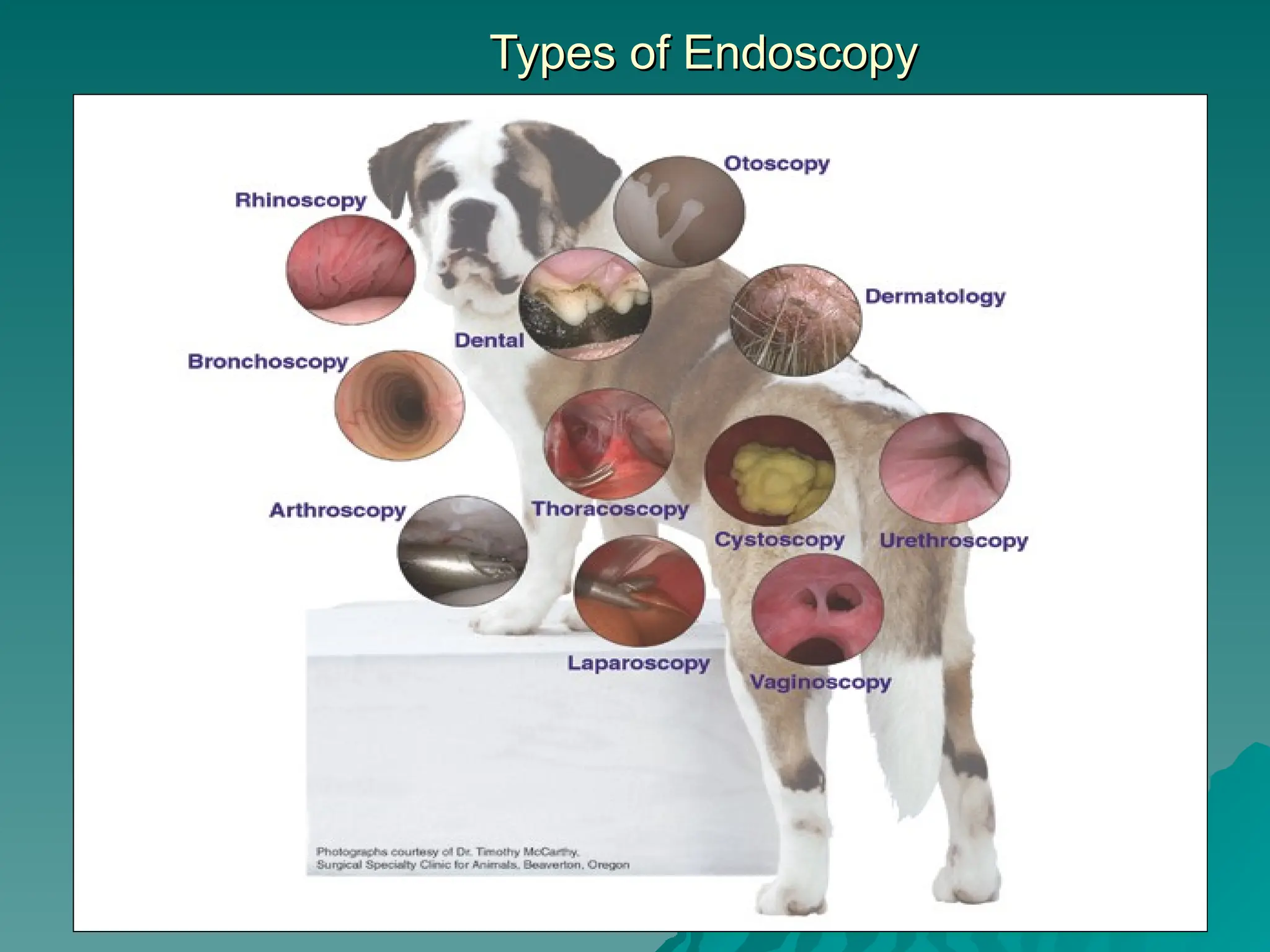
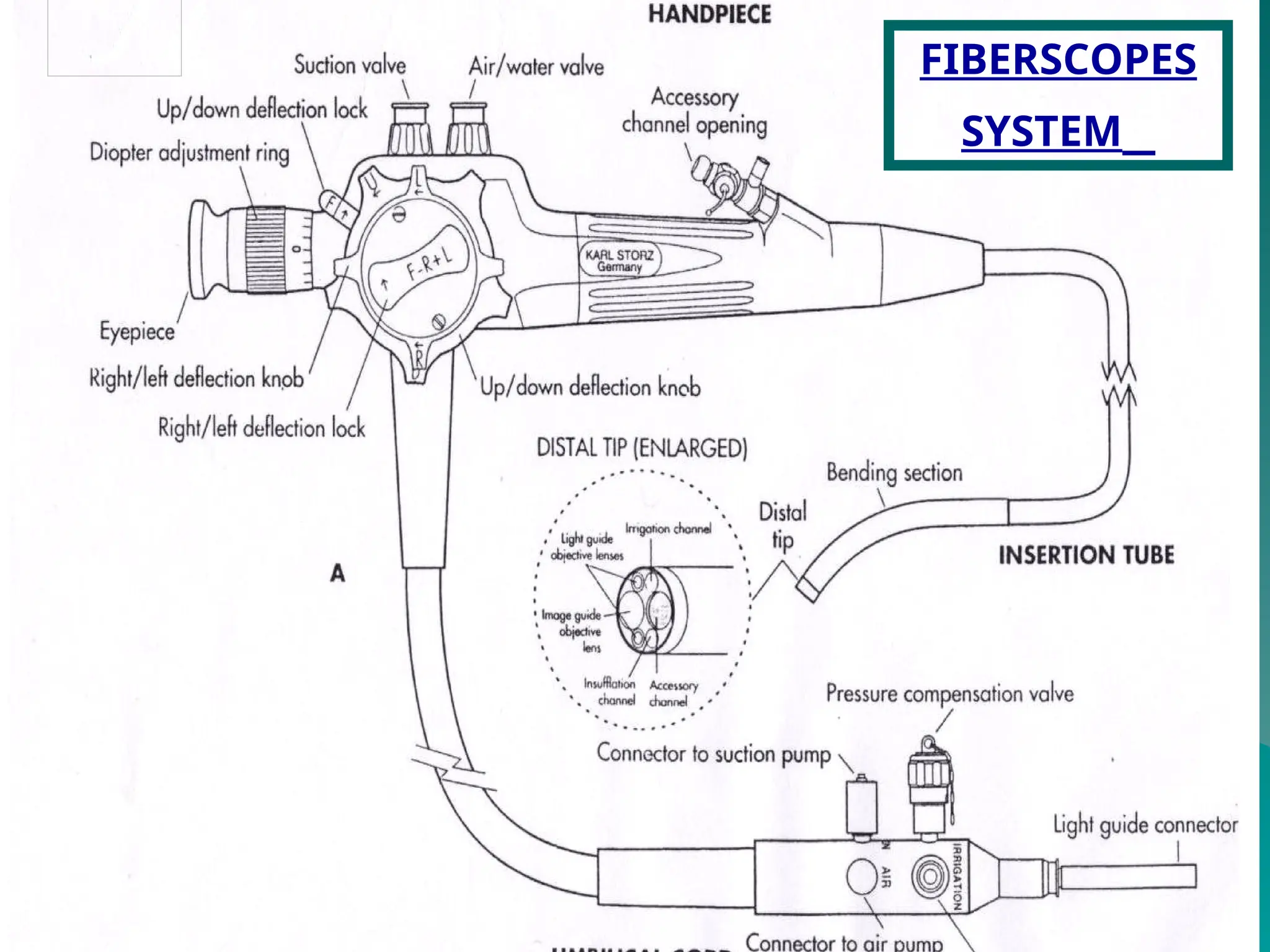
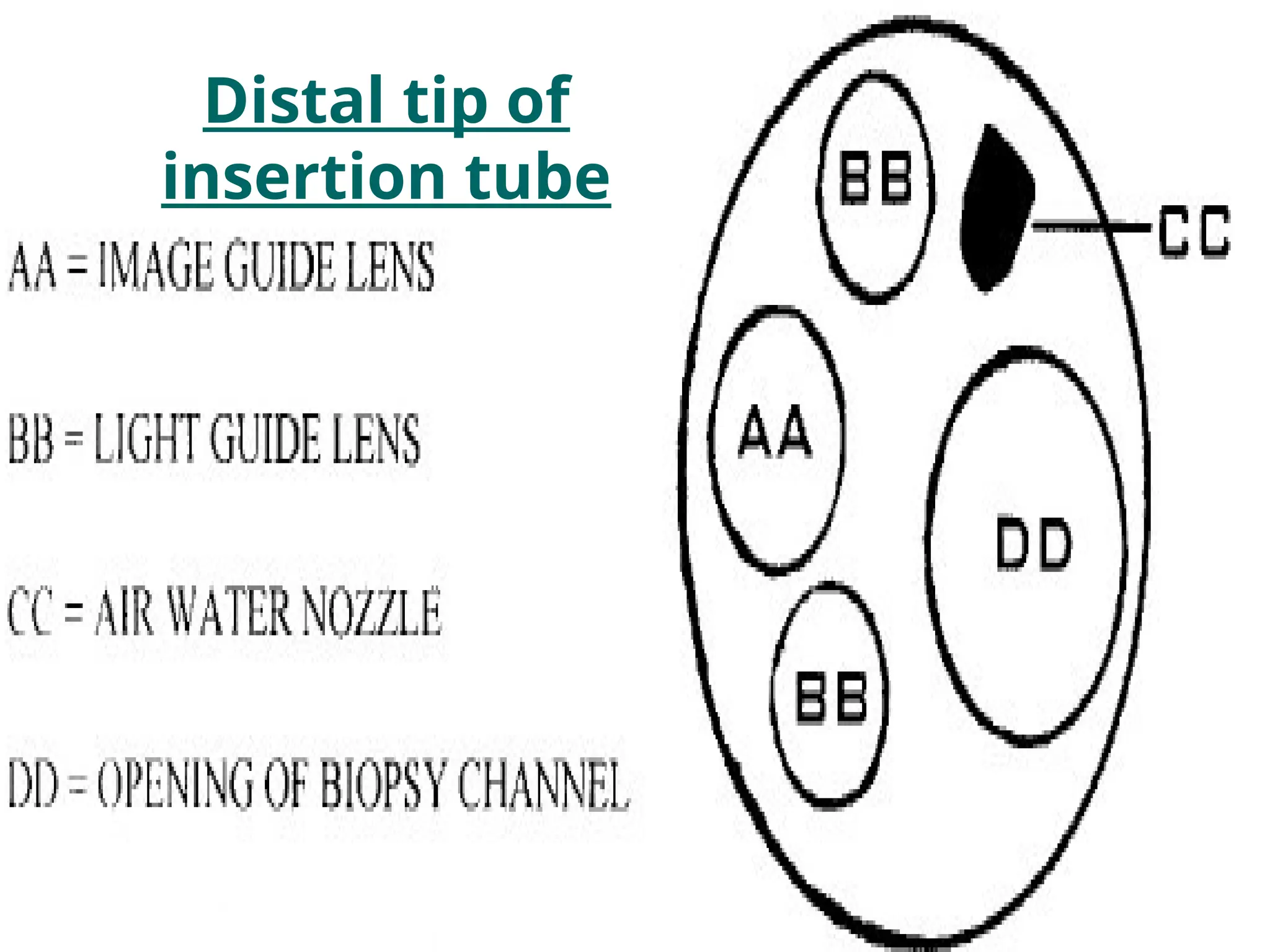
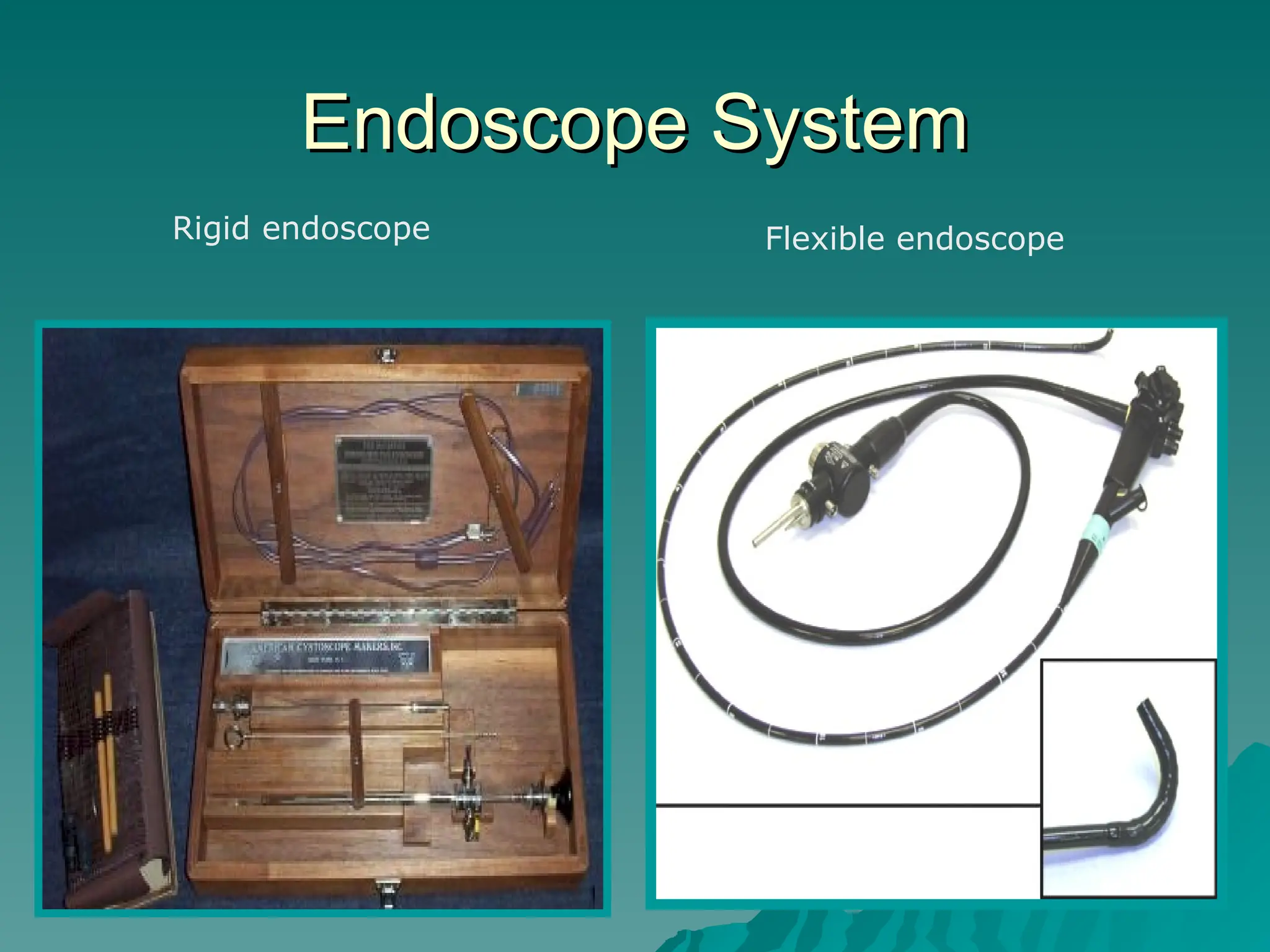
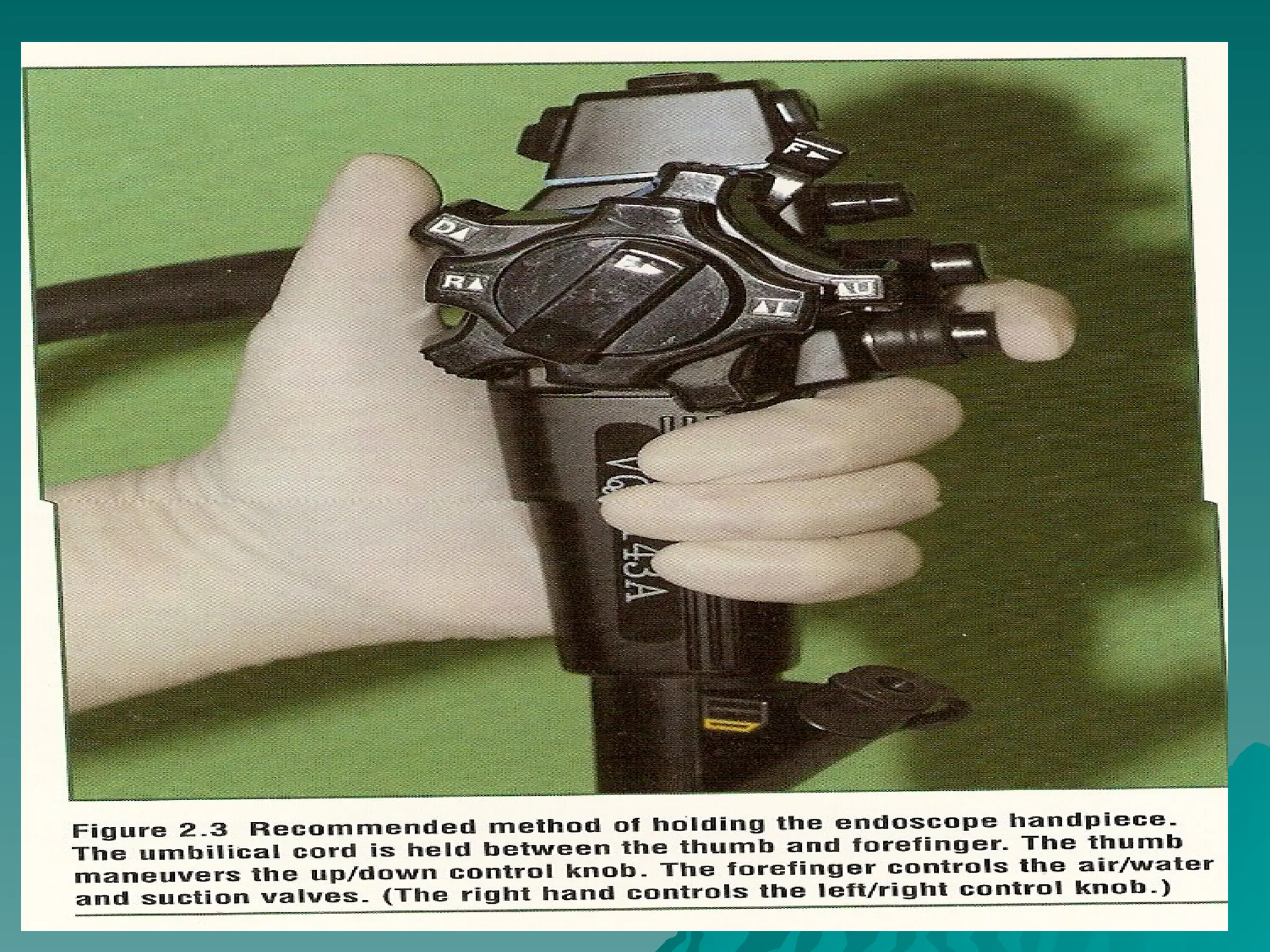
