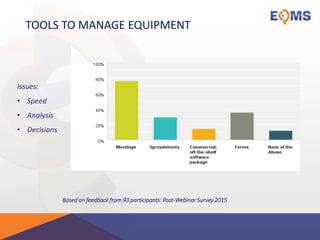
The document outlines the objectives and key topics related to effective business equipment management, emphasizing its importance in enhancing ROI, reducing risk, and supporting regulatory compliance. It identifies seven key problems that organizations face in managing equipment, which include improper operation and regulatory compliance issues. The presentation also stresses the significance of maintaining accurate records and implementing best practices for safety and efficiency.