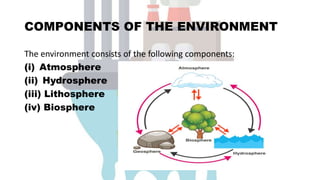
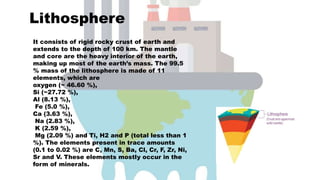
Environmental chemistry examines chemicals and pollutants in the environment, focusing on their sources, reactions, transportation, and harmful effects caused by human activities. The environment consists of four main components: atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere, each playing a critical role in sustaining life and interacting with pollutants. Environmental pollutants are substances that negatively impact human health and the ecosystem's natural processes.