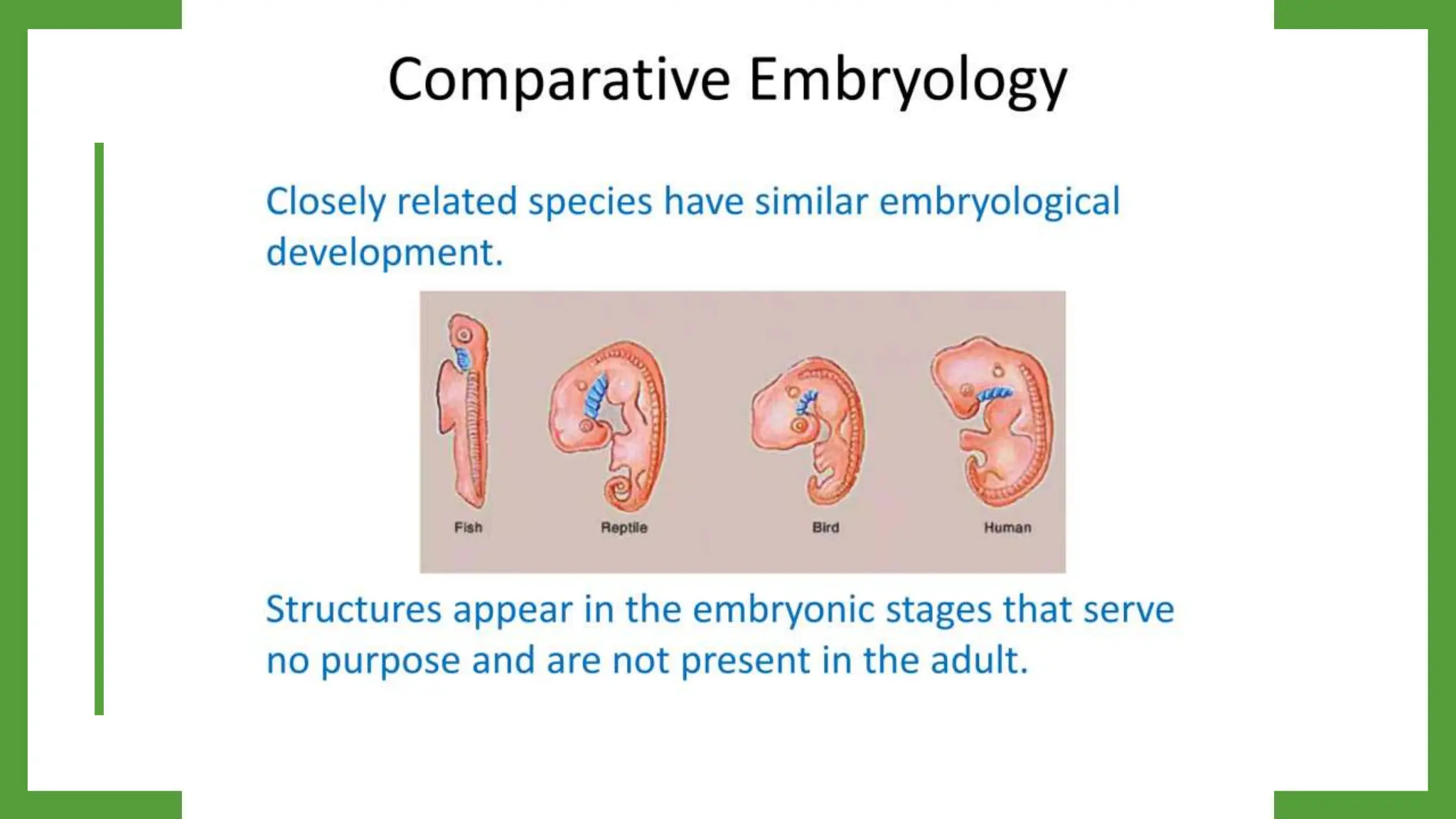
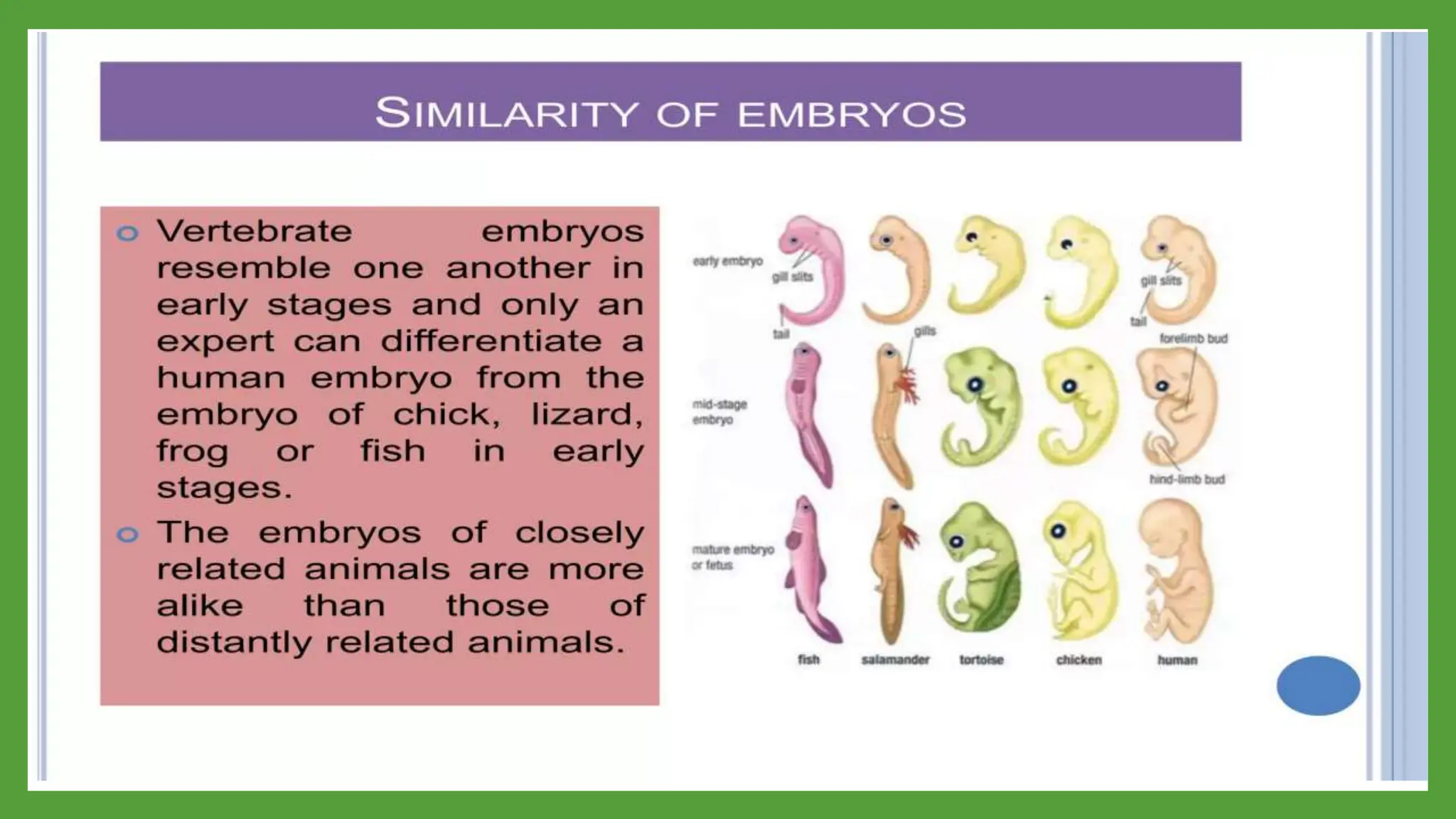
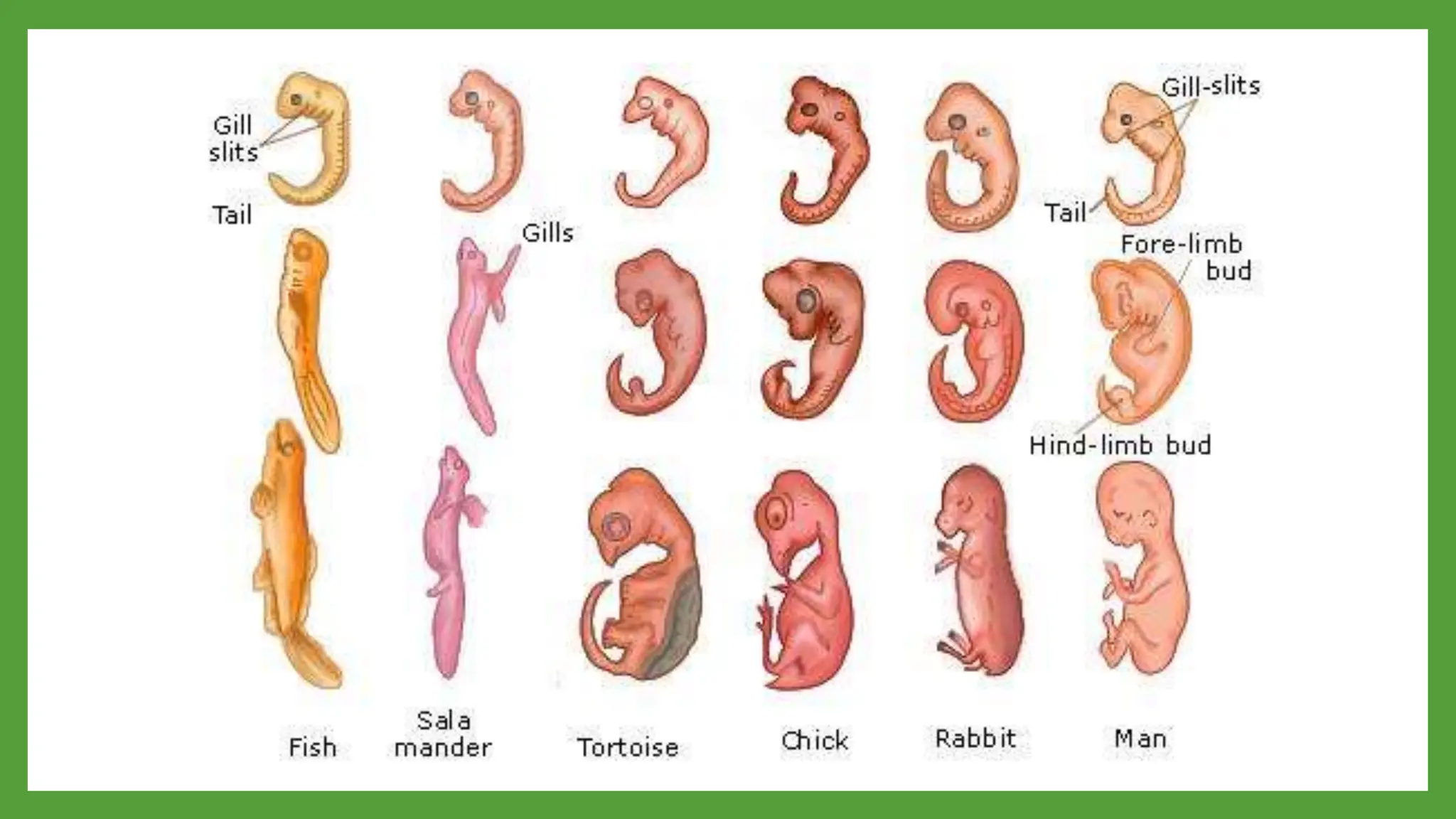
