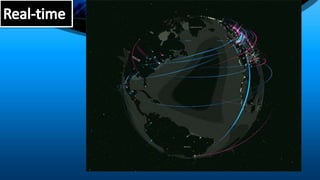
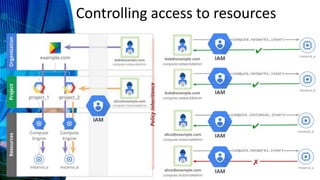
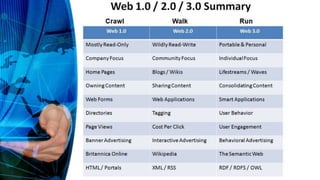
This document defines key terms and concepts related to computers, technology, ethics, and the internet. It discusses empowerment and technology, defines platforms and different types of websites. It also covers computer ethics topics like privacy, integrity, and controlling access to resources. The document then discusses issues around globalization, laws, business, and the information rich/poor divide. It provides an overview of the internet and how it has evolved from Web 1.0 to 2.0 to 3.0. It also outlines strengths and weaknesses of internet research.