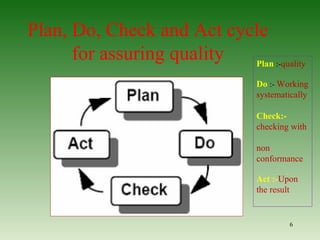
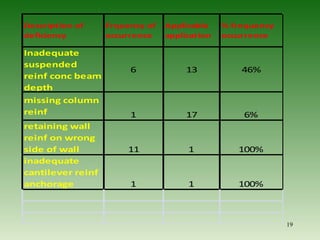
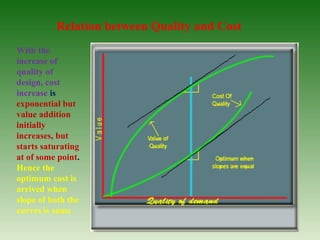
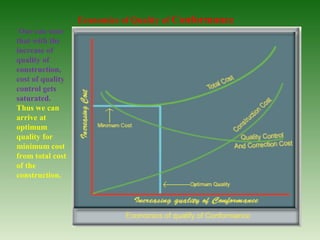
This document discusses ensuring quality in civil construction projects. It defines quality as excellence that meets certain standards. Quality control procedures implement proper mixing, compaction, placement and curing of construction materials. Following a plan-do-check-act cycle can help assure quality. Common construction mistakes that reduce quality are also outlined, such as inadequate compaction, improper reinforcement, and poor workmanship. Causes of poor quality include ignorance, substandard materials and design, and lack of supervision. The relationship between quality, cost and value is examined.