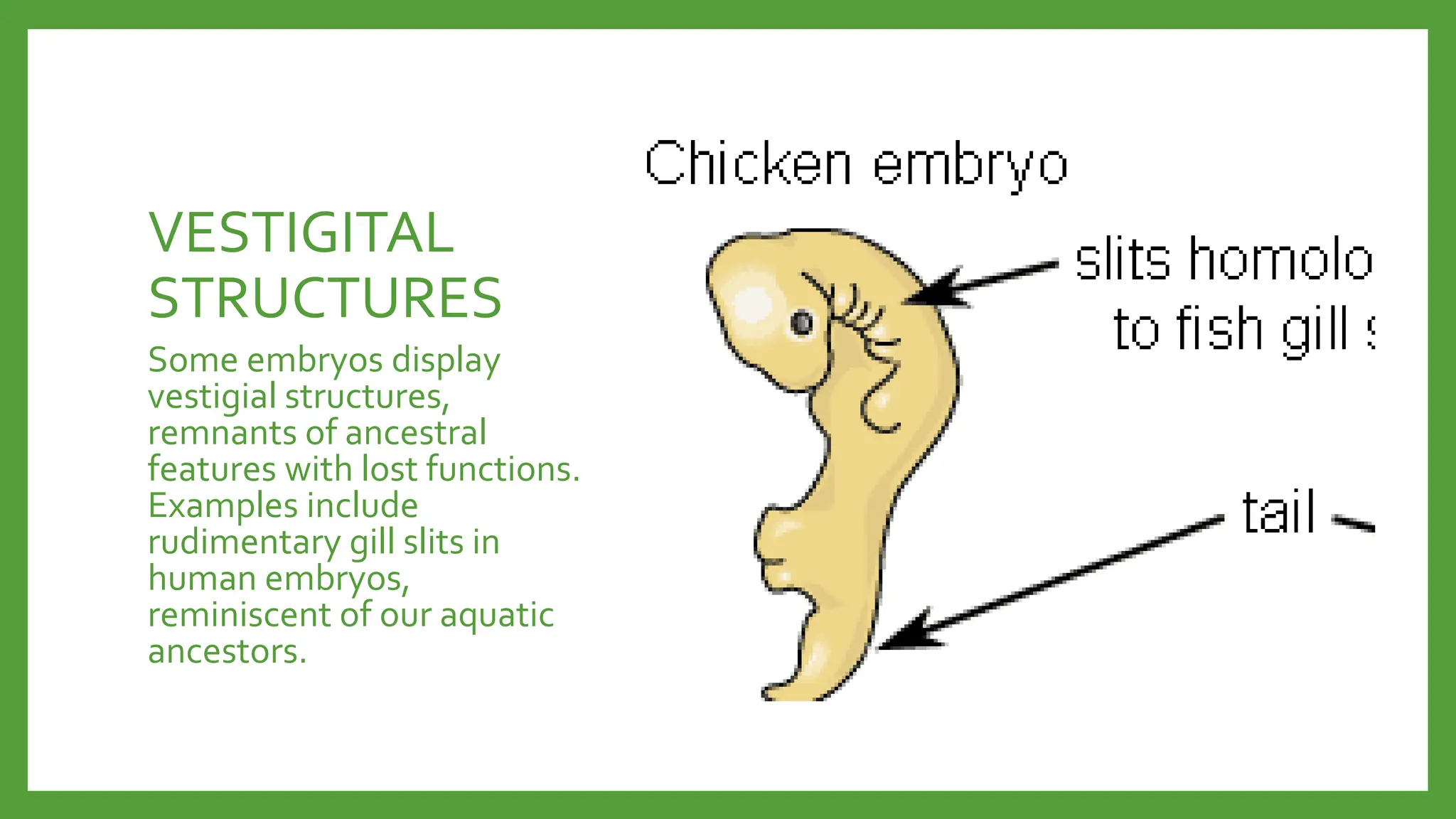
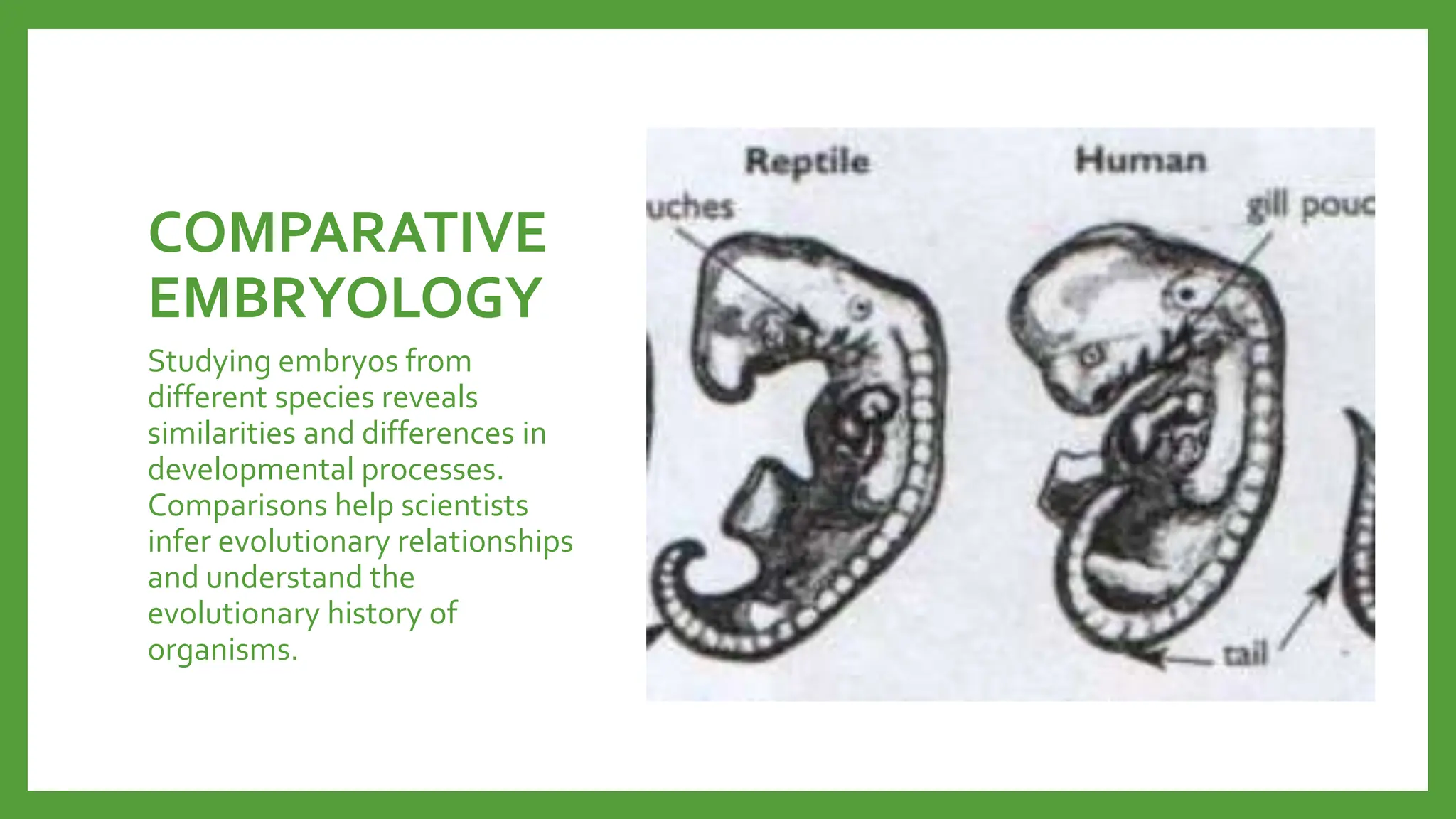
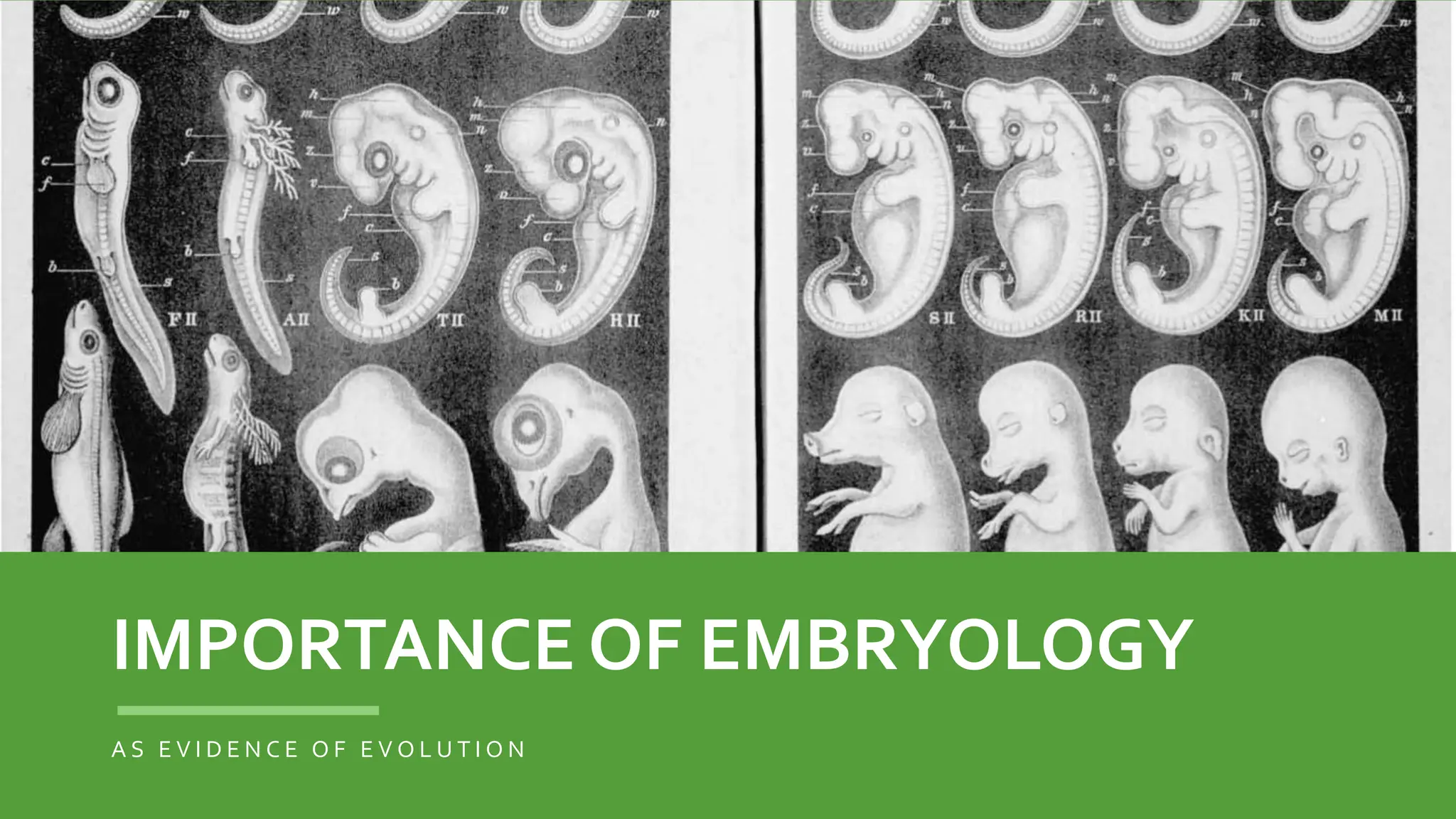
