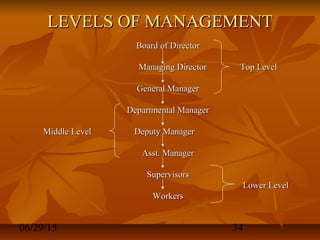
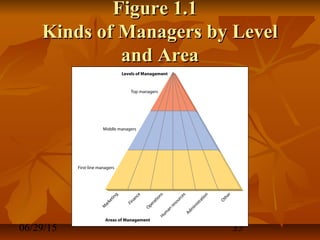
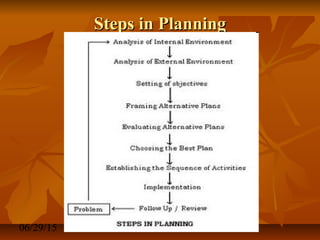
This document discusses definitions and concepts of management. It defines management as a set of activities including planning, organizing, leading, and controlling organizational resources to achieve goals efficiently and effectively. A manager is someone who carries out these management functions. Management involves planning and decision making, organizing, leading, and controlling human, financial, physical, and information resources using a process to attain organizational goals. Management can be viewed as both a science, relying on logical problem-solving techniques, and an art, involving intuition and personal skills. The document also examines different interpretations and levels of management.