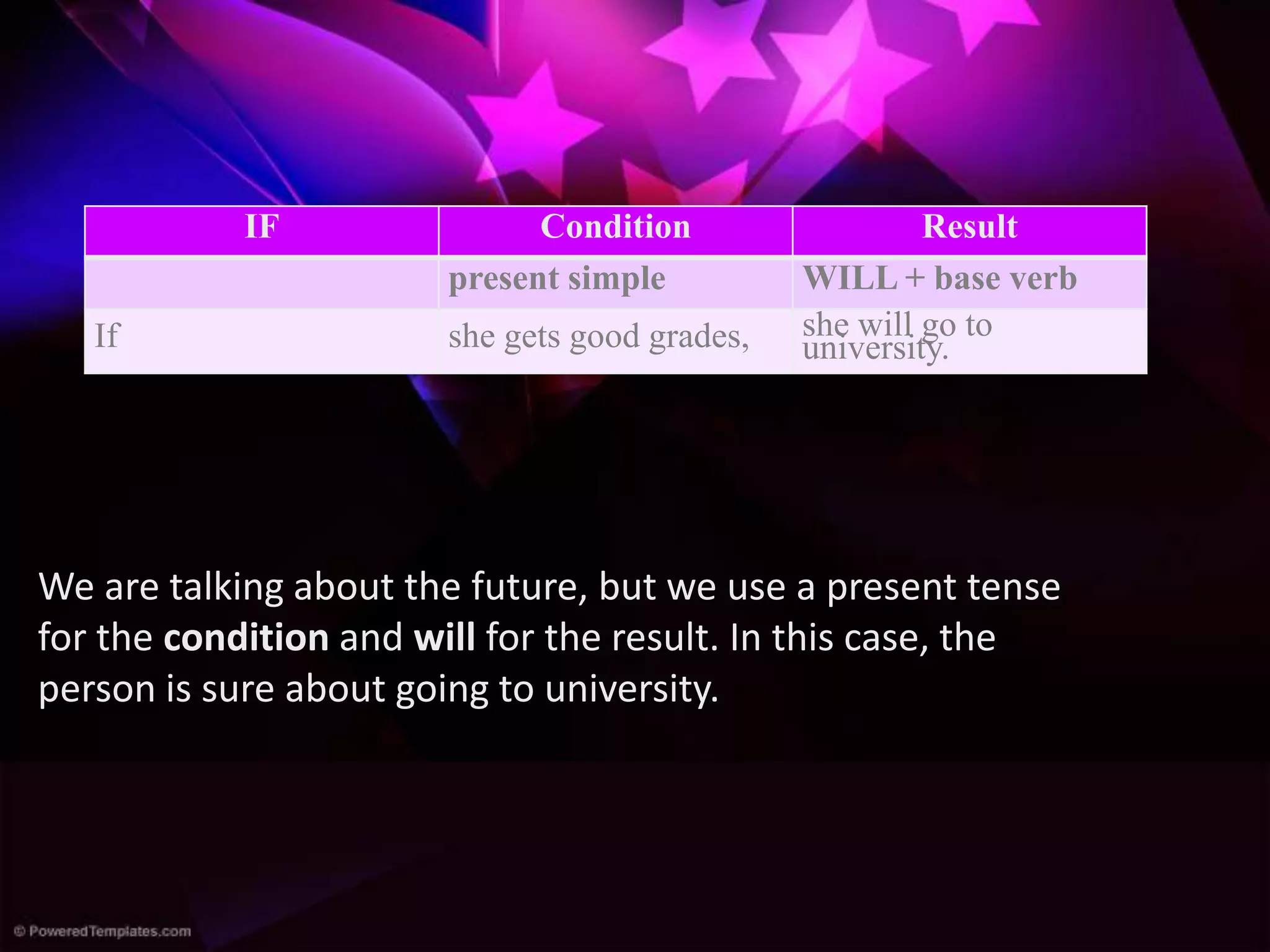
The document discusses the four main types of conditionals in English: zero, first, second, and third conditional.
The zero conditional refers to certainties using the present tense. The first conditional refers to real possibilities in the future using present for conditions and will for results. The second conditional refers to unlikely present or future possibilities using past tense conditions and would for results. The third conditional refers to imaginary past possibilities using past perfect conditions and would have for results.