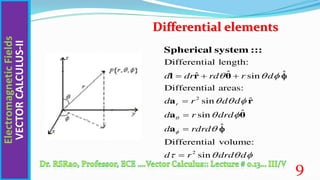
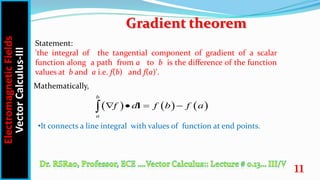
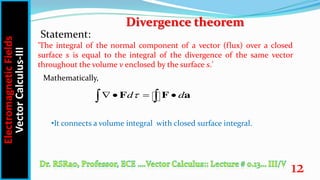
This document discusses key concepts in vector calculus including paths, surfaces, volumes, and three important theorems - the gradient theorem, divergence theorem, and curl theorem. It defines paths, surfaces, and volumes and explains that they can be scalar or vector quantities depending on whether they represent lengths, areas, or volumes. It also introduces the concepts of differential length, area, and volume and expresses them mathematically in Cartesian, cylindrical and spherical coordinate systems. Finally, it states the mathematical formulations of the three theorems - the gradient theorem relates a line integral to function values, the divergence theorem relates a volume integral to a surface integral, and the curl theorem relates a surface integral to a closed line integral.