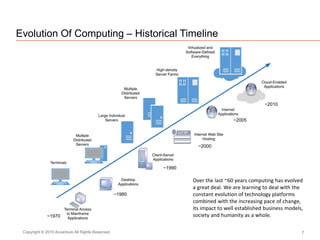
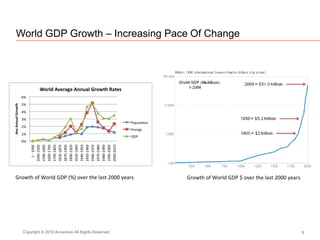
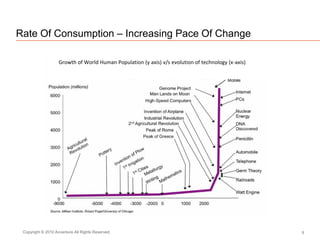
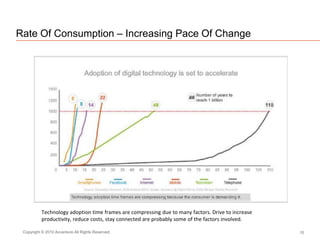
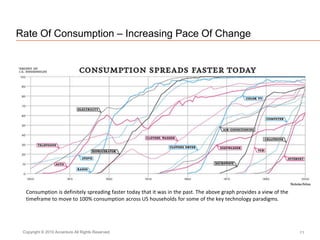
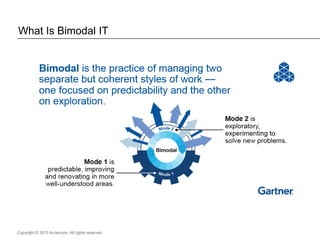
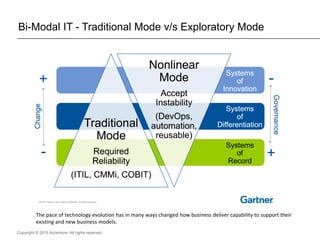
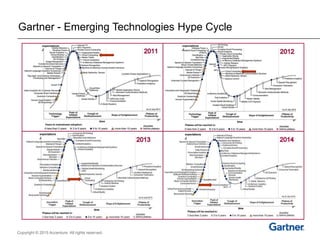
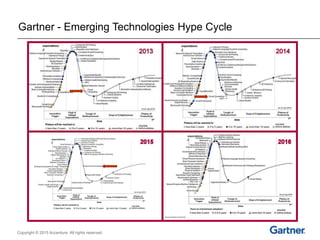
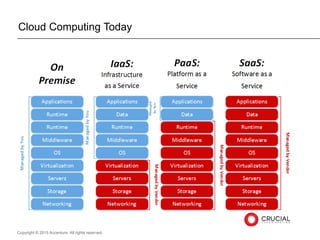
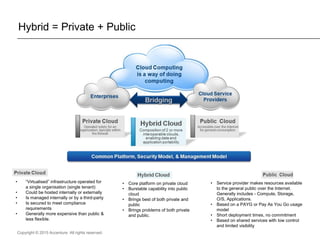
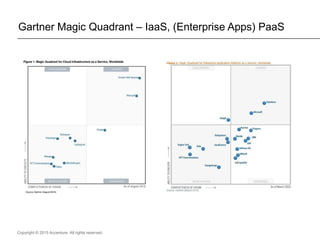
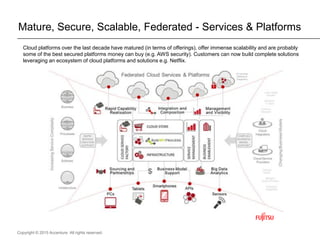
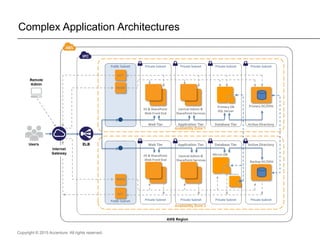
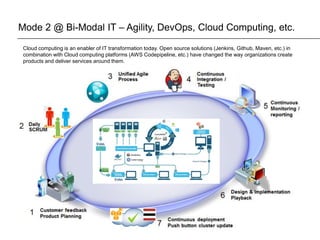
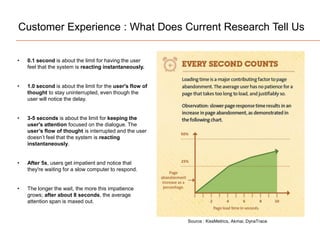
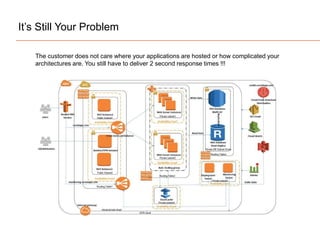
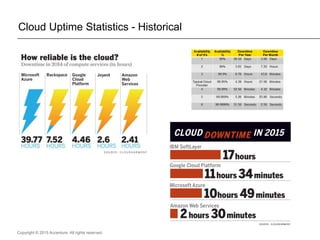
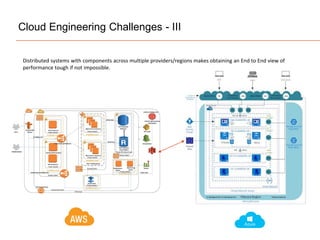
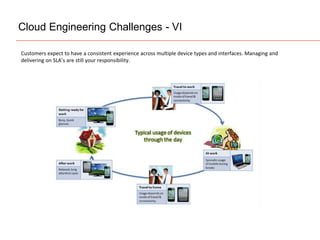
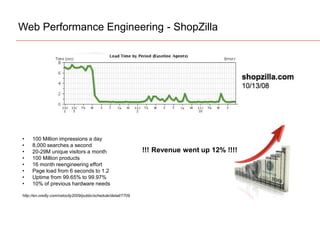
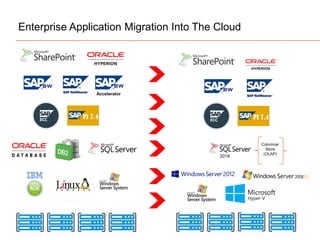
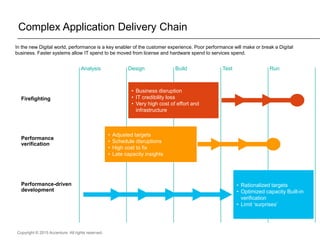
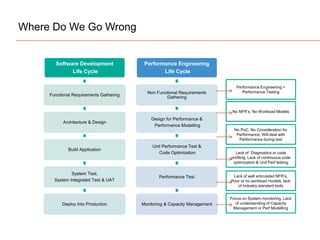
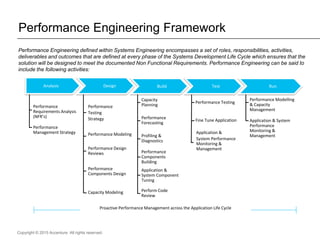
The document presents insights on software testing and cloud computing, focusing on performance engineering and management in the context of evolving technology. It discusses challenges and opportunities in cloud adoption, highlights customer expectations for performance, and includes case studies demonstrating effective performance engineering strategies. Additionally, it outlines common pitfalls and recommendations for successful cloud migration and performance management.