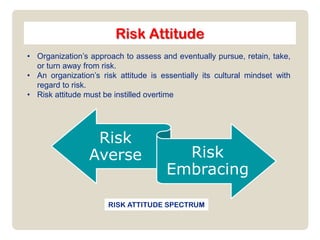
1) Risk criteria help determine what risks are significant for an organization based on its objectives and context. Governance criteria include risk capacity, attitude, appetite, and tolerance. 2) Risk capacity refers to the maximum level of risk an organization can assume. Risk attitude is an organization's cultural mindset towards risk. Risk appetite is the amount of risk an organization is willing to accept. Risk tolerance are the boundaries for risk-taking. 3) Assessment criteria measure the potential size of risk outcomes, such as impact and likelihood. Impact types include financial, reputational, legal and more. Likelihood estimates the possibility a risk event will occur.