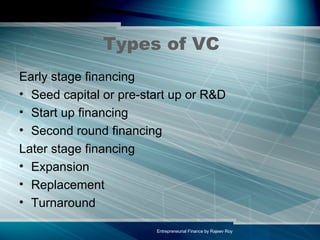
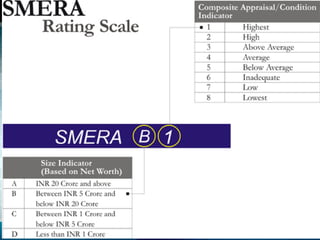
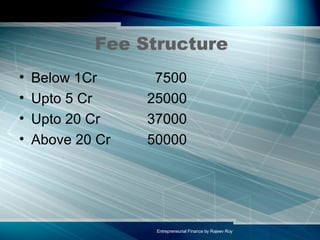
This document summarizes key aspects of entrepreneurial finance and venture capital. It discusses what venture capital is, how venture capital firms are structured, the advantages and disadvantages of venture capital for entrepreneurs, and common terms in venture capital agreements. It also provides an overview of venture capital in India, including some major venture capital firms, average fund sizes, and challenges in the Indian market.