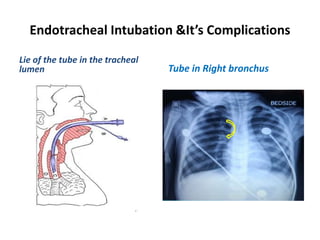
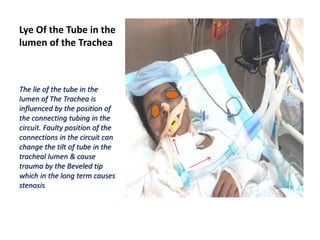
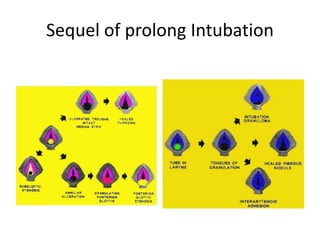
Endotracheal intubation is performed for general anesthesia, assisted ventilation, securing the airway, and cardio pulmonary resuscitation. With improved critical care and survival, complications of intubation are becoming more evident. Complications can be prevented by proper tube care, selecting the proper tube size, and ensuring proper tube position in the airway. Prolonged intubation over 5-7 days may require tracheostomy. Improper tube position can cause mucosal trauma and injury to the vocal cords or arytenoids, resulting in stenosis. Any voice changes or breathing difficulties after extubation should be evaluated by an ENT surgeon.