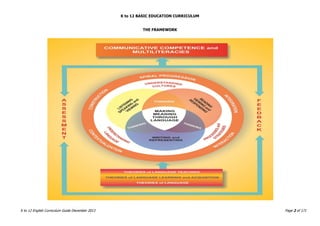
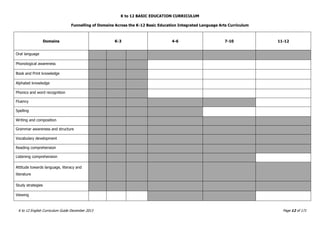
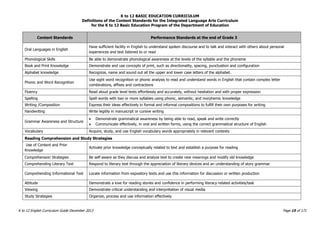
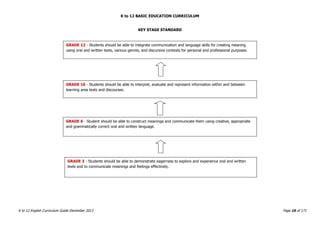
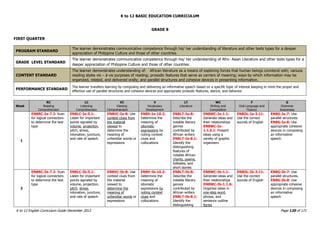
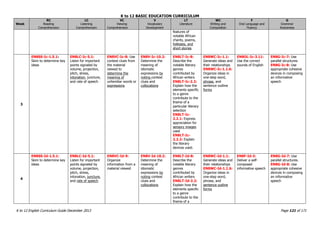
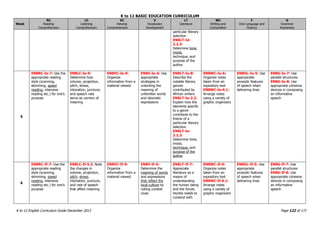
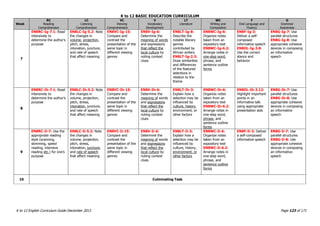
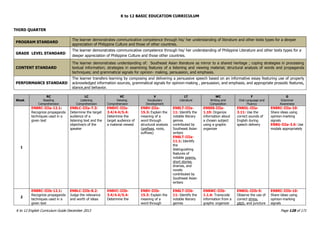
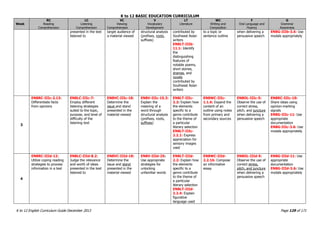
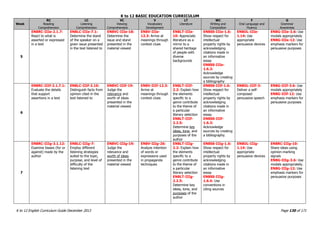
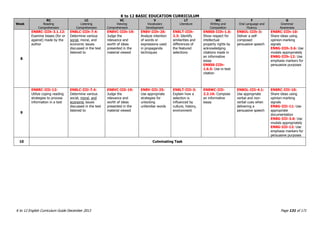
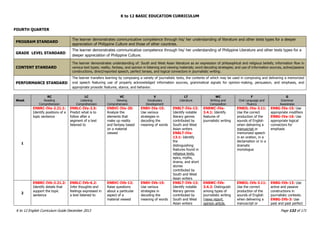
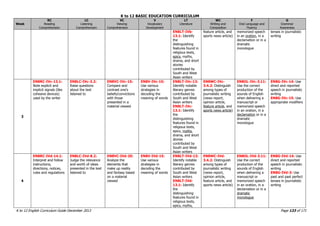
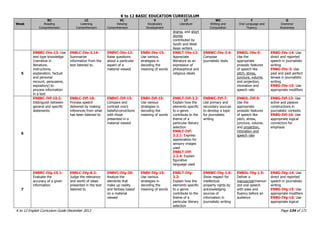
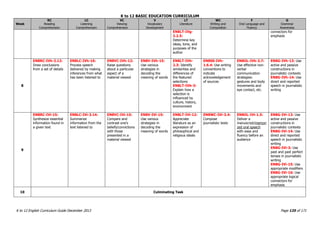
The K to 12 English Curriculum Guide emphasizes the importance of language in communication and personal development, outlining guiding principles for language acquisition and effective teaching. It addresses the needs of Generation Z learners, who are adept with technology but may struggle with attention and focus, aiming to develop communicative competence and multiliteracies. The curriculum promotes interactive and contextualized learning, integrating language skills to prepare students for a globalized society.