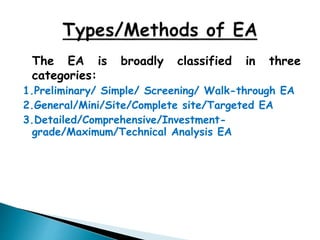
This document discusses energy audits. It defines an energy audit as the verification, monitoring, and analysis of energy use to identify opportunities to improve energy efficiency. Energy audits are broadly classified into three categories: preliminary, general, and detailed. A preliminary audit involves a brief review of utility bills and walk-through of a facility to identify major areas of energy waste. A general audit collects more detailed operational data over 12-36 months. A detailed audit provides an in-depth analysis of energy use through detailed data collection and system monitoring to develop an accurate energy use baseline. The document also outlines a 10 step plan for conducting a detailed energy audit in three phases: pre-audit, audit, and post-audit implementation.