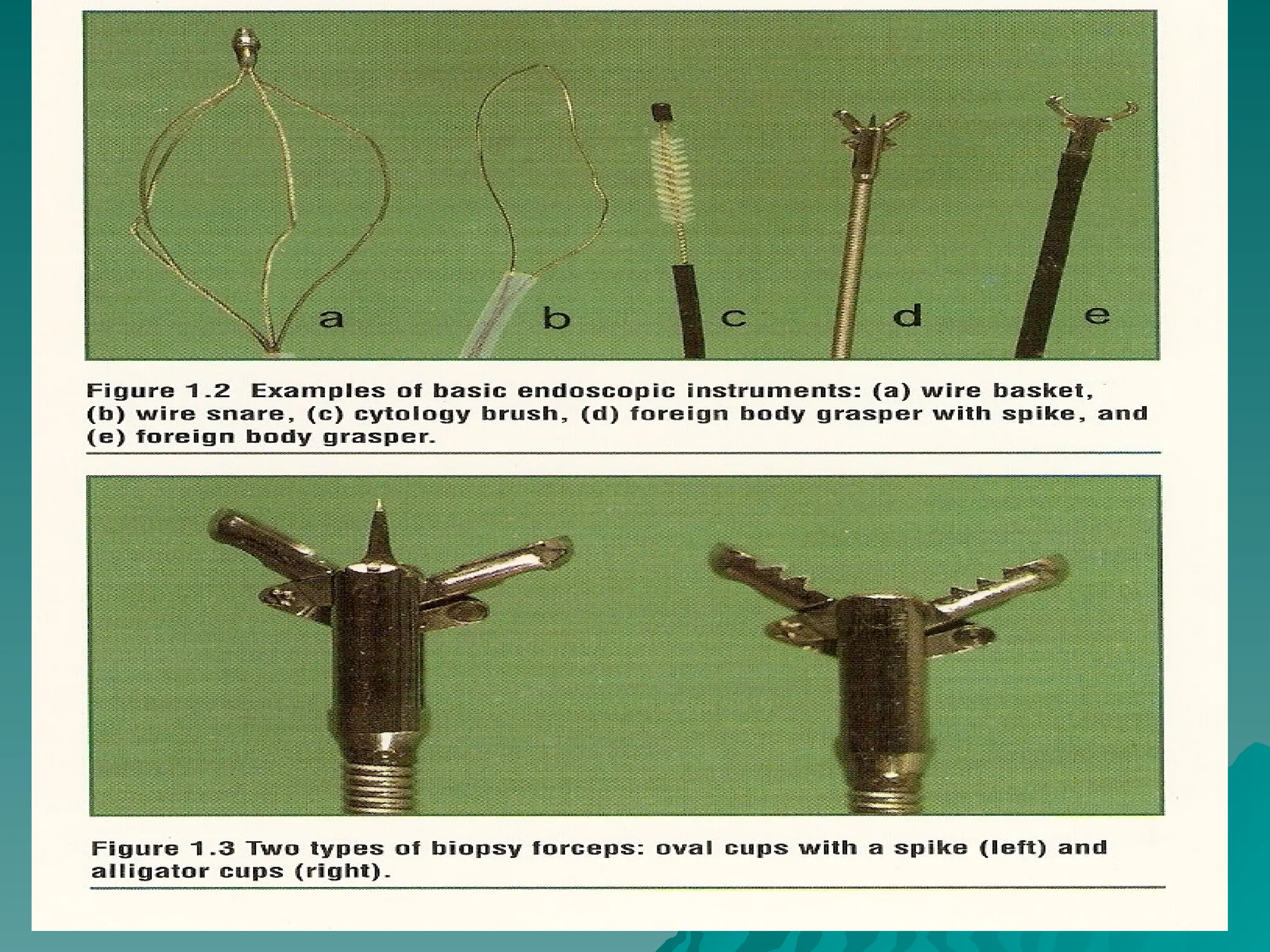
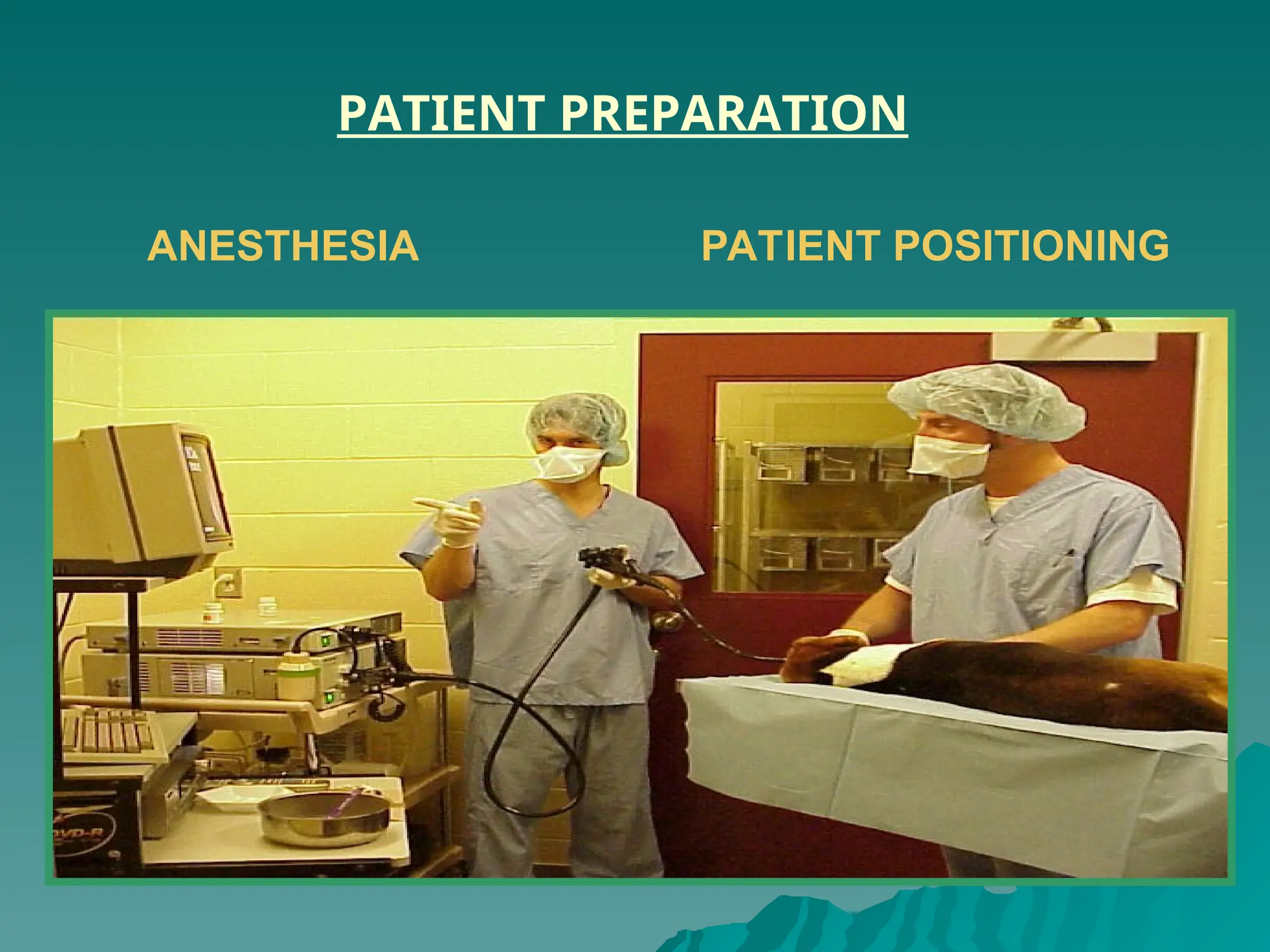
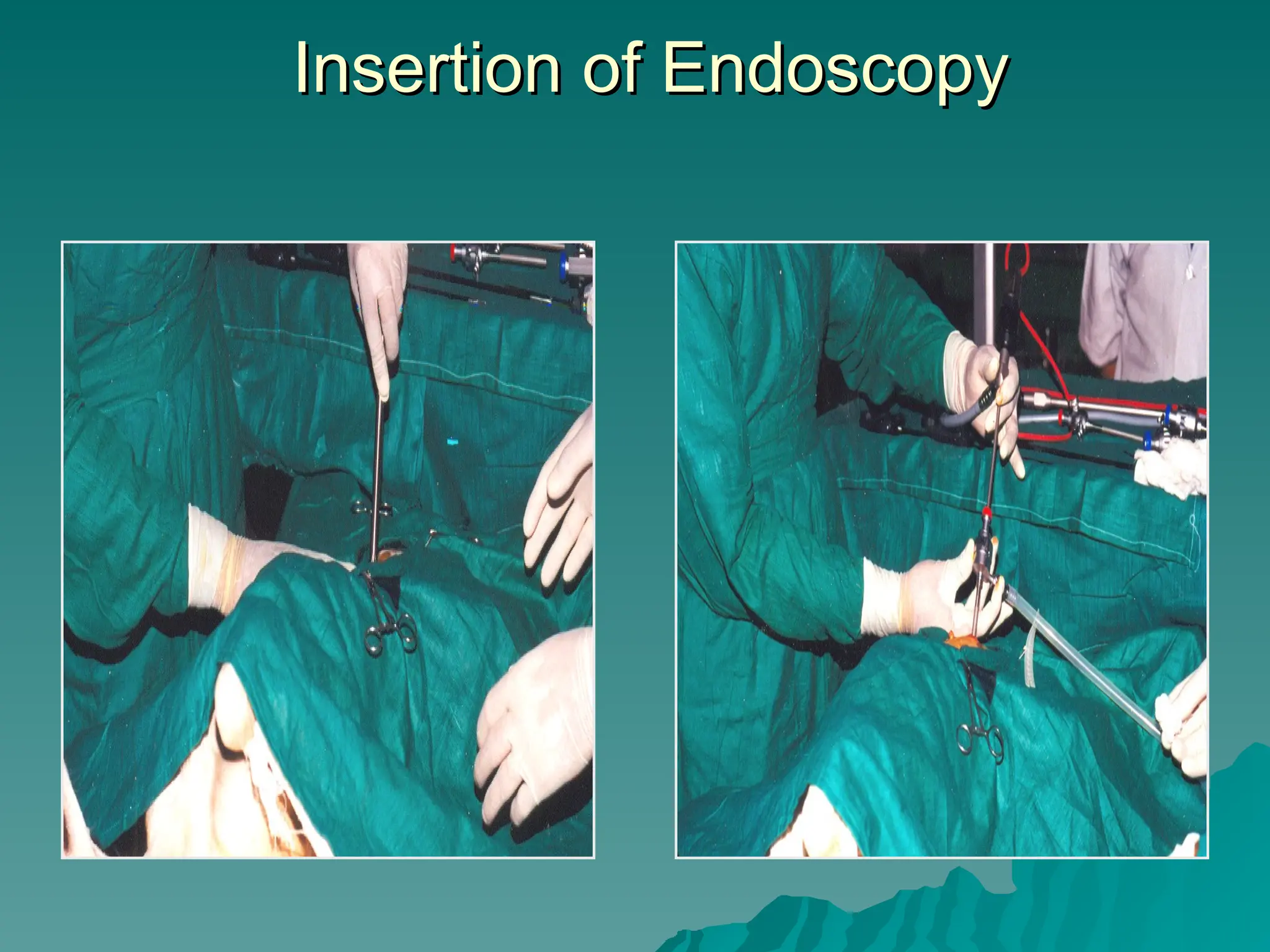
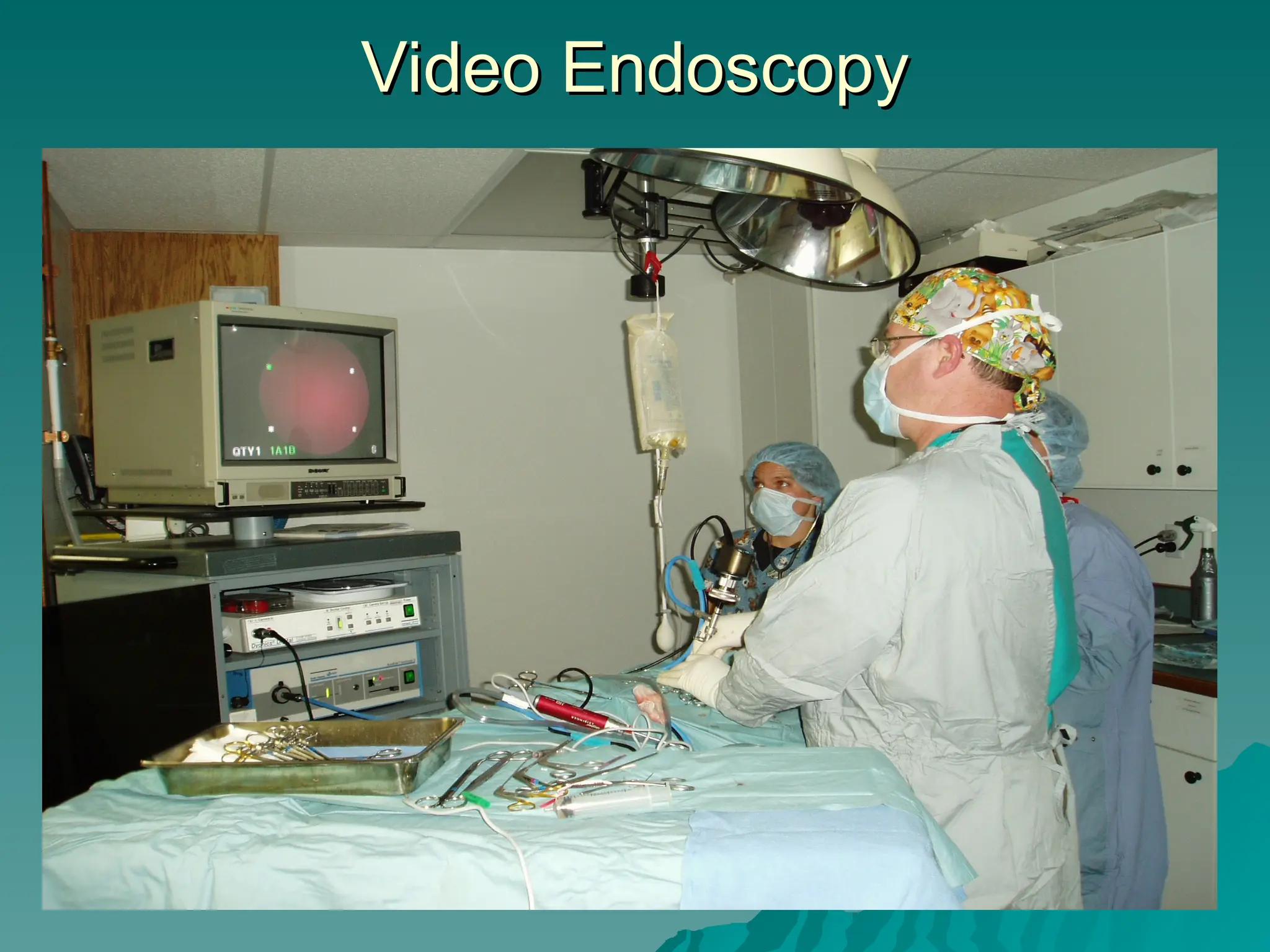
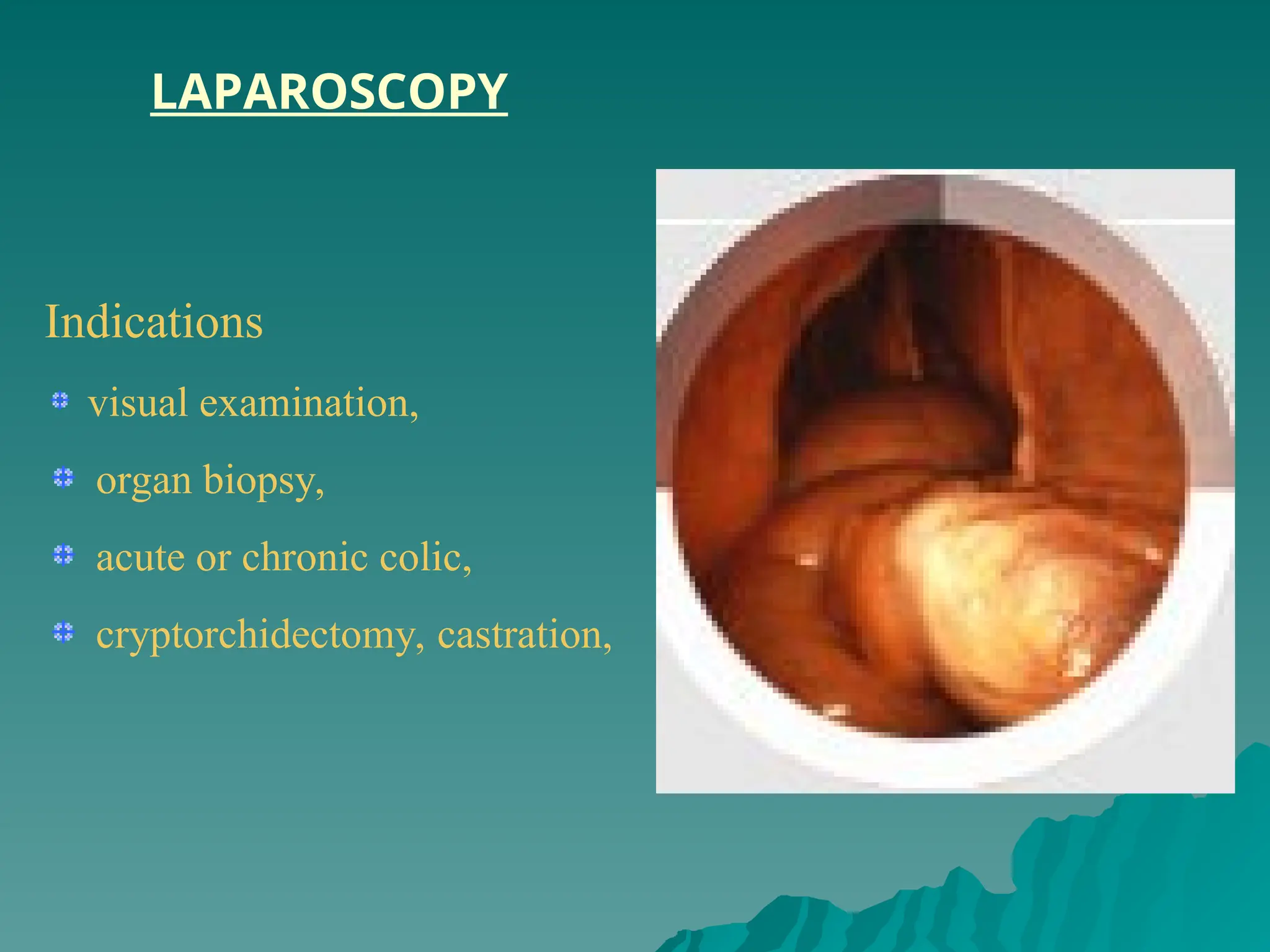
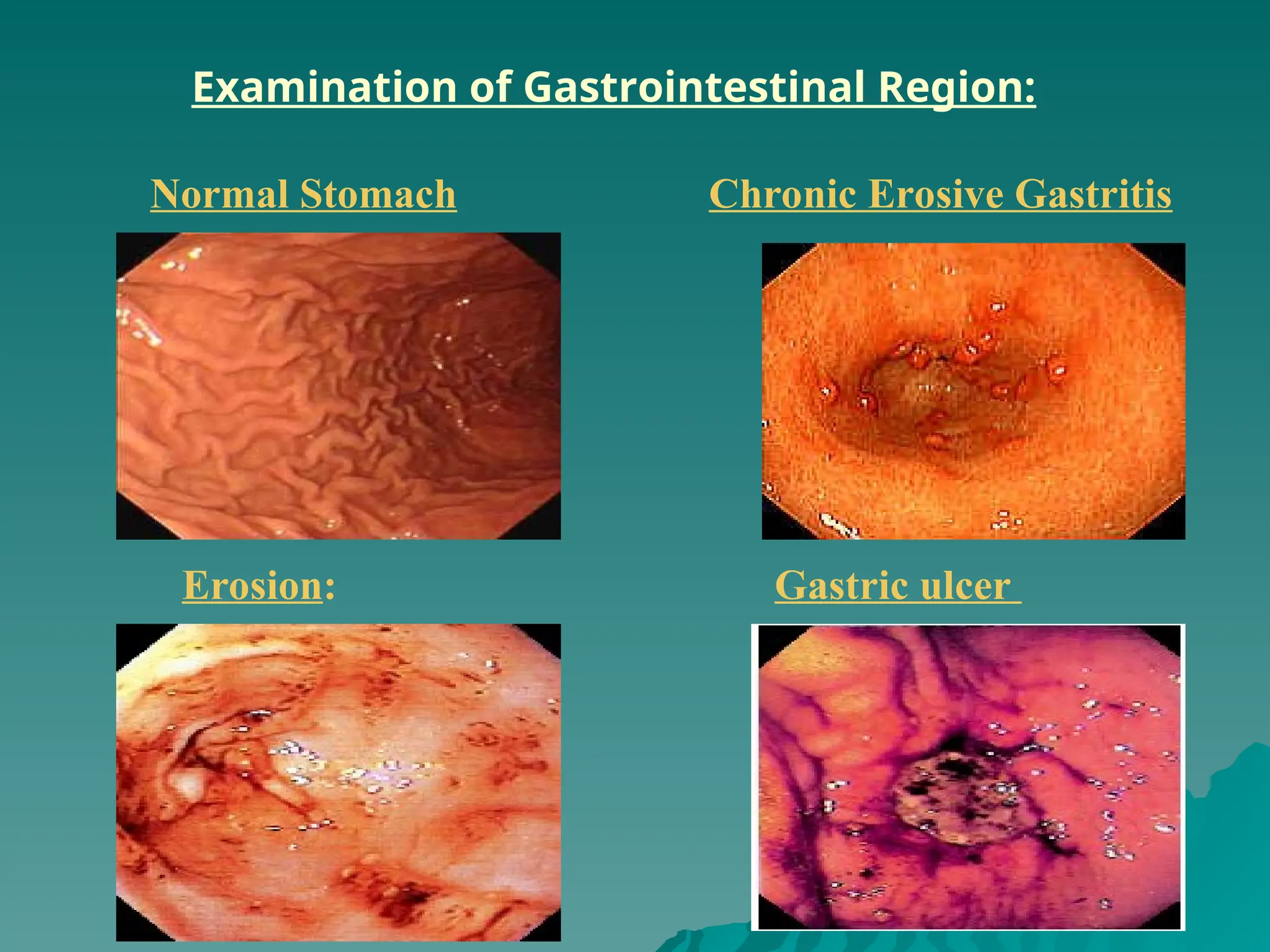
