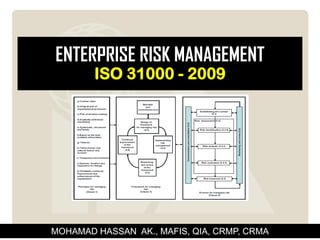
1) The document discusses the process of establishing an enterprise risk management (ERM) system based on the ISO 31000 standard, including obtaining management commitment, designing an ERM framework, and implementing, monitoring, and improving the system.
2) Key steps in designing an ERM framework include understanding the organization's context, determining where ERM should be positioned, developing a risk management policy, and assigning roles and responsibilities.
3) Internal audit can play an important role in establishing the ERM system by leading implementation, providing consulting support and assurance services, and helping to identify, analyze, and evaluate risks.