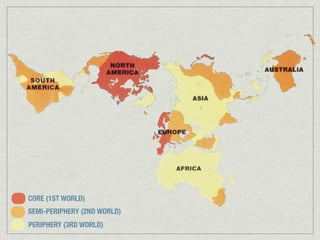
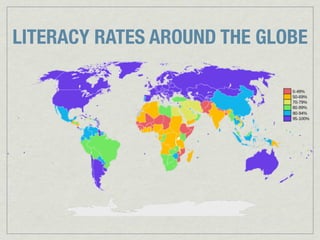
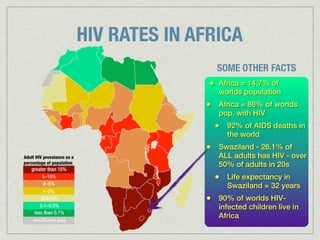
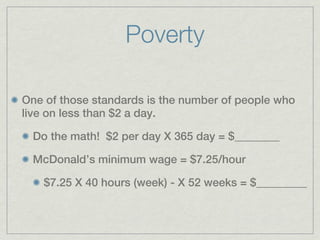
The document discusses the characteristics and challenges of emerging nations in sub-Saharan Africa, categorizing them as 'third world' due to low literacy rates, health crises related to HIV/AIDS, and poor quality of life. It highlights the historical context of apartheid in South Africa and emphasizes the need for a comprehensive understanding of life in third-world countries through various socio-economic factors. The main focus is on gathering data to define and analyze what constitutes life in these nations.