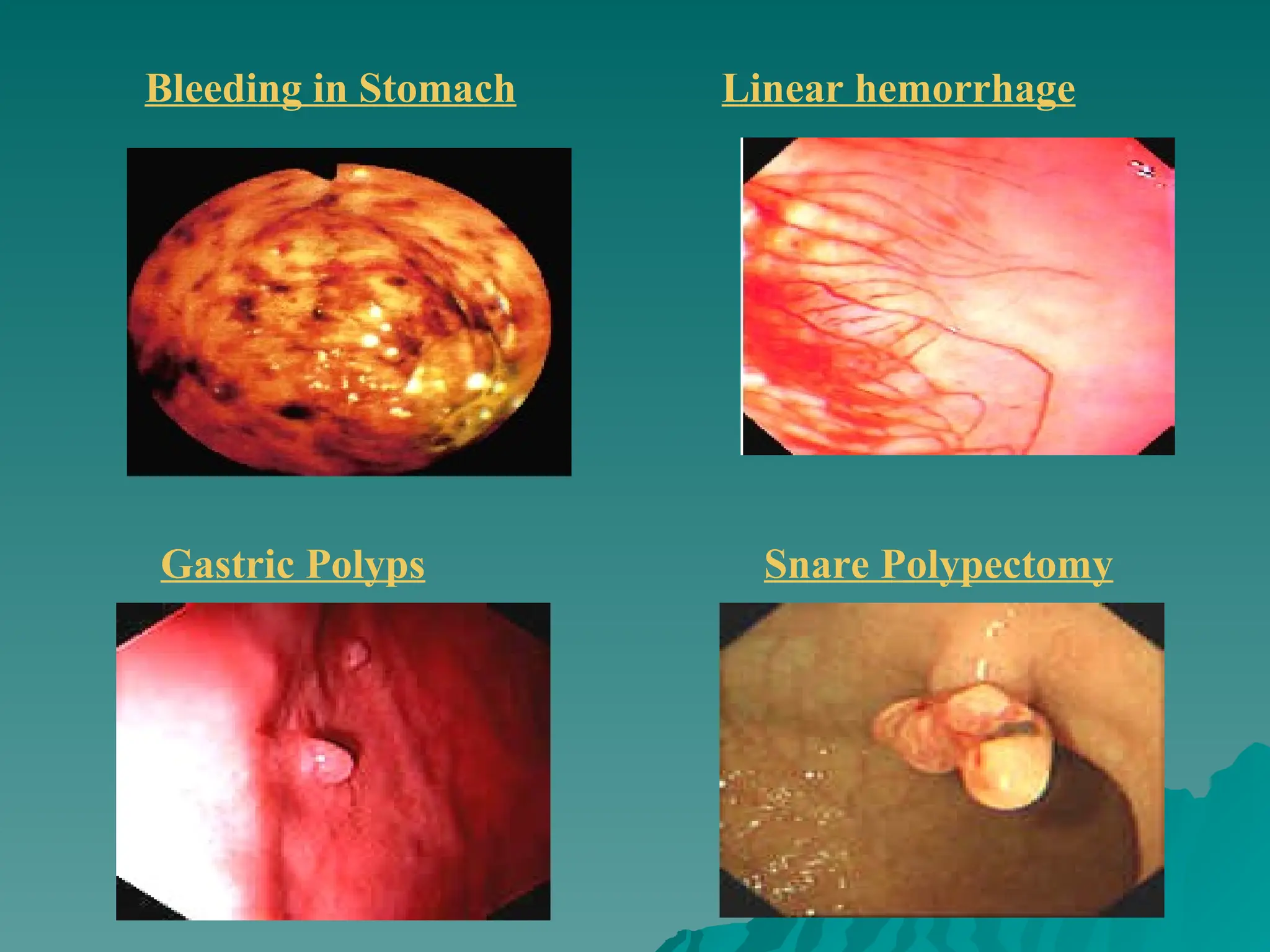
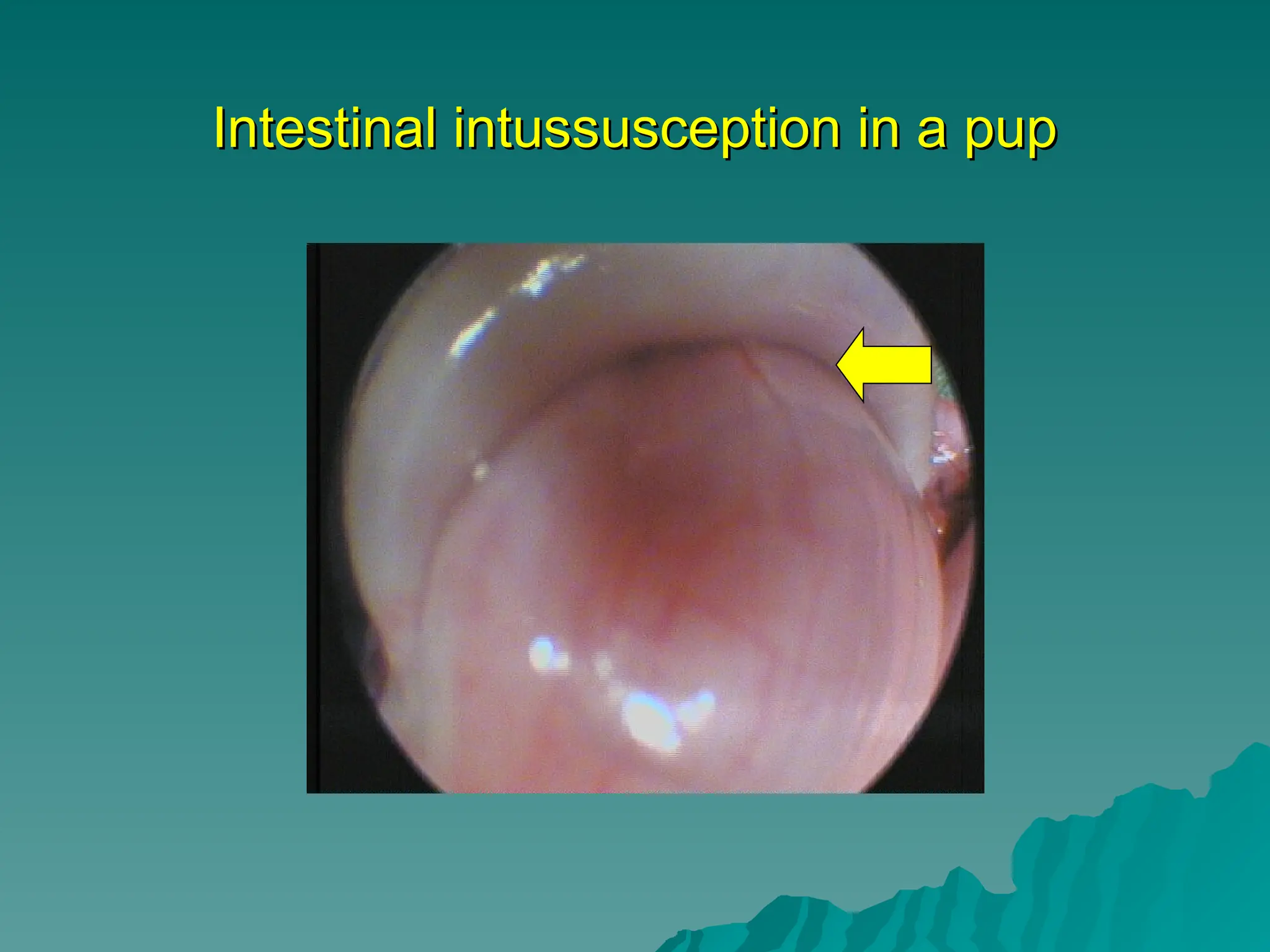
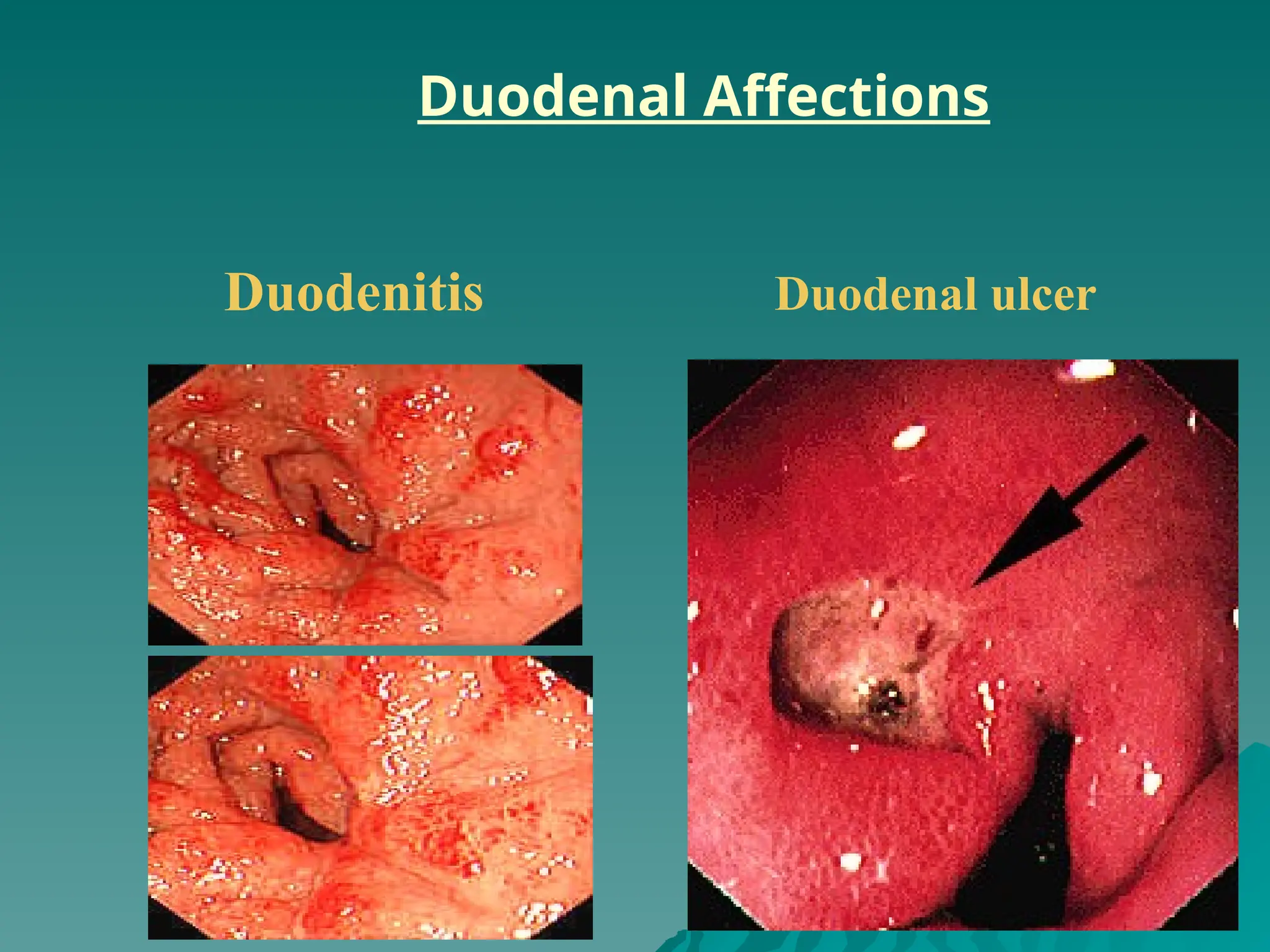
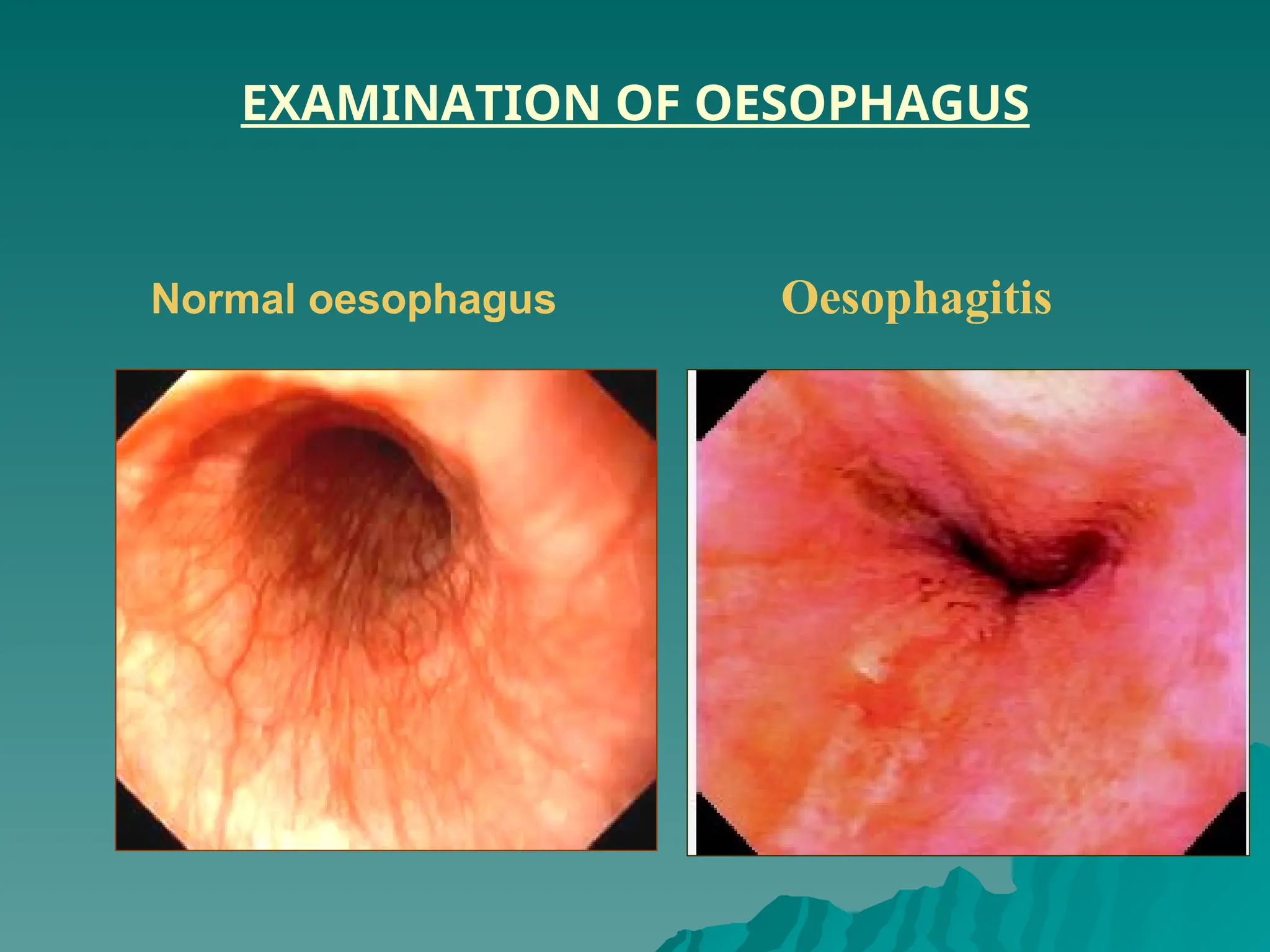
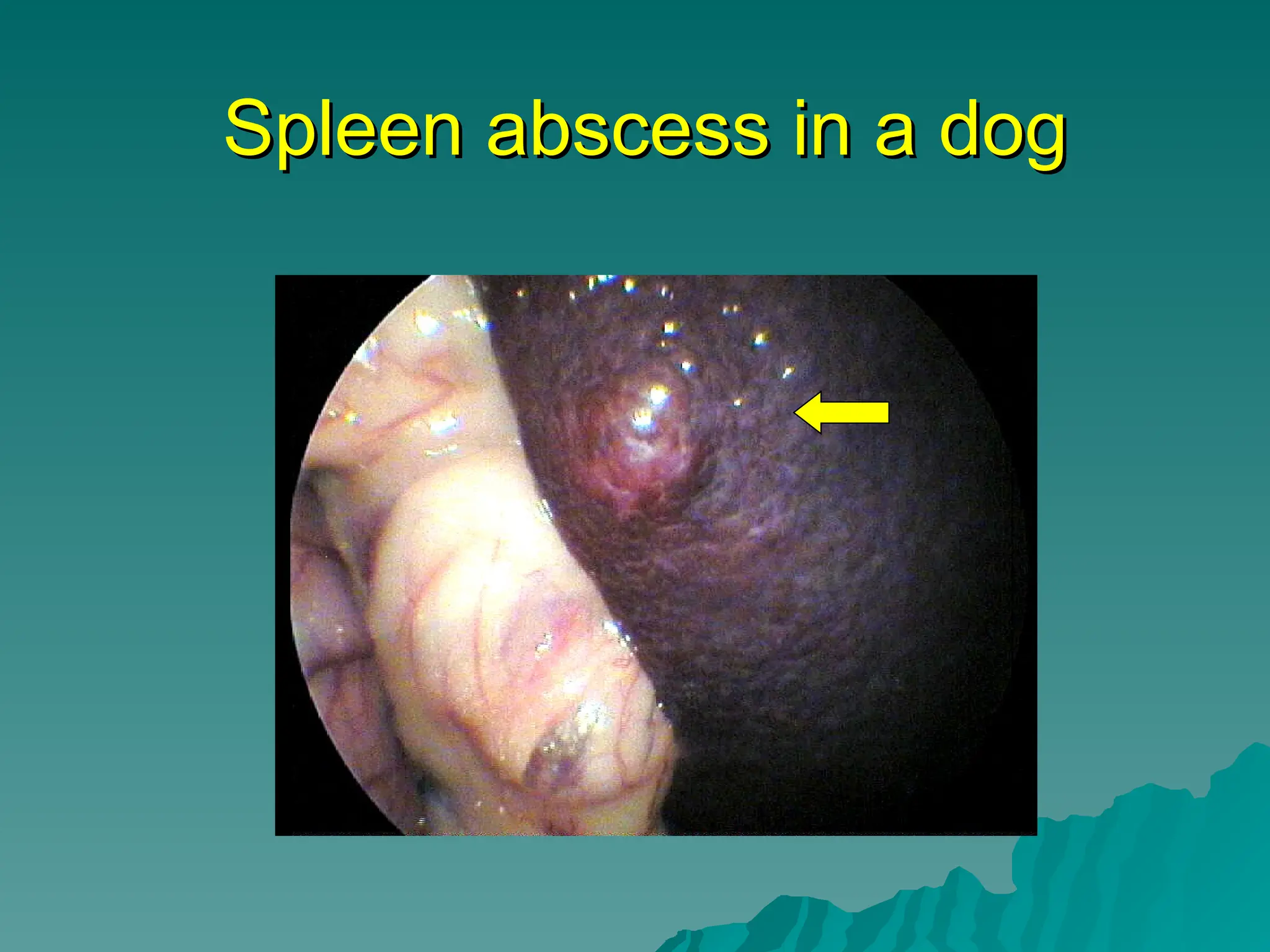
