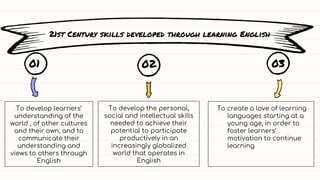
This document presents an English language curriculum for elementary and secondary students in Ecuador whose first language is not English. The curriculum is designed to help students communicate effectively in today's globalized world while recognizing their cultural backgrounds. It is based on a communicative language approach and content and language integrated learning (CLIL) to develop students' language skills through other subjects. The curriculum incorporates five threads - oral communication, reading, writing, language through the arts, and communication and cultural awareness. It takes a learner-centered approach that recognizes students learn in different ways and focuses on developing their language skills and critical thinking.