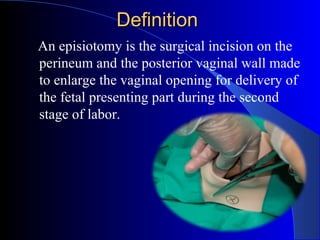
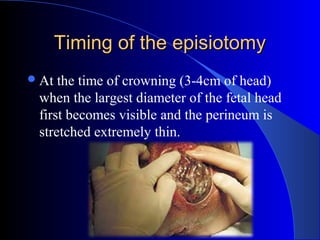
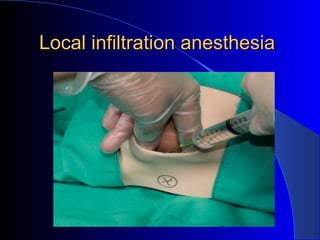
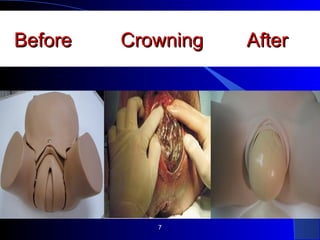
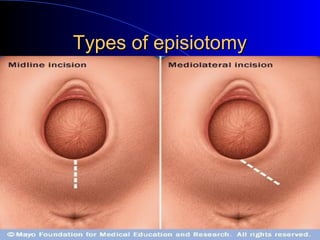
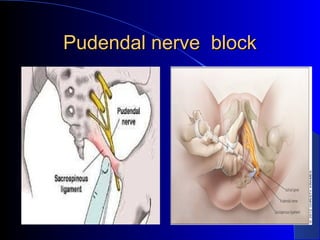
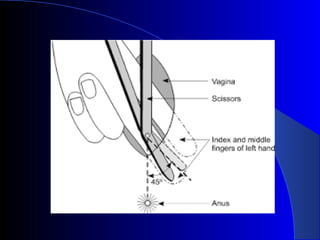
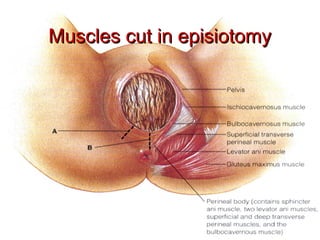
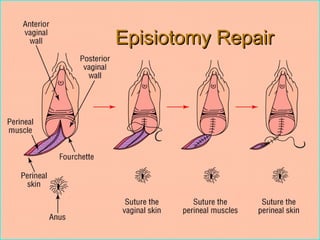
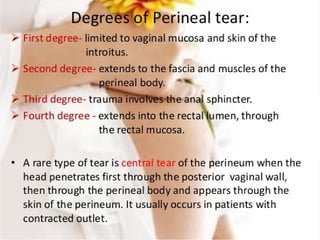
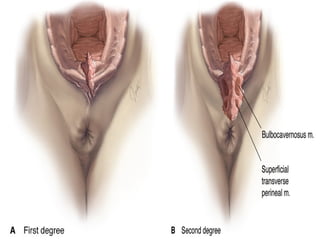
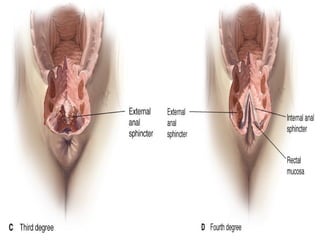
This document defines an episiotomy as a surgical incision made in the perineum and posterior vaginal wall during childbirth to enlarge the vaginal opening. It discusses the objectives, indications, timing, types, and steps for performing a mediolateral episiotomy. It also covers repairing the episiotomy, potential complications, and post-operative care recommendations such as applying ice, keeping the wound clean and dry, and encouraging sitz baths.