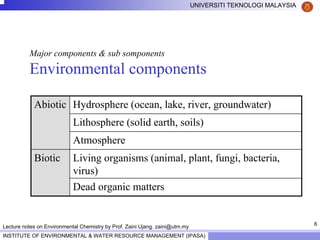
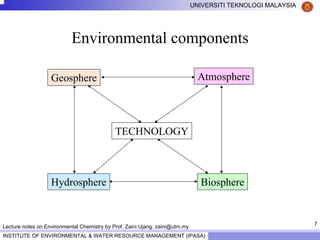
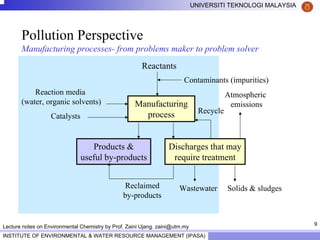
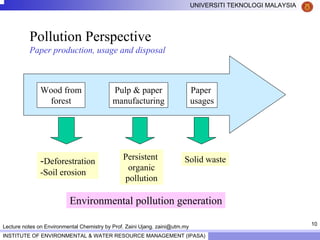
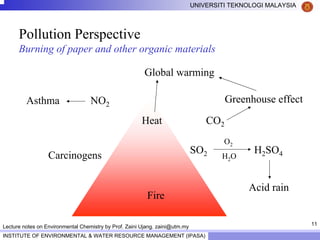
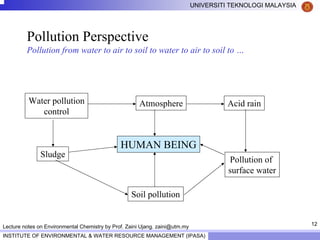
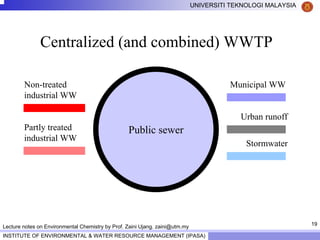
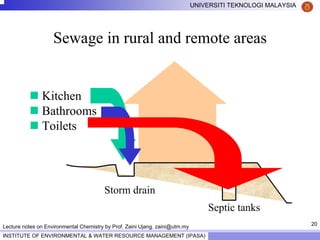
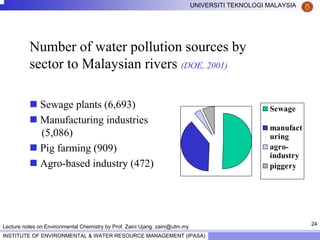
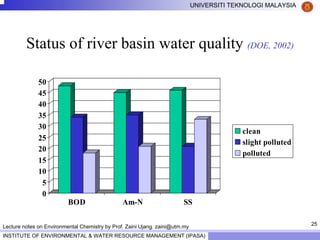
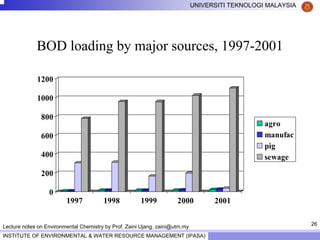
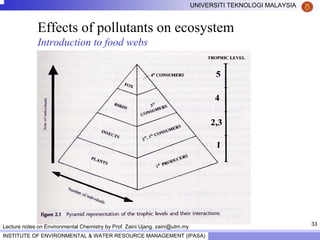
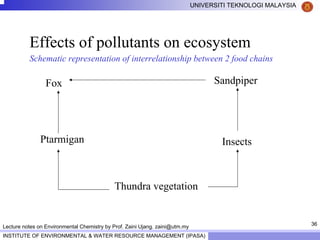
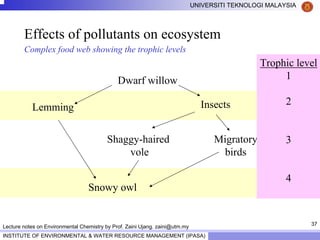
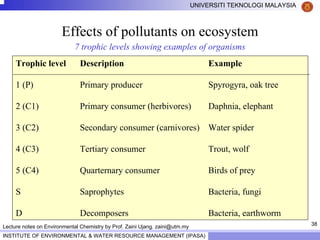
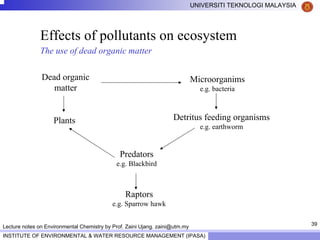
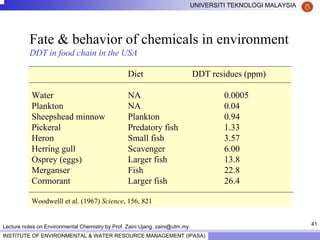
This document contains lecture notes from Prof. Zaini Ujang on environmental chemistry. The notes cover topics such as pollution perspectives, major pollutants in water, atmosphere and soil, ecological systems and disturbances, and an introduction to environmental components and ecosystems. The lecture outline includes pollution perspective, major pollutants, effects of pollutants, fate of chemicals in the environment, and environmental monitoring techniques.