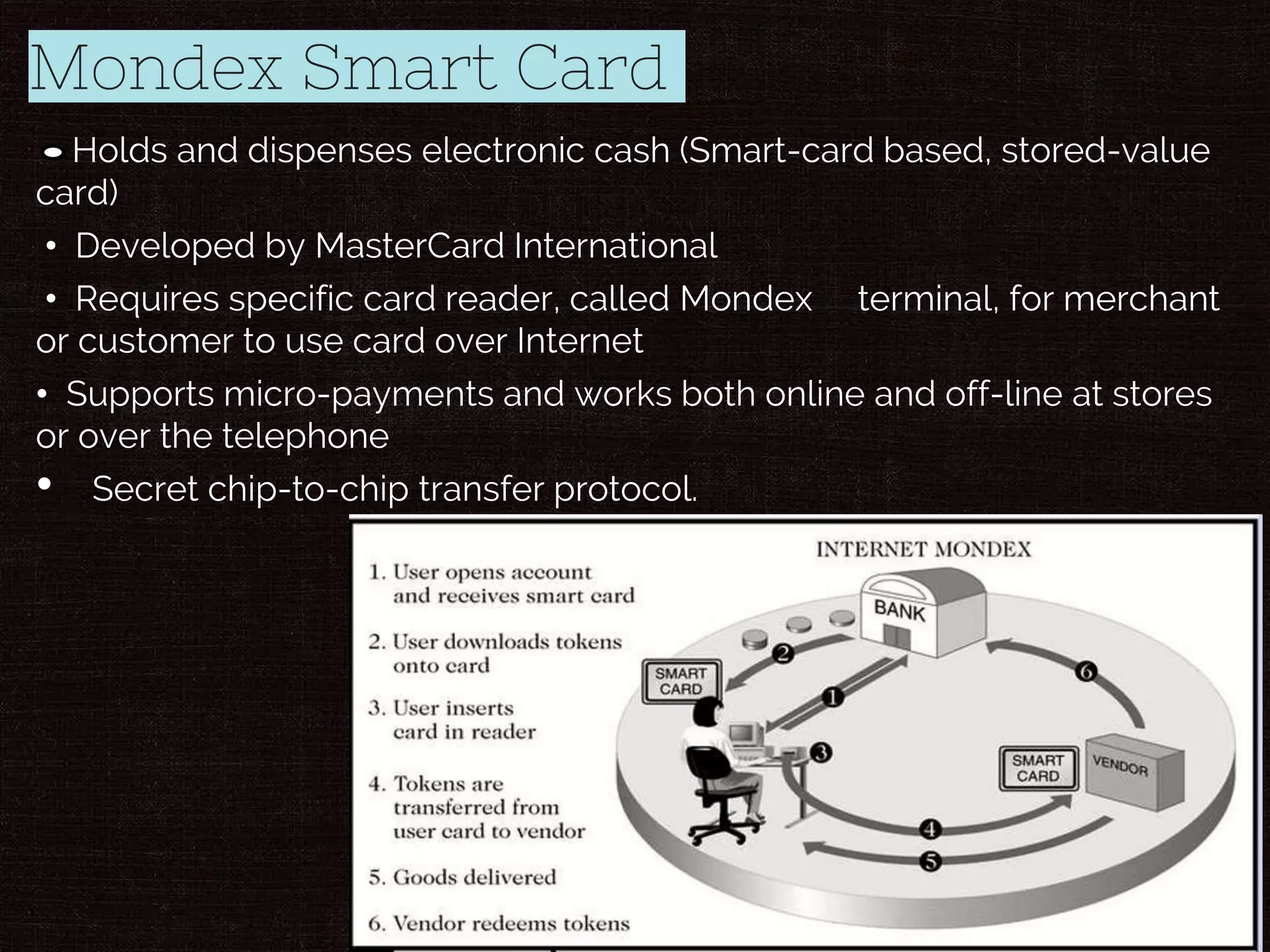
This document provides an introduction to electronic payments and e-commerce. It discusses various modes of electronic payment such as payment cards, electronic cash, check free payments, electronic wallets, and smart cards. The advantages and disadvantages of these methods are outlined. Emerging trends in electronic payments are also examined, including growing smartphone adoption and mobile payment technologies like near-field communication. The future of payments is predicted to be increasingly mobile-centric.