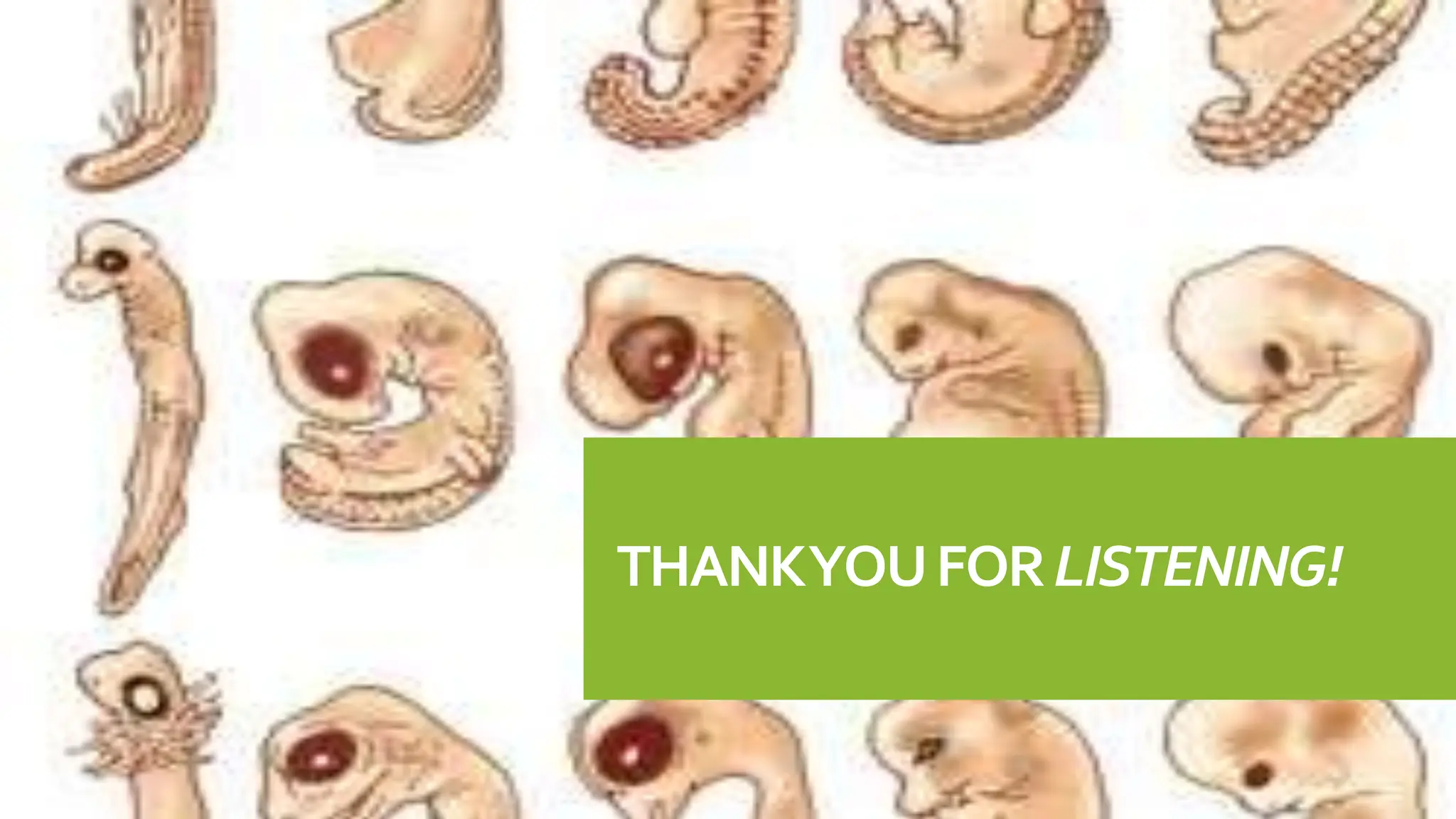
Embryology provides evidence for evolution as the development of embryos across diverse species tends to be conserved. Structures present in embryonic forms of some groups often disappear in adults, while being maintained in other groups. For example, all vertebrate embryos exhibit gill slits and tails early in development, even though these structures disappear in terrestrial adult forms. Comparisons of embryonic development across species reveal similarities that reflect their shared ancestry and evolutionary relationships, as well as differences that demonstrate each species' distinct traits.