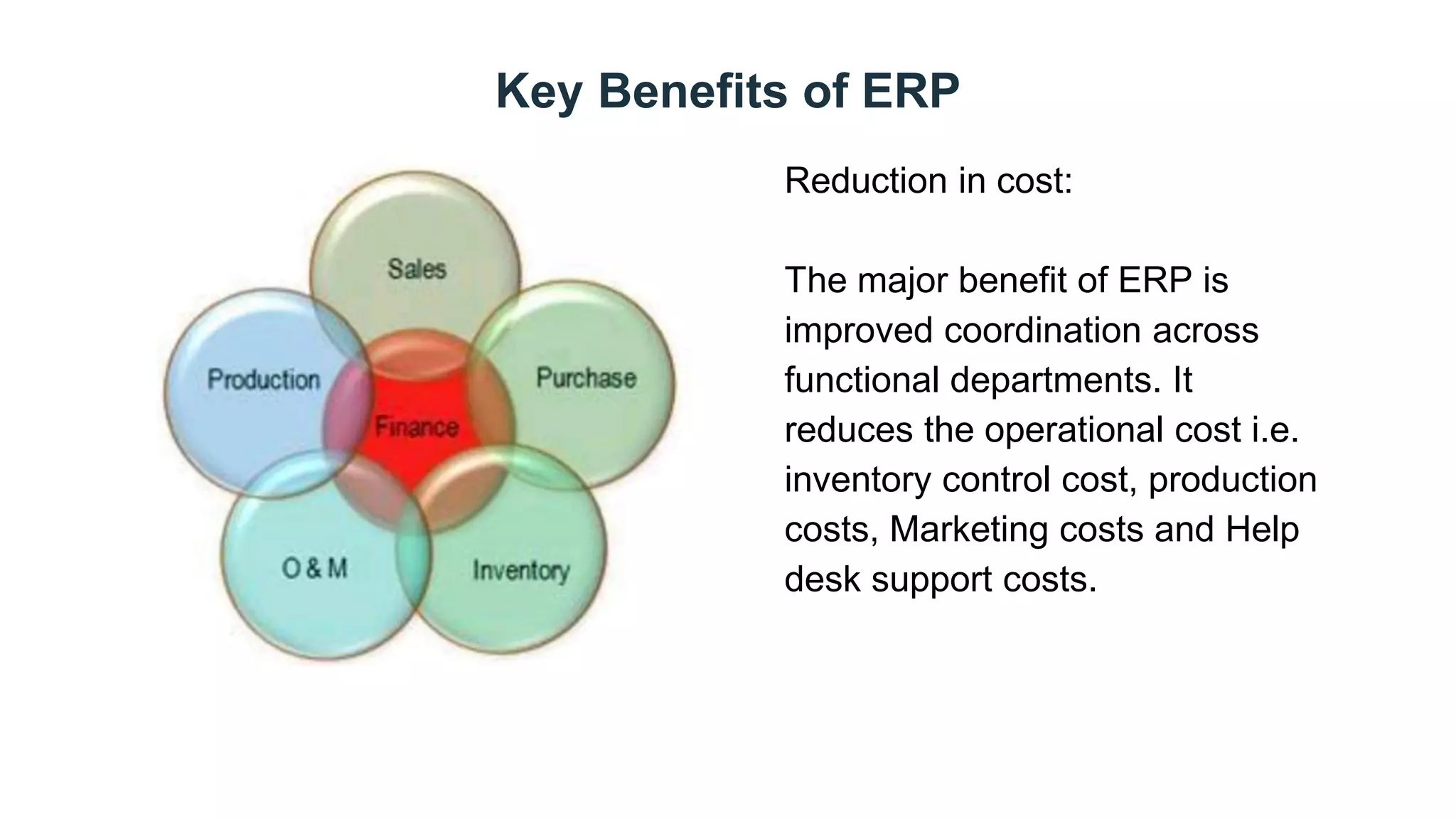
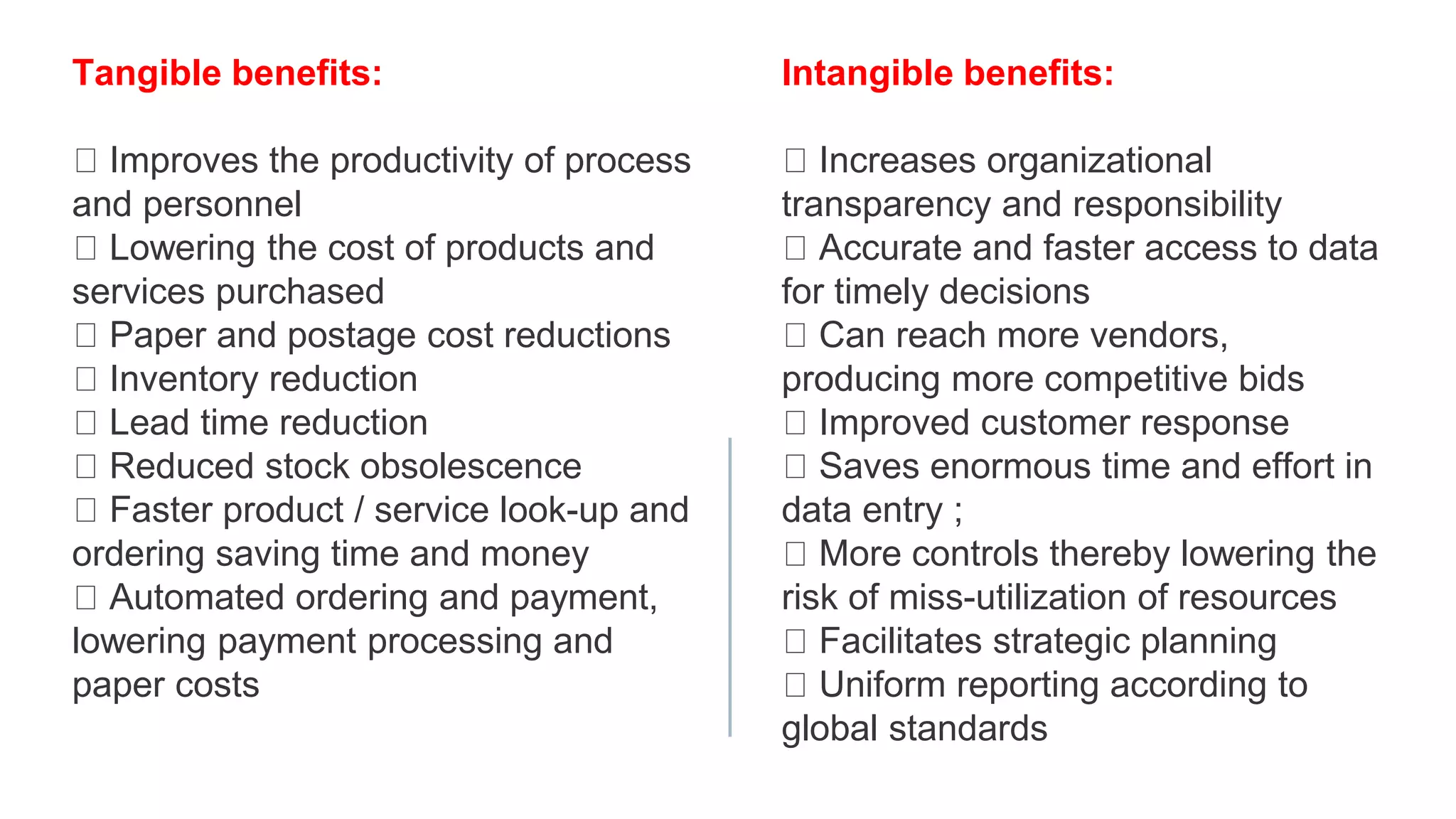
This document discusses Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. It defines ERP as a system that combines all of a company's functions and information into a single system to unify operations. ERP software can manage processes like production planning, purchasing, inventory, customer service and tracking orders. The document outlines benefits of ERP like improved integration, efficiency, and reduced costs through features like inventory reduction and increased productivity. It also discusses why companies implement ERP systems, including trends toward packaged software solutions and the need to link internal and external business processes.