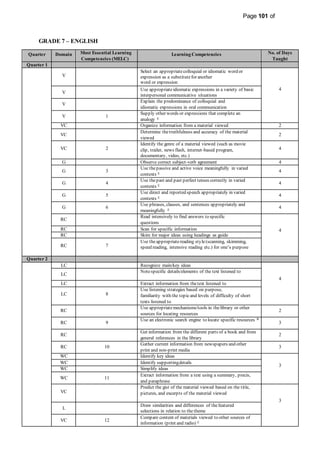
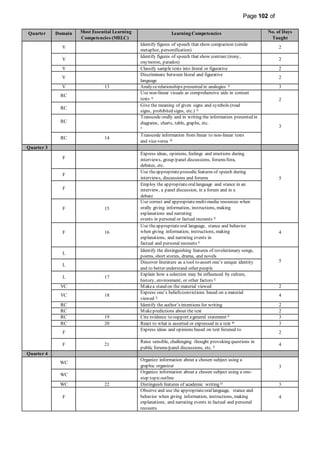
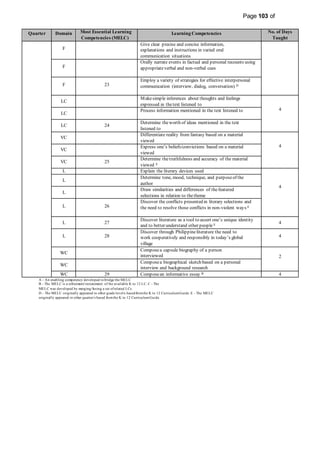
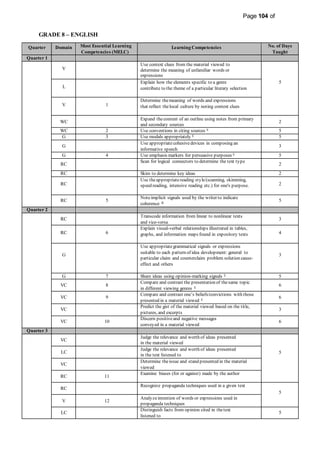
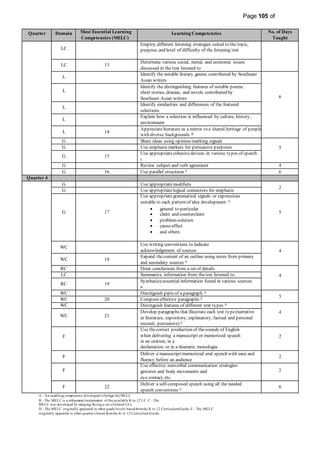
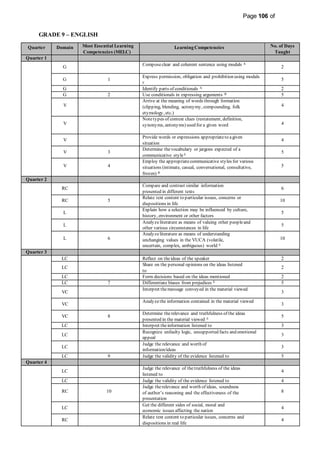
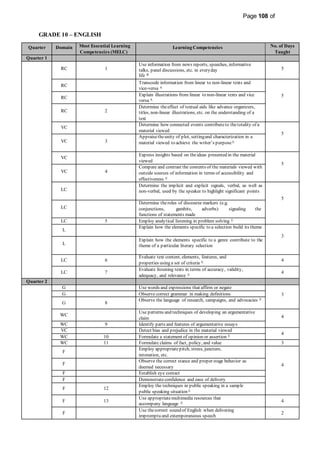
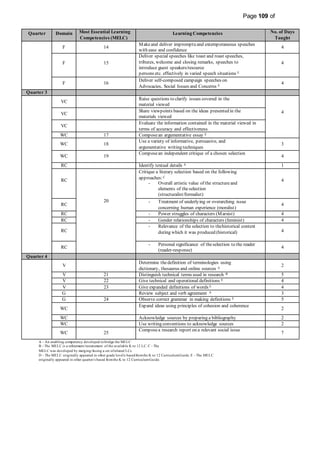
This document provides information on the PIVOT 4A Budget of Work (BOW) in English for Grade 7 at Cabantian National High School. It outlines the features and elements of the BOW, including the most essential learning competencies (MELCs) mapped from the K to 12 curriculum. It provides details on how to use the BOW, including identifying the MELCs and learning competencies to teach for each quarter and domain. The BOW is then presented for Grade 7 English, outlining the MELCs, learning competencies, and number of days taught for each quarter.