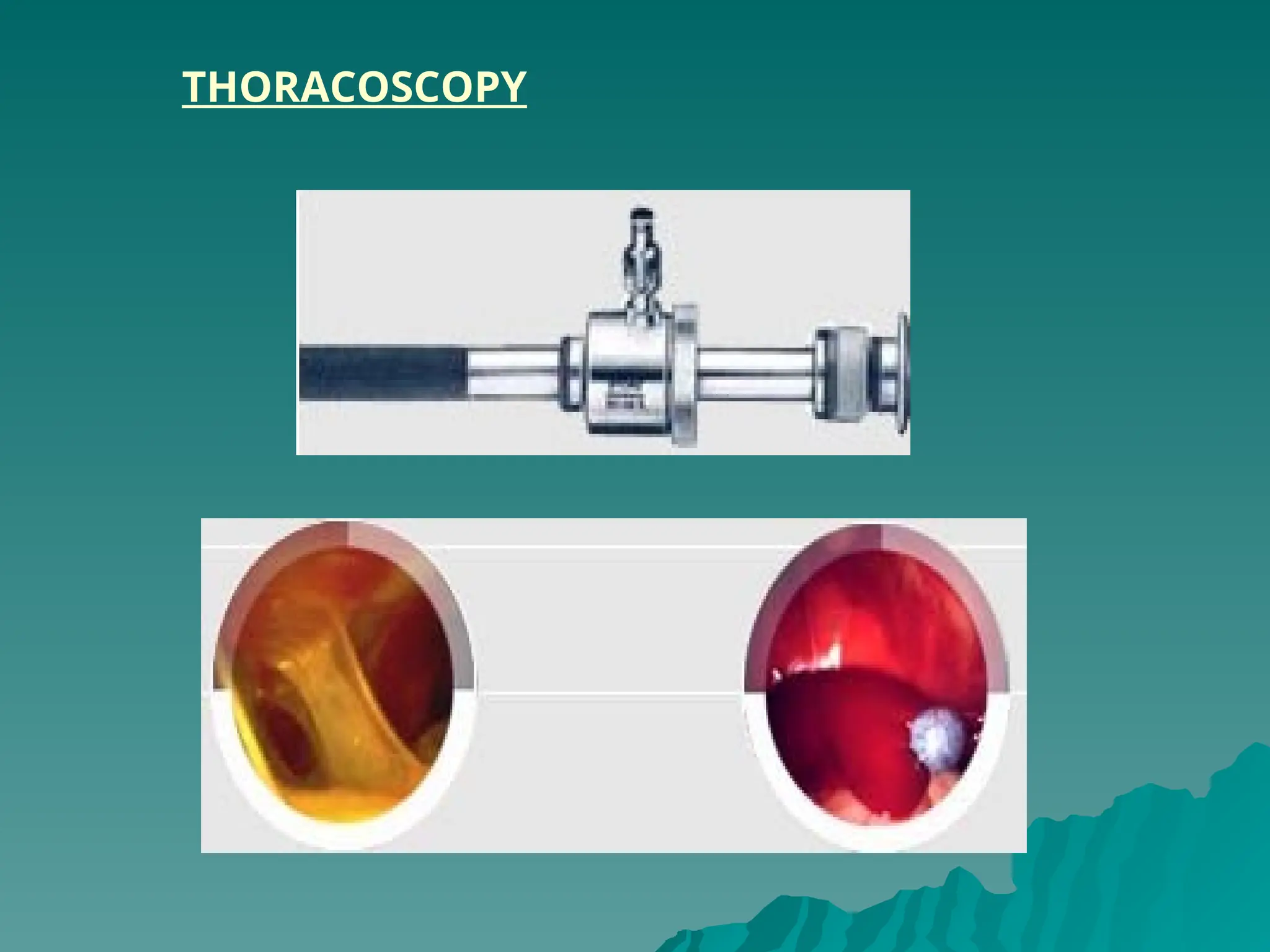
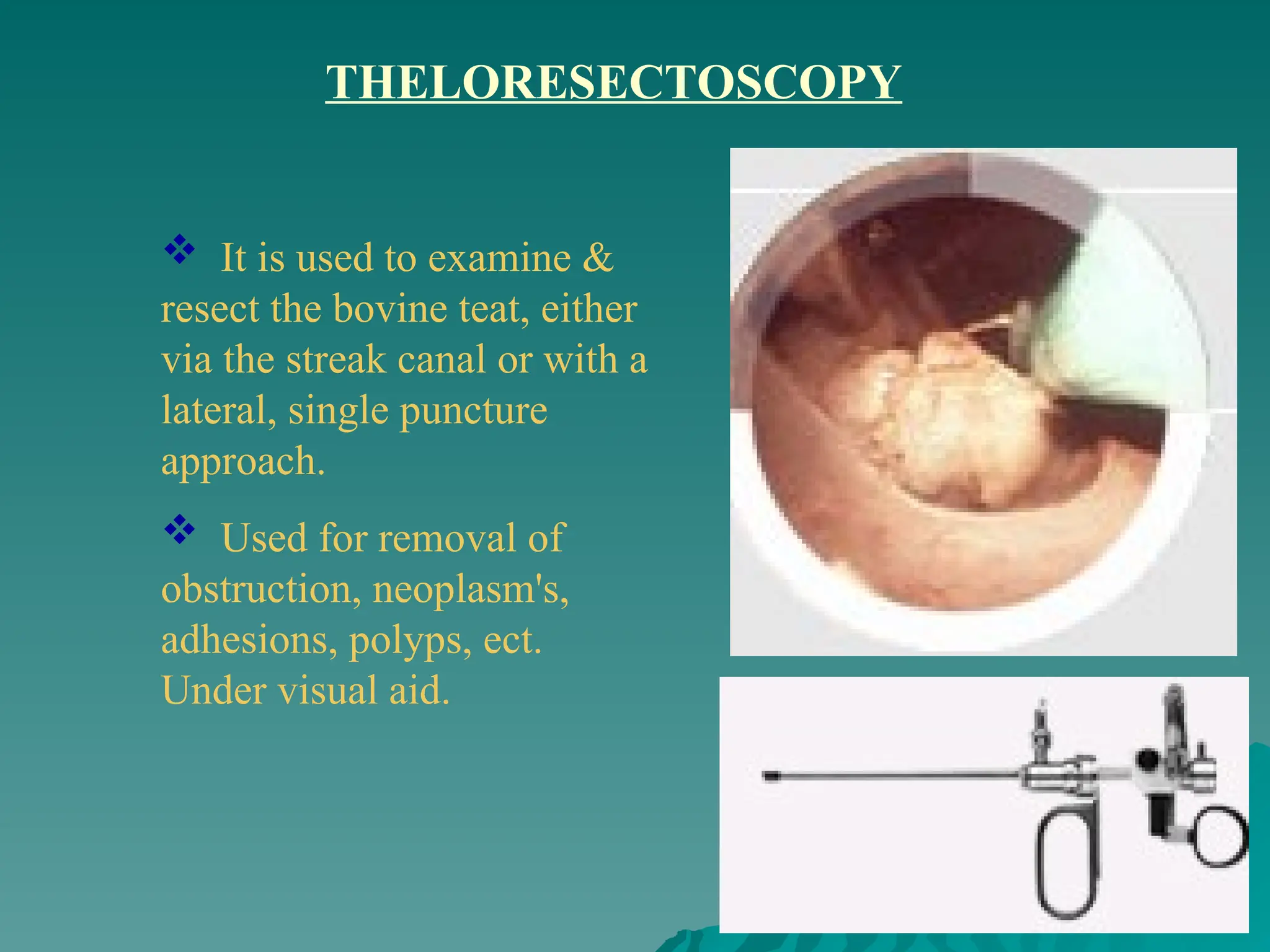
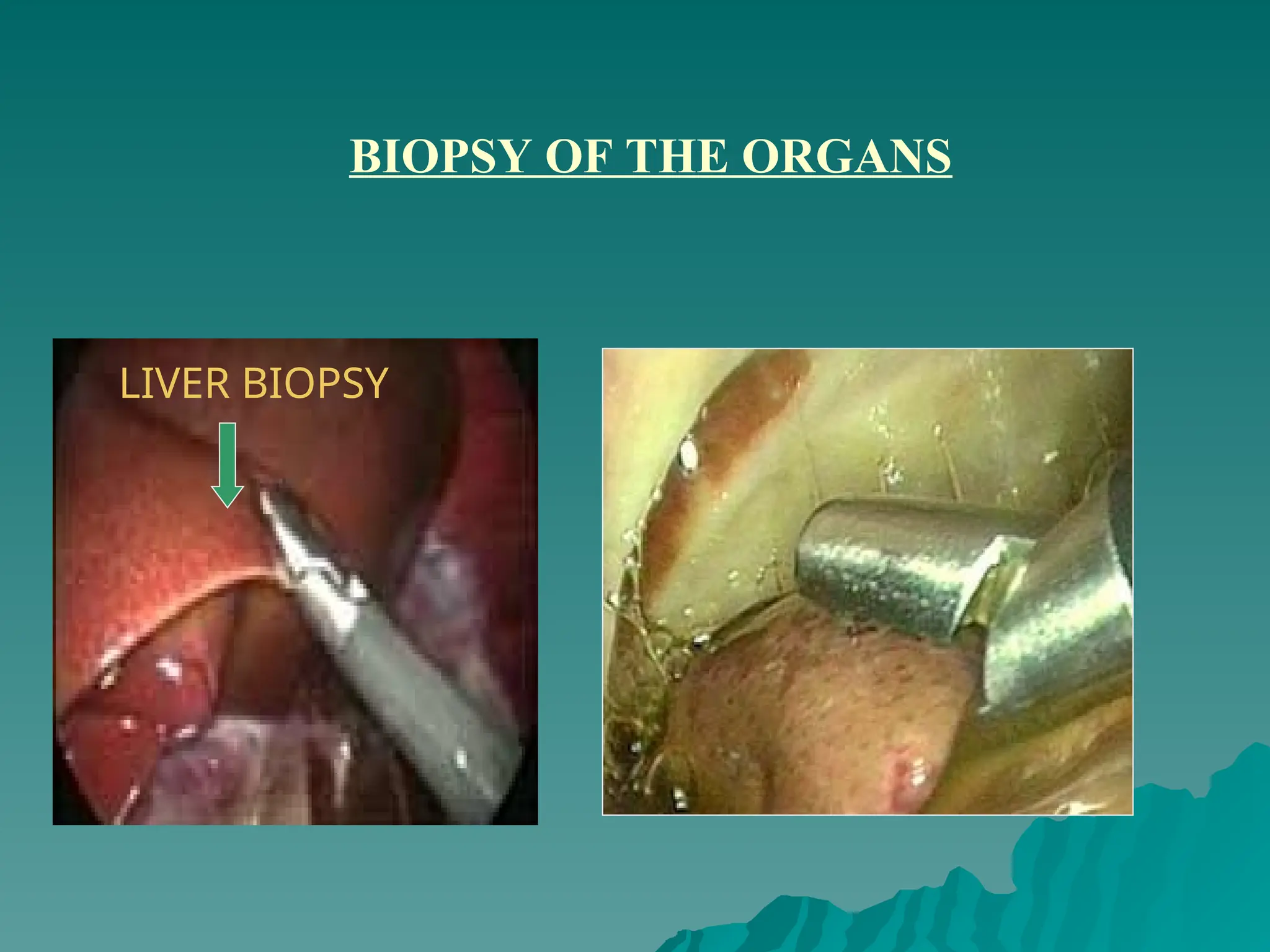
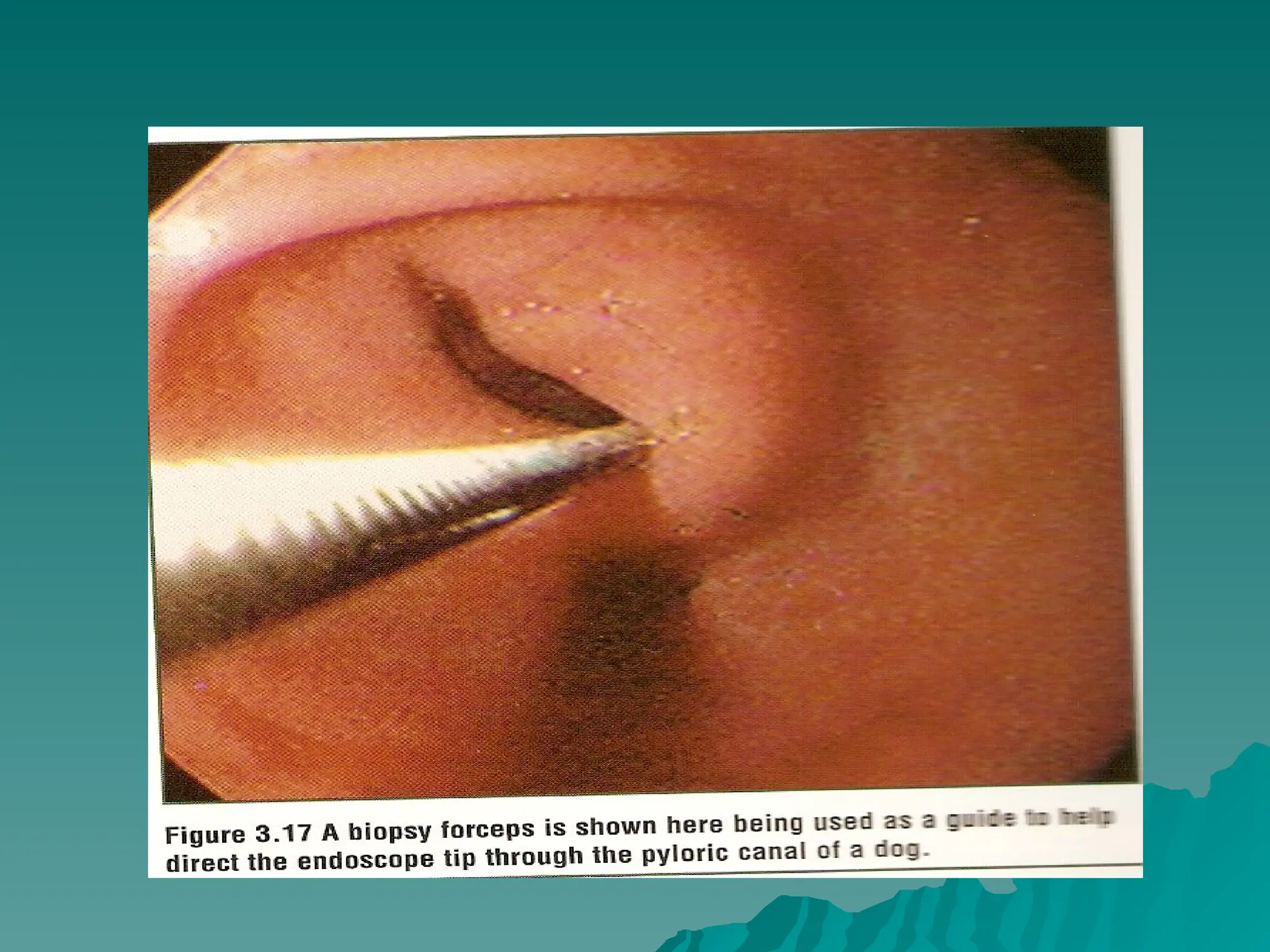
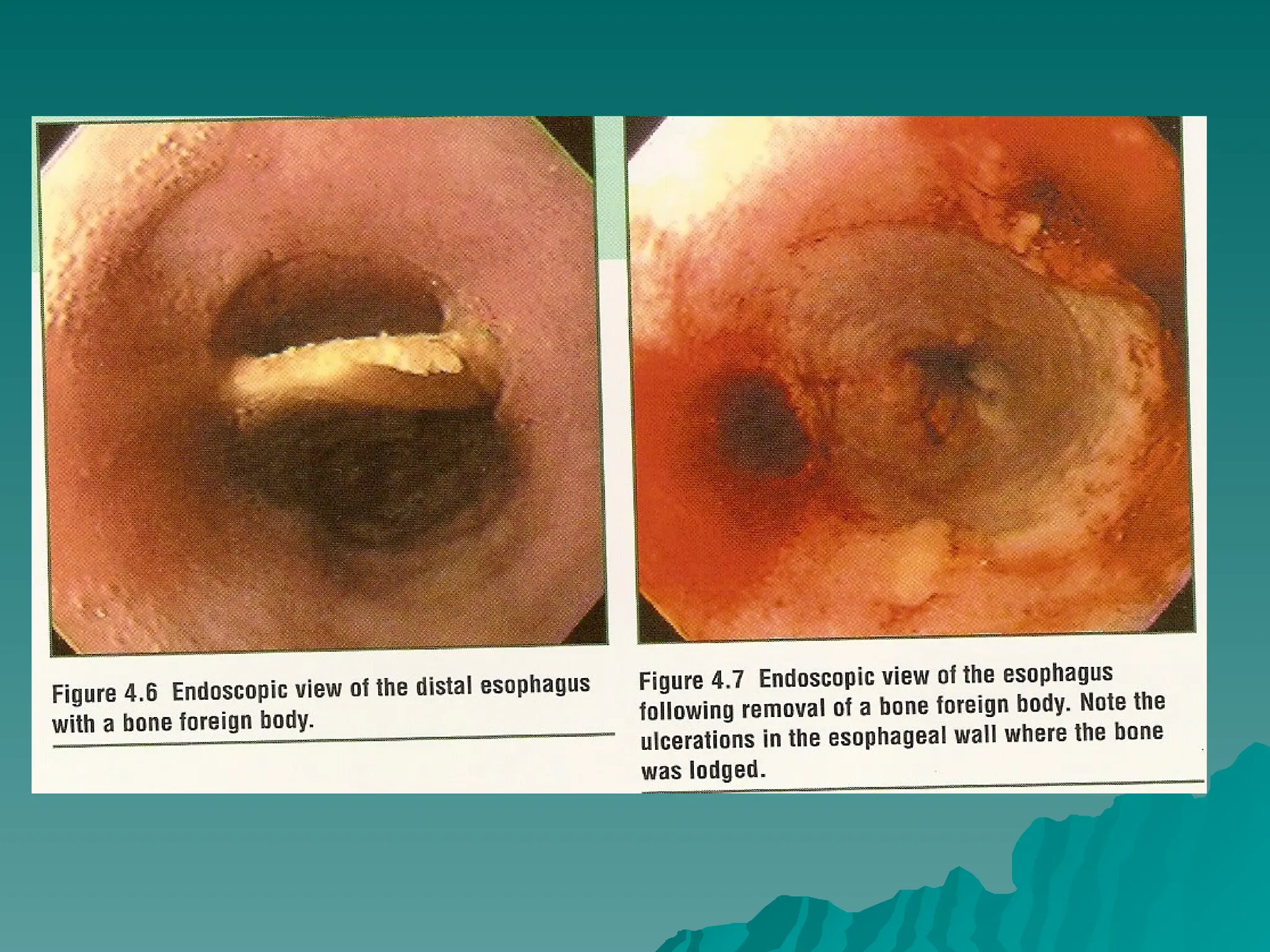
