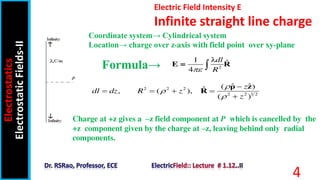
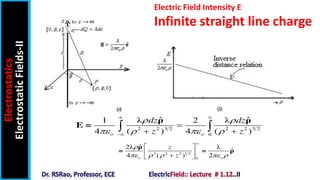
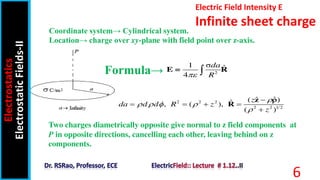
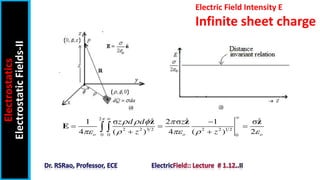
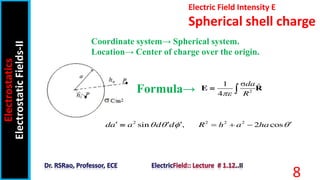
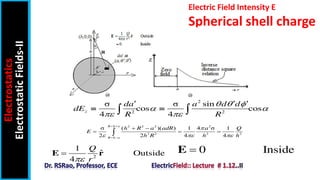
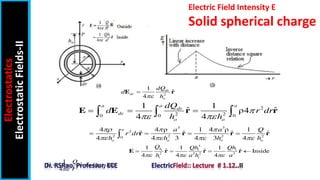
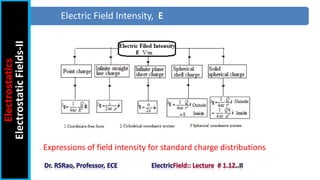
The document discusses electric field intensity due to various charge distributions. It covers infinite straight line charges, infinite plane sheet charges, spherical shell charges, and solid spherical charges. For each charge distribution, it describes the appropriate coordinate system, locating the charge distribution over the system, and selecting the correct field formula to calculate the electric field intensity. Expressions for the electric field intensity both inside and outside the charge distribution are provided. The goal is to derive expressions for the electric field intensity for standard charge distributions in electrostatics.