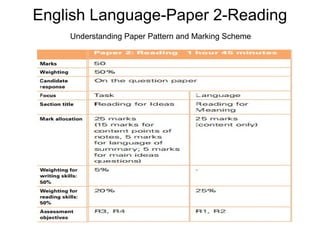
The document provides an overview of the English Language Paper 2 exam for reading comprehension. It discusses the exam structure, which has two sections: Section 1 focuses on reading for ideas, while Section 2 focuses on more in-depth reading for meaning. For each section, the document outlines the types of questions, question formats, marking schemes, and strategies for answering different question types such as factual versus opinion questions, literal versus inferential comprehension questions, and lifting versus own words responses. Overall, the document aims to help students understand the exam format and requirements to improve their reading comprehension skills and exam performance.



![English Language-Paper 2-Reading
Understanding Section 1 Reading for Ideas
“An insert of Non-fictional / Factual passage is given of around seven
hundred words, comprises of seven paragraphs.”
Question 1 (a) Notes [15 marks]
In order to attempt this question students have to skim and scan the required answer and
have lift from the passage and jot them in the relevant section. Here students are NOT
required to use their own words. the first point in each section of notes is done for you. You
will be awarded up to 15 marks for content points.
Question 1 (b) Summary [5 marks]
Now use your notes to write a summary in which you describe the content. This time, you
will be awarded up to 5 marks for using your own words wherever possible and for
accurate use of language.
Your summary, which must be in continuous writing (not note form), must be no longer than
160 words, including the 10 words given below.
Question 2 [3 marks]
Decide whether each of the following statements is true or false
and tick the boxes you have chosen.
Question 3 [2 marks]
Write opinion(s) / Fact(s) from the passage.
Note: Occasionally, Question 4 [1 mark] is also there; in that case question 3 carries [1
mark]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/final-170507021744/85/English-Language-1123-Essential-2k17-comprehension-5-320.jpg)








![English Language-Paper 2-Reading
Understanding Section 2 Reading for Meaning
Categorical Comprehension Questions
Combining Information Comprehension: (2 to 3 marks)
Combining comprehension require you to combine two or more separated
information, you must follow the normal procedure for selection and retrieval of
information as you do in literal and lifting.
Example:
The sun beat down on the pavements of the town. It was home to three thousand or so inhabitants,
with its quaint little market stalls selling hot food, its winding streets and crowded shops. Outside
the town, boys played on the banks of the dried up river.
Question: How can you tell that the weather is hot? Give two reasons for your answer. [2 marks]
Answer:
1. I know it is hot because the sun beat down the on the pavements.
2. I know it is hot because the river had dried up.
Example: The Storm
Huge waves pounded the stone walls built to keep the sea at bay, smashing free huge blocks of
marble and flinging them aside like pebbles, until the walls cracked and then collapsed.
Question: ‘Huge waves” pounded the sea walls. Explain fully the comparison used to show the strength of
these waves. [2 marks]
Answer: They smashed free blocks of marble and flung them aside like pebbles.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/final-170507021744/85/English-Language-1123-Essential-2k17-comprehension-14-320.jpg)

![English Language-Paper 2-Reading
Understanding Section 2 Reading for Meaning
Categorical Comprehension Questions
Quotation Comprehension: (1 - 2 marks)
In quotation comprehension, you are asked to find a word or expression in the text
which means the same as other word or expression which comes either from the
text or which is a synonym provided by the writer of the question.
Example: Amy
The next moment, though,, she saw something more reassuring. In the far corner of the cave a large
white cloth screen was erected, musicians were gathering and people were taking their places for some
sort of show.
An old man made his entrance by the side of the screen, dressed in a tattered, grimy cloak, but it was his
intense expression that startled Amy. Her feelings of uneasiness returned as she watched him gaze
round the audience.
Amy panicked wildly. She ran outside, stumbling down the steps, blundering past the crowd, desperate
from the ghastly presence of the cave.
Question 1: Amy saw something ‘reassuring’. What single word used later in the passage shows that
later she was no longer feeling reassured? [1 mark]
Answer 1: Uneasiness.
Question 2: Pick out and write down the single word which shows that the older man’s clothes were dirty.
[1 mark]
Answer 2: Grimy
Question 3: Amy ‘ran outside’. Write down two separate words which shows that she was frightened as
she ran. [2 marks]
Answer 3: Stumbling and blundering.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/final-170507021744/85/English-Language-1123-Essential-2k17-comprehension-16-320.jpg)



![English Language-Paper 2-Reading
Understanding Section 2 Reading for Meaning
Categorical Comprehension Questions
Writer’s Craft Comprehension: (1-2 marks)
Example: The Market in Mumbai
Rohit meandered through the market in Mumbai. He was on holiday after all, and the day was
stretched out before him like a century.
Question 1: Explain fully what effect the writer gains by her use of the word ‘meandered’. [2 marks]
Answer: He wandered/had no fix aim/was relaxed (any two for 1 mark each)
Question 2 Rohit was on holidays for the day. Why, therefore, does the writer compare the day to a
century? [1 mark]
Answer: he was relaxed/ felt he had plenty of time.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/final-170507021744/85/English-Language-1123-Essential-2k17-comprehension-20-320.jpg)