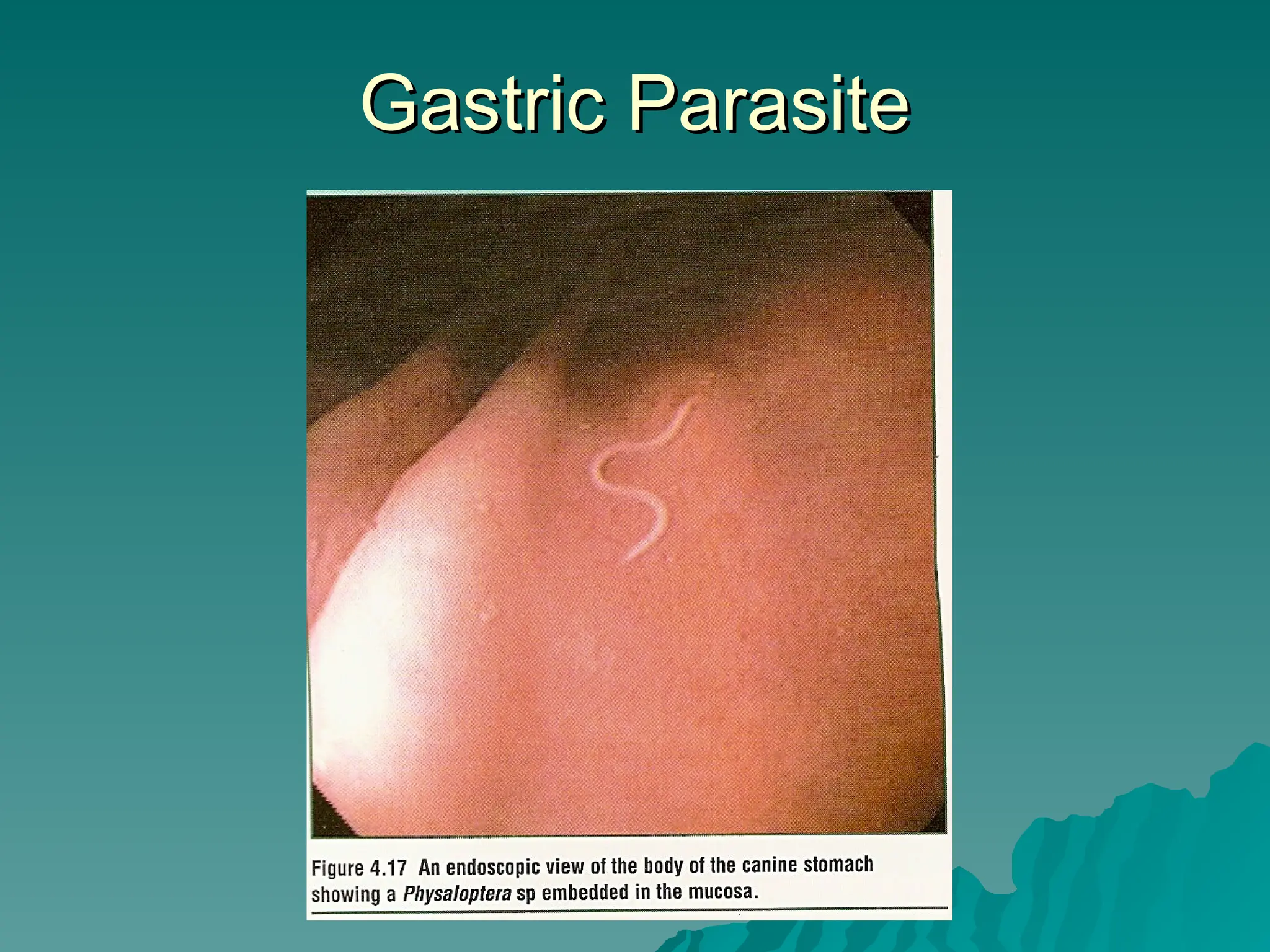
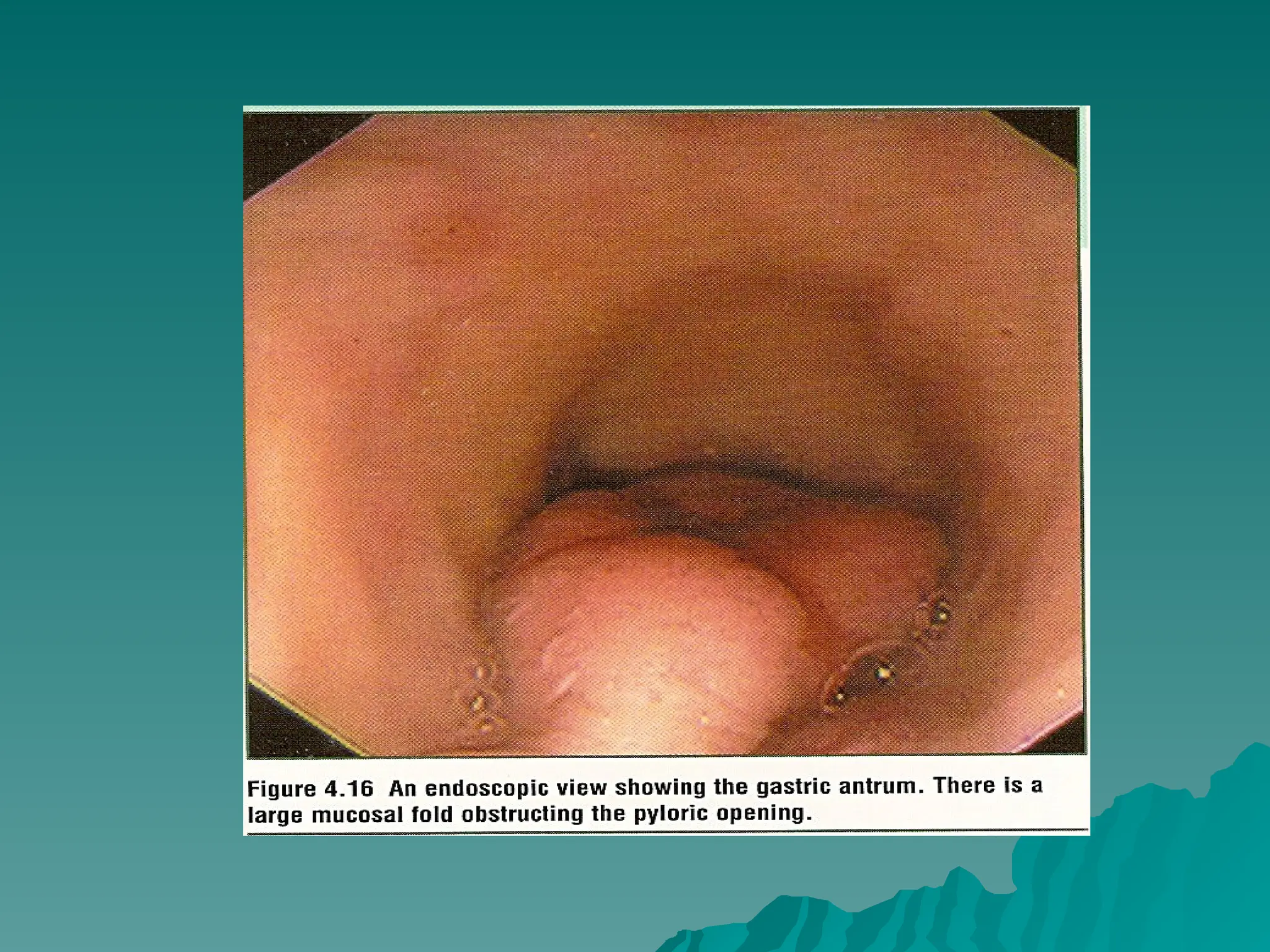
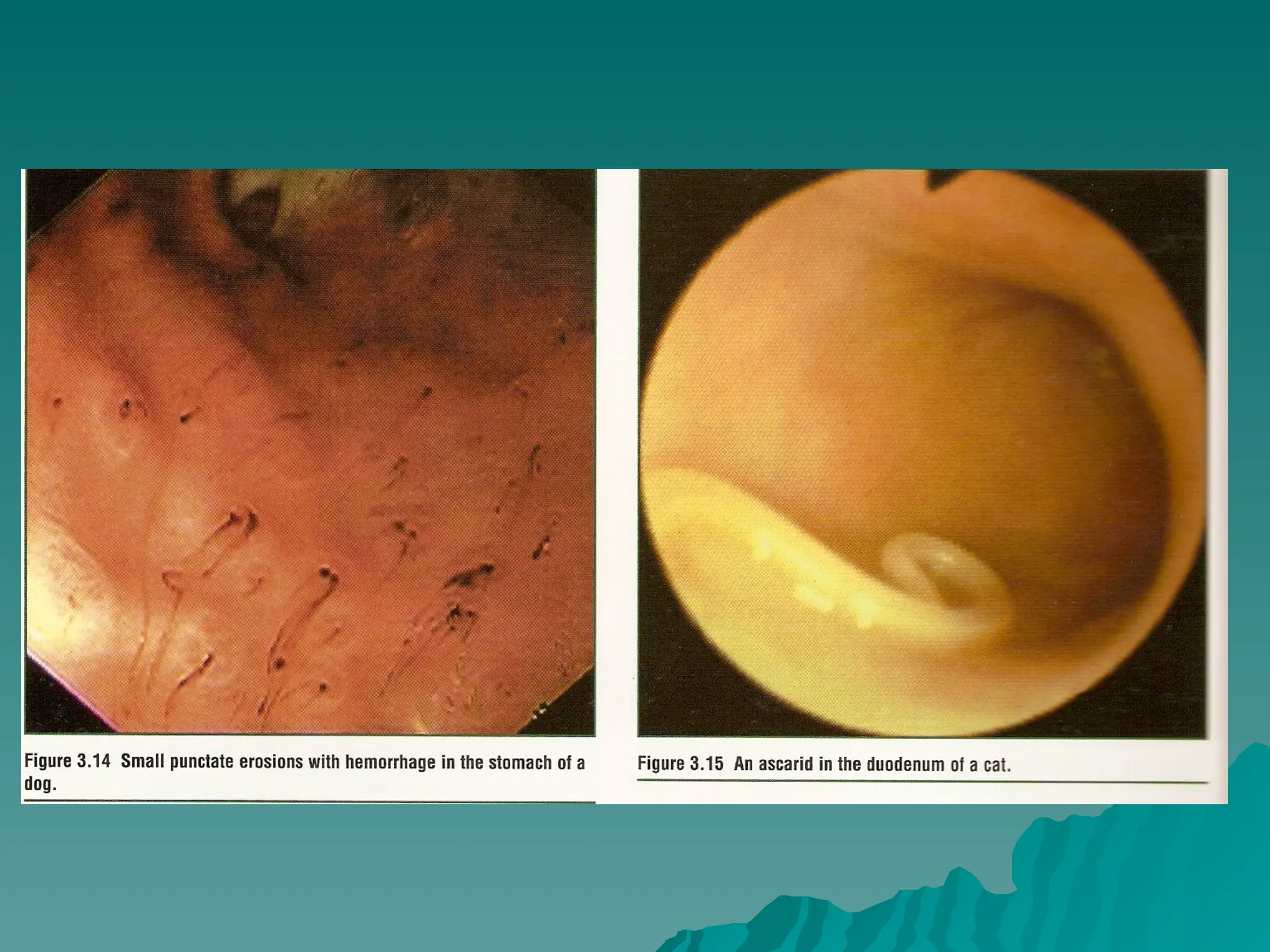
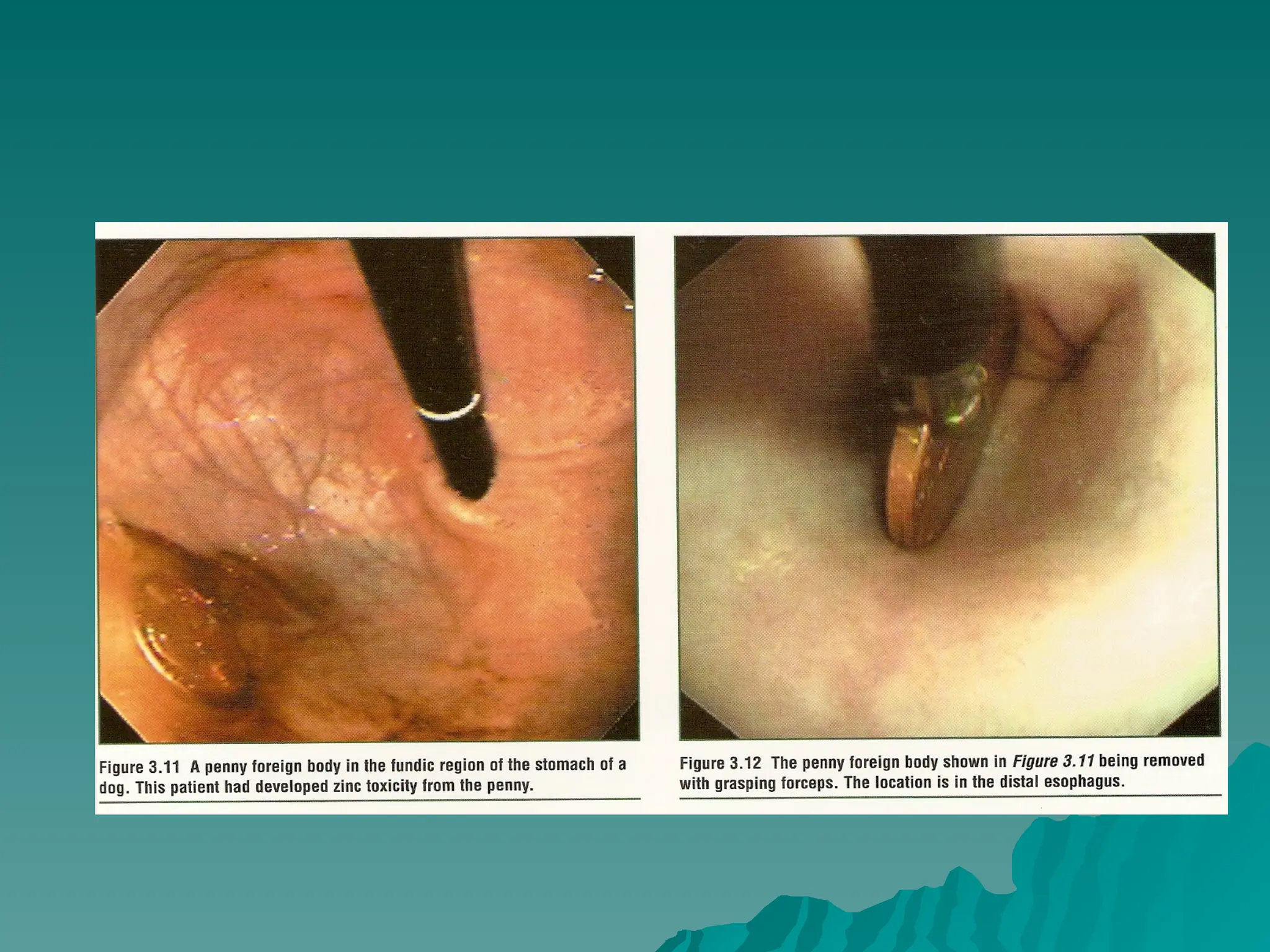
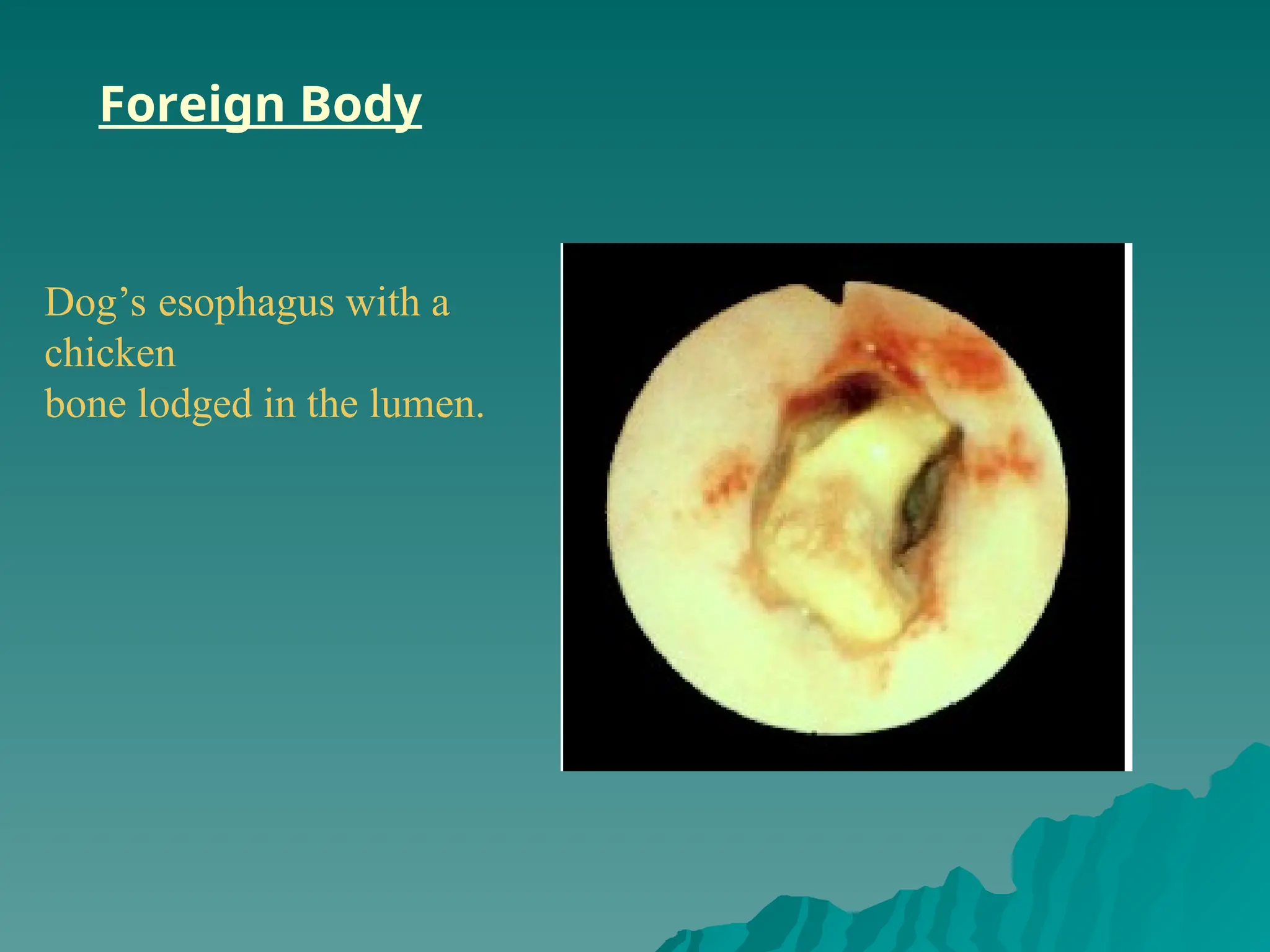
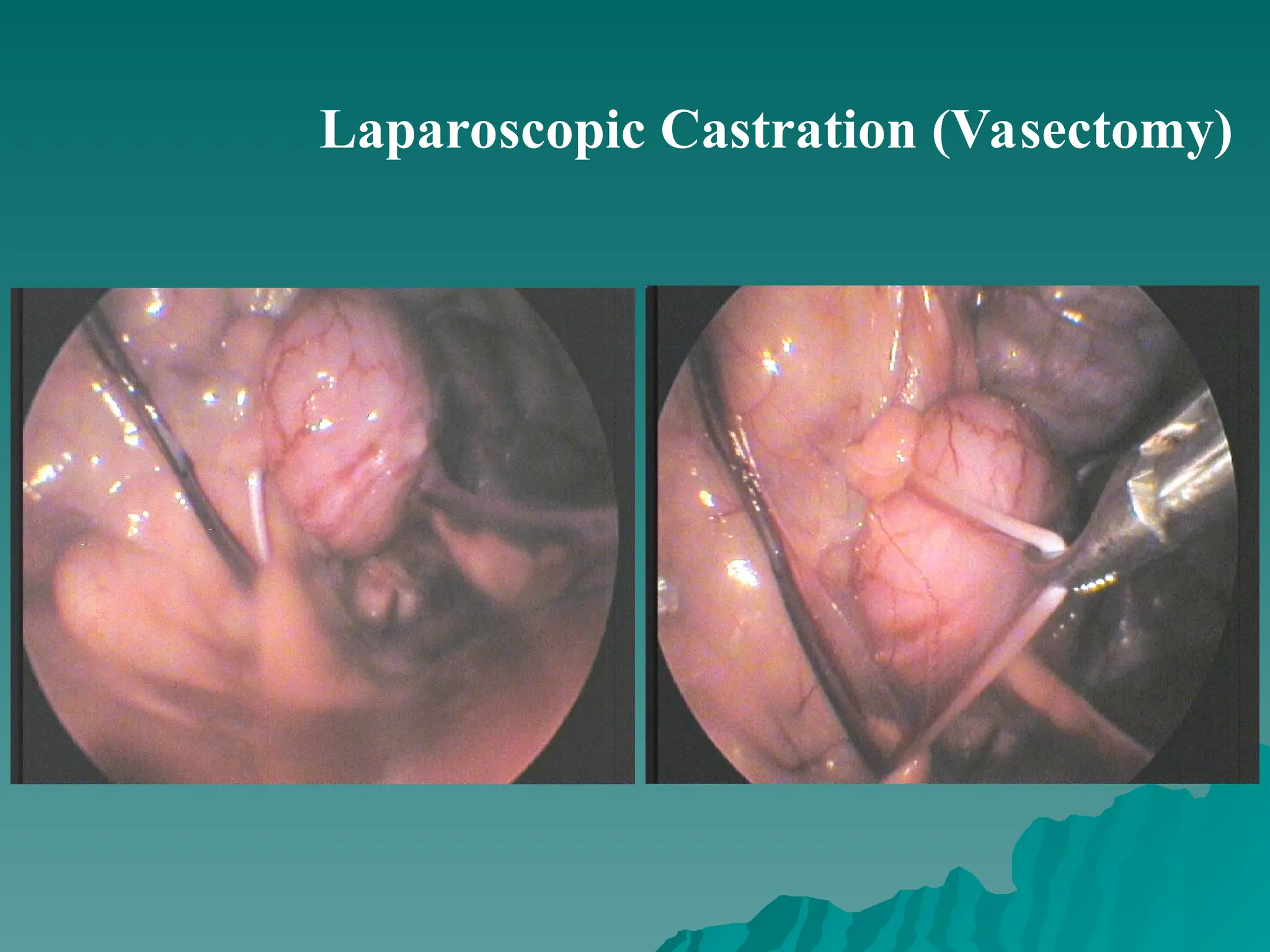
