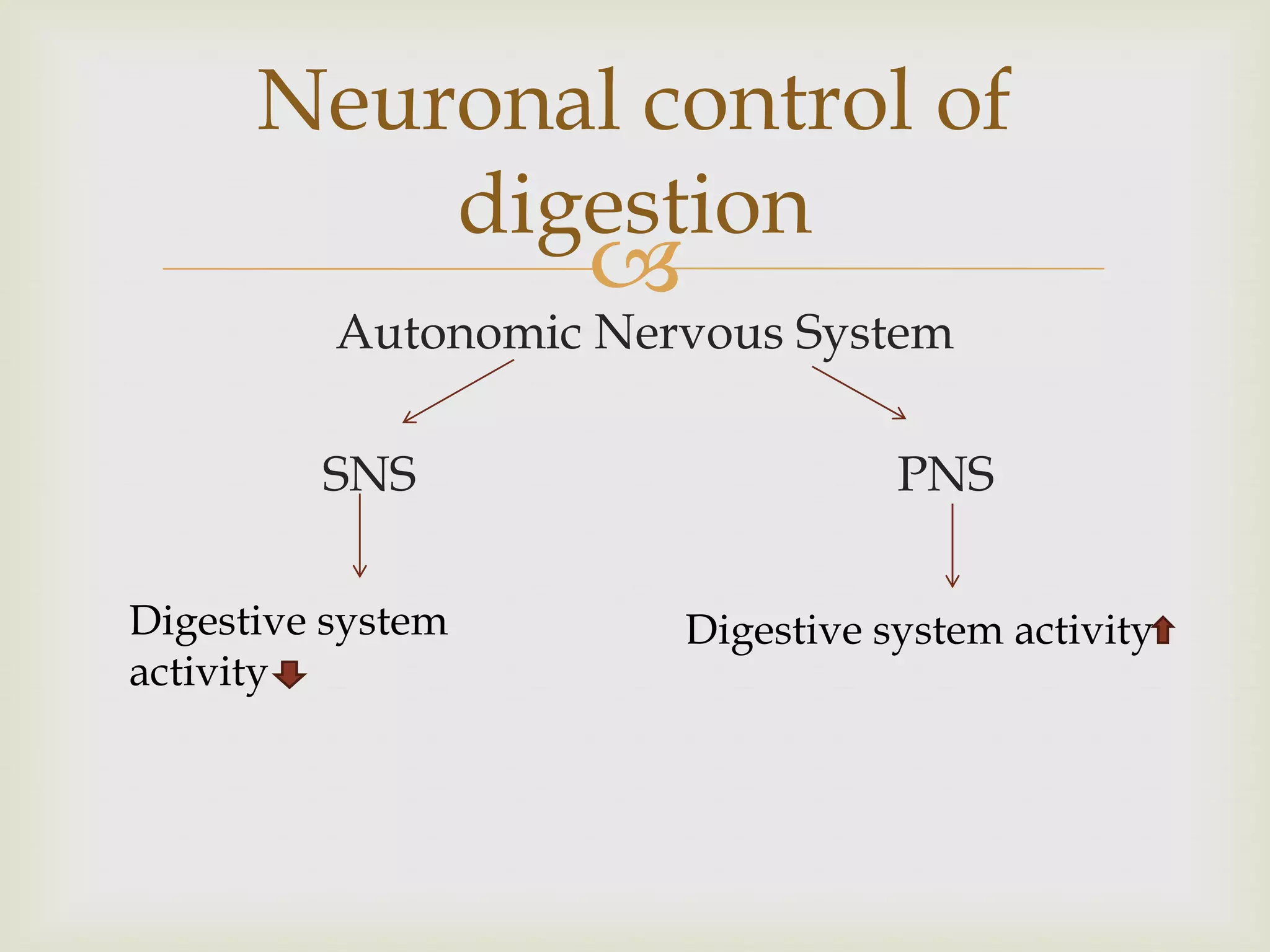
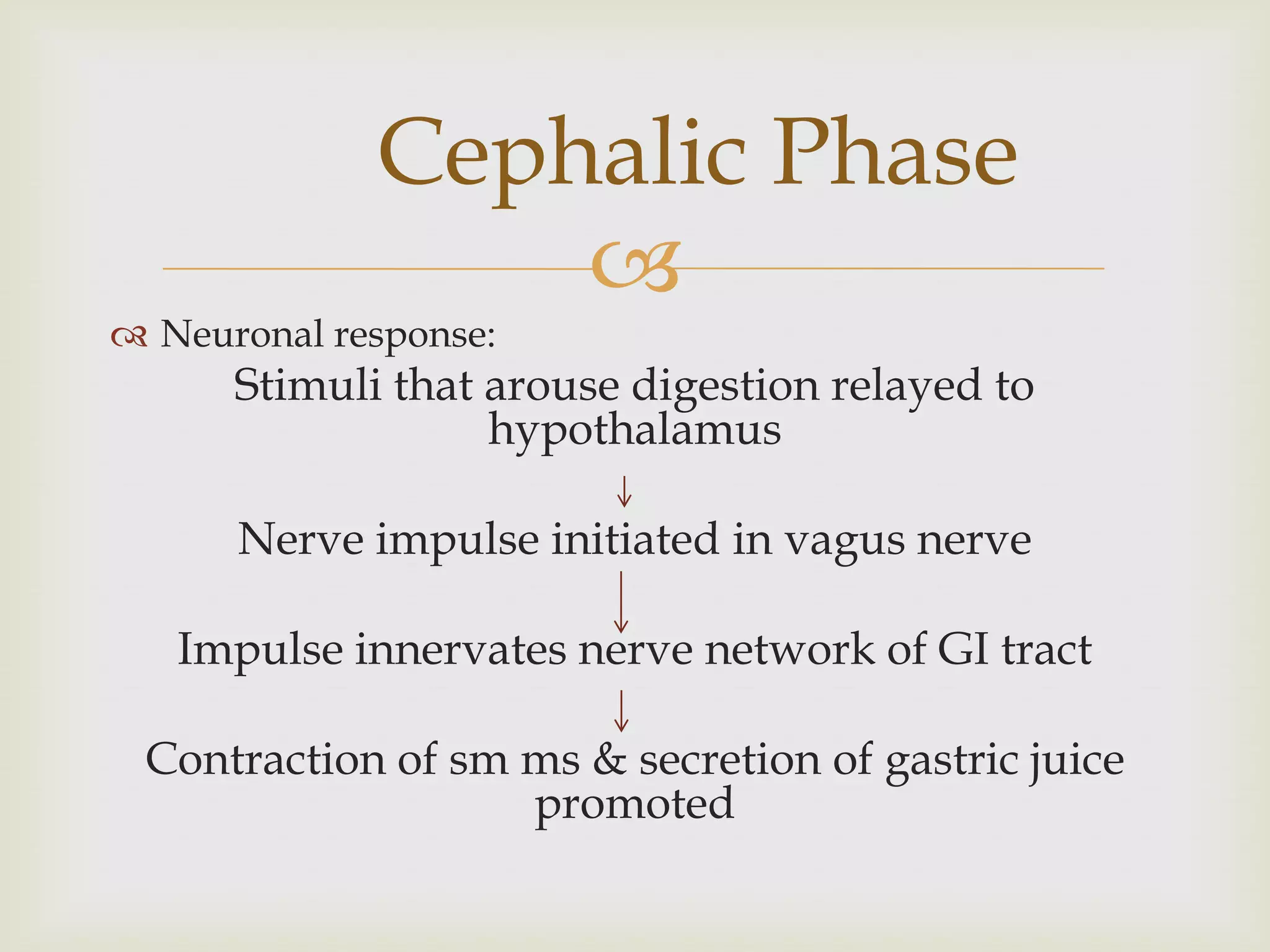
The digestive system is controlled by both the nervous system and hormones. The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems regulate digestive activity through nerves like the greater splanchnic, lumbar splanchnic, and sacral splanchnic nerves (sympathetic) and the vagus nerves (parasympathetic). Key hormones that control digestion include gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin, and GIP. These hormones stimulate or inhibit processes like gastric juice secretion, bile production, and pancreatic juice secretion. Digestion is regulated in three phases: cephalic, gastric, and intestinal phases which involve neural and hormonal responses to prepare the GI tract for digestion and movement of food.