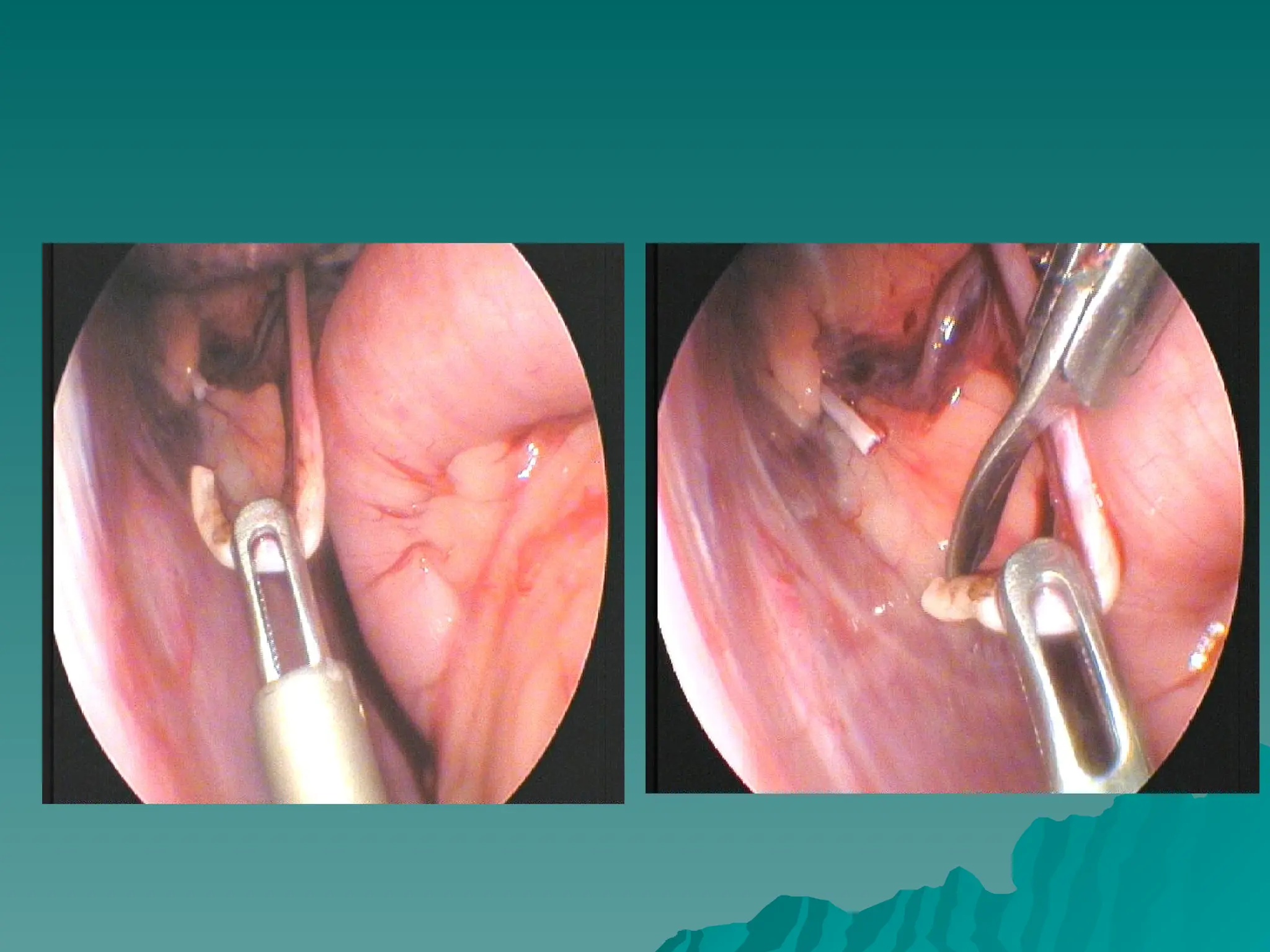
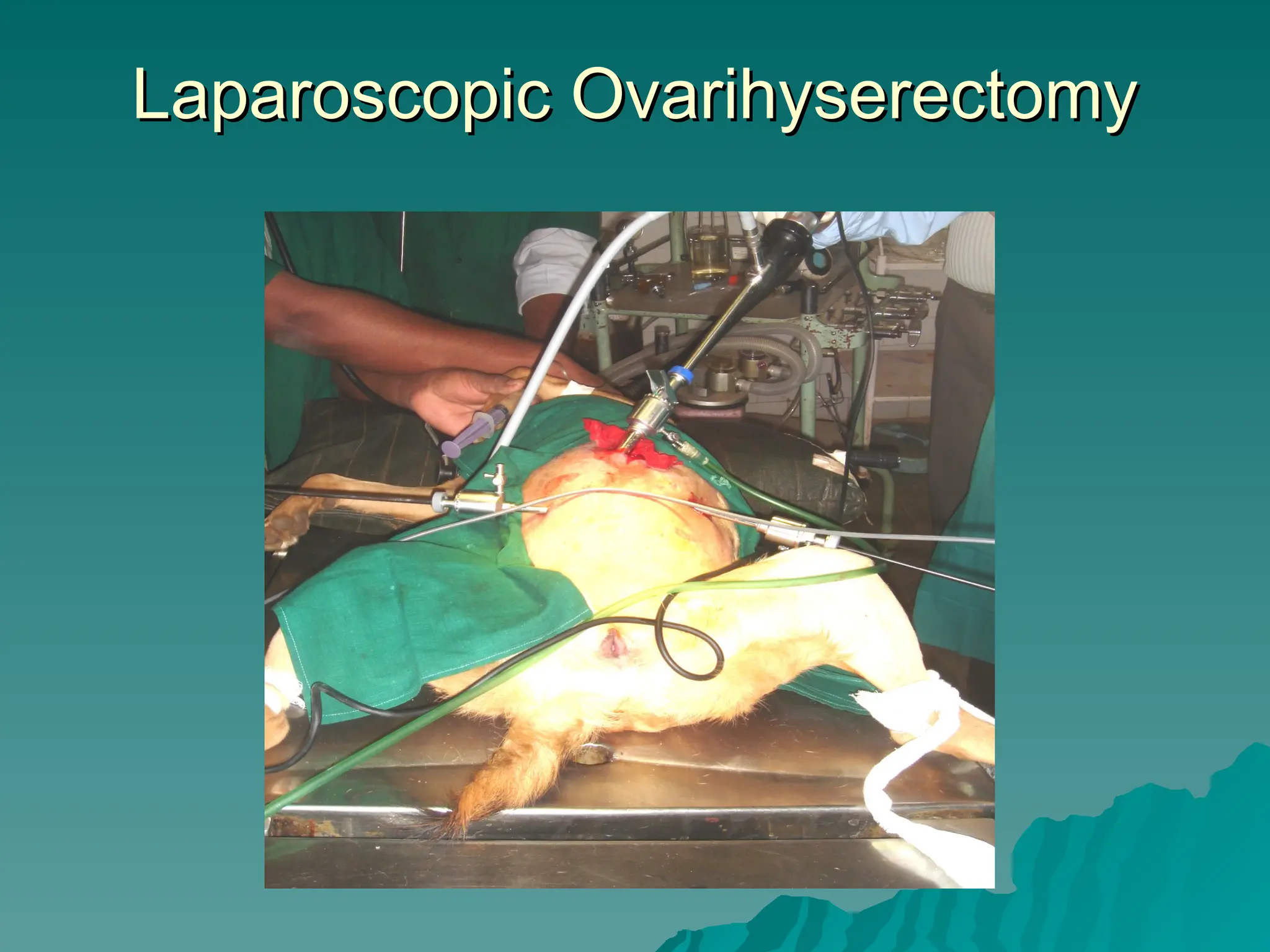
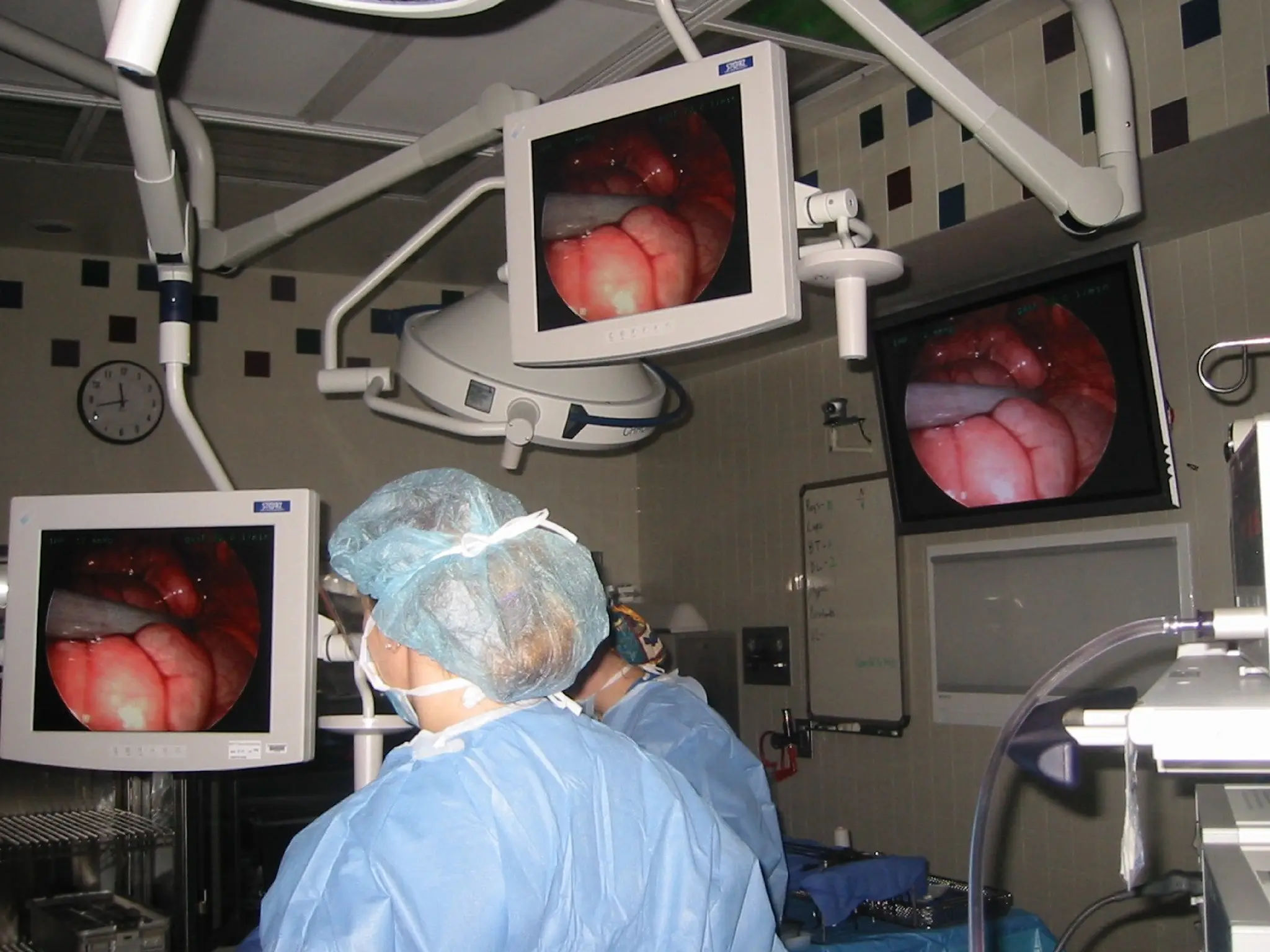
The document presents an overview of endoscopy, defined as the ability to look inside the body using small cameras attached to flexible or rigid tubes, which aids in diagnosing various gastrointestinal disorders in animals. It details the history and evolution of endoscopy, its types, principles, advantages, and disadvantages, emphasizing its significance in veterinary medicine. The document also highlights the various applications and procedures enabled by endoscopy, including biopsies and therapeutic interventions.